
Insurance is a means of protection from financial loss in which, in exchange for a fee, a party agrees to compensate another party in the event of a certain loss, damage, or injury. It is a form of risk management, primarily used to hedge against the risk of a contingent or uncertain loss.
An expense is an item requiring an outflow of money, or any form of fortune in general, to another person or group as payment for an item, service, or other category of costs. For a tenant, rent is an expense. For students or parents, tuition is an expense. Buying food, clothing, furniture, or an automobile is often referred to as an expense. An expense is a cost that is "paid" or "remitted", usually in exchange for something of value. Something that seems to cost a great deal is "expensive". Something that seems to cost little is "inexpensive". "Expenses of the table" are expenses for dining, refreshments, a feast, etc.
Tax deduction is a simplified phrase for meaning income that is able to be taxed and is commonly a result of expenses, particularly those incurred to produce additional income. Tax deductions are a form of tax incentives, along with exemptions and tax credits. The difference between deductions, exemptions, and credits is that deductions and exemptions both reduce taxable income, while credits reduce tax.
Under United States tax law, itemized deductions are eligible expenses that individual taxpayers can claim on federal income tax returns and which decrease their taxable income, and are claimable in place of a standard deduction, if available.
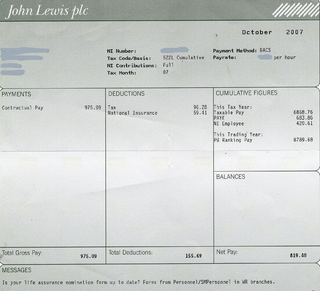
A payroll is a list of employees of a company who are entitled to receive compensation as well as other work benefits, as well as the amounts that each should obtain. Along with the amounts that each employee should receive for time worked or tasks performed, payroll can also refer to a company's records of payments that were previously made to employees, including salaries and wages, bonuses, and withheld taxes, or the company's department that deals with compensation. A company may handle all aspects of the payroll process in-house or can outsource aspects to a payroll processing company.
Health insurance or medical insurance is a type of insurance that covers the whole or a part of the risk of a person incurring medical expenses. As with other types of insurance, risk is shared among many individuals. By estimating the overall risk of health risk and health system expenses over the risk pool, an insurer can develop a routine finance structure, such as a monthly premium or payroll tax, to provide the money to pay for the health care benefits specified in the insurance agreement. The benefit is administered by a central organization, such as a government agency, private business, or not-for-profit entity.
The Canada Revenue Agency is the revenue service of the Canadian federal government, and most provincial and territorial governments. The CRA collects taxes, administers tax law and policy, and delivers benefit programs and tax credits. Legislation administered by the CRA includes the Income Tax Act, parts of the Excise Tax Act, and parts of laws relating to the Canada Pension Plan, employment insurance (EI), tariffs and duties. The agency also oversees the registration of charities in Canada, and enforces much of the country's tax laws.
A health savings account (HSA) is a tax-advantaged medical savings account available to taxpayers in the United States who are enrolled in a high-deductible health plan (HDHP). The funds contributed to an account are not subject to federal income tax at the time of deposit. Unlike a flexible spending account (FSA), HSA funds roll over and accumulate year to year if they are not spent. HSAs are owned by the individual, which differentiates them from company-owned Health Reimbursement Arrangements (HRA) that are an alternate tax-deductible source of funds paired with either high-deductible health plans or standard health plans.
In the United States, a flexible spending account (FSA), also known as a flexible spending arrangement, is one of a number of tax-advantaged financial accounts, resulting in payroll tax savings. One significant disadvantage to using an FSA is that funds not used by the end of the plan year are forfeited to the employer, known as the "use it or lose it" rule. Under the terms of the Affordable Care Act however a plan may permit an employee to carry over up to $550 into the following year without losing the funds but this does not apply to all plans and some plans may have lower limits.
Income tax in the Netherlands is regulated by the Wet inkomstenbelasting 2001.

Employee benefits and benefits in kind, also called fringe benefits, perquisites, or perks, include various types of non-wage compensation provided to employees in addition to their normal wages or salaries. Instances where an employee exchanges (cash) wages for some other form of benefit is generally referred to as a "salary packaging" or "salary exchange" arrangement. In most countries, most kinds of employee benefits are taxable to at least some degree. Examples of these benefits include: housing furnished or not, with or without free utilities; group insurance ; disability income protection; retirement benefits; daycare; tuition reimbursement; sick leave; vacation ; social security; profit sharing; employer student loan contributions; conveyancing; long service leave; domestic help (servants); and other specialized benefits.
Per diem or daily allowance is a specific amount of money that an organization gives an individual, typically an employee, per day to cover living expenses when travelling on the employer's business.
A Health Reimbursement Arrangement, also known as a Health Reimbursement Account (HRA), is a type of US employer-funded health benefit plan that reimburses employees for out-of-pocket medical expenses and, in limited cases, to pay for health insurance plan premiums.

The United States federal government and most state governments impose an income tax. They are determined by applying a tax rate, which may increase as income increases, to taxable income, which is the total income less allowable deductions. Income is broadly defined. Individuals and corporations are directly taxable, and estates and trusts may be taxable on undistributed income. Partnerships are not taxed, but their partners are taxed on their shares of partnership income. Residents and citizens are taxed on worldwide income, while nonresidents are taxed only on income within the jurisdiction. Several types of credits reduce tax, and some types of credits may exceed tax before credits. An Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT) applies at the federal and some state levels.
Disability Insurance, often called DI or disability income insurance, or income protection, is a form of insurance that insures the beneficiary's earned income against the risk that a disability creates a barrier for completion of core work functions. For example, the worker may be unable to maintain composure in the case of psychological disorders or sustain an injury, illness or condition that causes physical impairment or incapacity to work. DI encompasses paid sick leave, short-term disability benefits (STD), and long-term disability benefits (LTD). The same concept is instantiated in some countries as income protection insurance.
An employer in the United States may provide transportation benefits to their employees that are tax free up to a certain limit. Under the U.S. Internal Revenue Code section 132(a), the qualified transportation benefits are one of the eight types of statutory employee benefits that are excluded from gross income in calculating federal income tax. The qualified transportation benefits are transit passes, vanpooling, bicycling, and parking associated with these things.
In the United States, health insurance helps pay for medical expenses through privately purchased insurance, social insurance, or a social welfare program funded by the government. Synonyms for this usage include "health coverage", "health care coverage", and "health benefits". In a more technical sense, the term "health insurance" is used to describe any form of insurance providing protection against the costs of medical services. This usage includes both private insurance programs and social insurance programs such as Medicare, which pools resources and spreads the financial risk associated with major medical expenses across the entire population to protect everyone, as well as social welfare programs like Medicaid and the Children's Health Insurance Program, which both provide assistance to people who cannot afford health coverage.
United States v. General Dynamics Corp., 481 U.S. 239 (1987), is a United States Supreme Court case, which hold that under 162(a) of the Internal Revenue Code and Treasury Regulation 1.461-1(a)(2), the "all events" test entitled an accrual-basis taxpayer to a federal income tax business-expense deduction, for the taxable year in which (1) all events had occurred which determined the fact of the taxpayer's liability, and (2) the amount of that liability could be determined with reasonable accuracy.
Taxes in Germany are levied by the federal government, the states (Länder) as well as the municipalities (Städte/Gemeinden). Many direct and indirect taxes exist in Germany; income tax and VAT are the most significant.
The financing of federal political entities in Canada is regulated under the Canada Elections Act. A combination of public and private funds finances the activities of these entities during and outside of elections.



