Related Research Articles
Project management is the process of leading the work of a team to achieve all project goals within the given constraints. This information is usually described in project documentation, created at the beginning of the development process. The primary constraints are scope, time, and budget. The secondary challenge is to optimize the allocation of necessary inputs and apply them to meet pre-defined objectives.

A work-breakdown structure (WBS) in project management and systems engineering is a deliverable-oriented breakdown of a project into smaller components. A work breakdown structure is a key project deliverable that organizes the team's work into manageable sections. The Project Management Body of Knowledge defines the work-breakdown structure as a "hierarchical decomposition of the total scope of work to be carried out by the project team to accomplish the project objectives and create the required deliverables."

The Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK) is a set of standard terminology and guidelines for project management. The body of knowledge evolves over time and is presented in A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, a book whose seventh edition was released in 2021. This document results from work overseen by the Project Management Institute (PMI), which offers the CAPM and PMP certifications.

The critical path method (CPM), or critical path analysis (CPA), is an algorithm for scheduling a set of project activities. It is commonly used in conjunction with the program evaluation and review technique (PERT). A critical path is determined by identifying the longest stretch of dependent activities and measuring the time required to complete them from start to finish.
In a project network, a dependency is a link among a project's terminal elements.
A project manager is a professional in the field of project management. Project managers have the responsibility of the planning, procurement and execution of a project, in any undertaking that has a defined scope, defined start and a defined finish; regardless of industry. Project managers are first point of contact for any issues or discrepancies arising from within the heads of various departments in an organization before the problem escalates to higher authorities, as project representative.
Scope creep in project management refers to changes, continuous or uncontrolled growth in a project’s scope