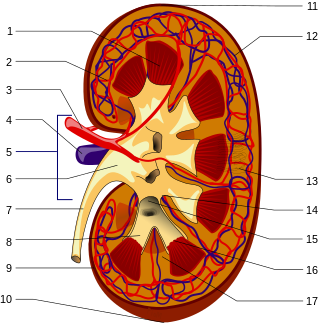
Nephrology is a specialty for both adult internal medicine and pediatric medicine that concerns the study of the kidneys, specifically normal kidney function and kidney disease, the preservation of kidney health, and the treatment of kidney disease, from diet and medication to renal replacement therapy. The word "renal" is an adjective meaning "relating to the kidneys", and its roots are French or late Latin. Whereas according to some opinions, "renal" and "nephro" should be replaced with "kidney" in scientific writings such as "kidney medicine" or "kidney replacement therapy", other experts have advocated preserving the use of renal and nephro as appropriate including in "nephrology" and "renal replacement therapy", respectively.

Kidney failure, also known as end-stage kidney disease, is a medical condition in which the kidneys can no longer adequately filter waste products from the blood, functioning at less than 15% of normal levels. Kidney failure is classified as either acute kidney failure, which develops rapidly and may resolve; and chronic kidney failure, which develops slowly and can often be irreversible. Symptoms may include leg swelling, feeling tired, vomiting, loss of appetite, and confusion. Complications of acute and chronic failure include uremia, hyperkalaemia, and volume overload. Complications of chronic failure also include heart disease, high blood pressure, and anaemia.

Assessment of kidney function occurs in different ways, using the presence of symptoms and signs, as well as measurements using urine tests, blood tests, and medical imaging.

Kidney disease, or renal disease, technically referred to as nephropathy, is damage to or disease of a kidney. Nephritis is an inflammatory kidney disease and has several types according to the location of the inflammation. Inflammation can be diagnosed by blood tests. Nephrosis is non-inflammatory kidney disease. Nephritis and nephrosis can give rise to nephritic syndrome and nephrotic syndrome respectively. Kidney disease usually causes a loss of kidney function to some degree and can result in kidney failure, the complete loss of kidney function. Kidney failure is known as the end-stage of kidney disease, where dialysis or a kidney transplant is the only treatment option.

Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a type of kidney disease in which a gradual loss of kidney function occurs over a period of months to years. Initially generally no symptoms are seen, but later symptoms may include leg swelling, feeling tired, vomiting, loss of appetite, and confusion. Complications can relate to hormonal dysfunction of the kidneys and include high blood pressure, bone disease, and anemia. Additionally CKD patients have markedly increased cardiovascular complications with increased risks of death and hospitalization.

Metabolic acidosis is a serious electrolyte disorder characterized by an imbalance in the body's acid-base balance. Metabolic acidosis has three main root causes: increased acid production, loss of bicarbonate, and a reduced ability of the kidneys to excrete excess acids. Metabolic acidosis can lead to acidemia, which is defined as arterial blood pH that is lower than 7.35. Acidemia and acidosis are not mutually exclusive – pH and hydrogen ion concentrations also depend on the coexistence of other acid-base disorders; therefore, pH levels in people with metabolic acidosis can range from low to high.
Renal osteodystrophy is currently defined as an alteration of bone morphology in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). It is one measure of the skeletal component of the systemic disorder of chronic kidney disease-mineral and bone disorder (CKD-MBD). The term "renal osteodystrophy" was coined in 1943, 60 years after an association was identified between bone disease and kidney failure.
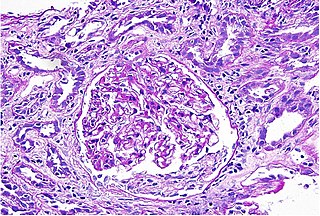
Interstitial nephritis, also known as tubulointerstitial nephritis, is inflammation of the area of the kidney known as the renal interstitium, which consists of a collection of cells, extracellular matrix, and fluid surrounding the renal tubules. It is also known as intestinal nephritis because the clinical picture may include mesenteric lymphadenitis in some cases of acute pyelonephritis. More specifically, in case of recurrent urinary tract infection, secondary infection can spread to adjacent intestine. In addition to providing a scaffolding support for the tubular architecture, the interstitium has been shown to participate in the fluid and electrolyte exchange as well as endocrine functions of the kidney.

Northwest Kidney Centers is a regional, not-for-profit community-based provider of kidney dialysis, public health education, and research into the causes and treatments of chronic kidney disease. Established in Seattle in 1962, it was the world's first out-of-hospital dialysis provider. It offers dialysis throughout the greater Seattle area in 20 free-standing clinics, eight hospitals and its home dialysis program. It opened its first clinic in Everett in 2020, the organization's first in Snohomish county.
The UK Kidney Association (UKKA), formerly the Renal Association, is the second oldest nephrology society in the world. The UKKA has over 1,400 doctors, scientists and multi-professional team members.

Robert Provenzano is an American nephrologist. He is also an Associate Clinical Professor of Medicine at Wayne State University School of Medicine.

Lori Hartwell is the Founder and President of the Renal Support Network, author of Chronically Happy: Joyful Living in Spite of Chronic Illness, and co-host of KidneyTalk, a biweekly webcast of issues of interest to those with Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD).
Nathan W. Levin is an American physician and founder of the Renal Research Institute, LLC., a research institute dedicated to improving the outcomes of patients with kidney disease, particularly those requiring dialysis. Levin is one of the most prominent and renowned figures in clinical nephrology as well as nephrology research. He has authored multiple book chapters and over 350 peer-reviewed publications, including articles in leading journals such as Nature, the New England Journal of Medicine, and The Lancet.
Onconephrology is a specialty in nephrology that deals with the study of kidney diseases in cancer patients. A nephrologist who takes care of patients with cancer and kidney disease is called an onconephrologist. This branch of nephrology encompasses nephrotoxicity associated with existing and novel chemotherapeutics, kidney disease as it pertains to stem cell transplant, paraneoplastic kidney disorders, paraproteinemias, electrolyte disorders associated with cancer, and more as discussed below.
Sucroferric oxyhydroxide, sold under the brand name Velphoro, is a non-calcium, iron-based phosphate binder used for the control of serum phosphorus levels in adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD) on haemodialysis (HD) or peritoneal dialysis (PD). It is used in form of chewable tablets.
Sree Bhushan Raju M.D., D.M., Diplomate of National Board, is a nephrologist from Telangana, India. He is currently Senior professor and Unit head, Dept of Nephrology, Nizam's Institute of Medical Sciences Panjagutta, Hyderabad. Which is one of the largest Nephrology teaching Department in India having ten DM seats. He is one of the principal investigators of CKD task force by Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) to evaluate the prevalence of CKD in adult urban population in India. He is currently an associate editor of Indian Journal of Nephrology, Indian Journal of Organ Transplantation and Frontiers in Medicine. He is a popular advocator of Public Health and early detection of non-communicable disease. He frequency writes editorials in various Regional and National News papers about quality of care, public health, health care systems
Chronic kidney disease–mineral and bone disorder (CKD–MBD) is one of the many complications associated with chronic kidney disease. It represents a systemic disorder of mineral and bone metabolism due to CKD manifested by either one or a combination of the following:
Professor David Wayne Johnson is an Australian nephrologist known for kidney treatments and transplants in Australia. In 2009 he was a Queensland State Finalist for Australian of the Year, for his work in the early recognition and care of people with chronic kidney disease and specifically for his work in detection of chronic kidney disease.
A renal diet is a diet aimed at keeping levels of fluids, electrolytes, and minerals balanced in the body in individuals with chronic kidney disease or who are on dialysis. Dietary changes may include the restriction of fluid intake, protein, and electrolytes including sodium, phosphorus, and potassium. Calories may also be supplemented if the individual is losing weight undesirably.
Peter Stenvinkel is a Swedish nephrologist and academic. He is a senior lecturer at Karolinska University Hospital and a professor of nephrology at Karolinska Institutet.









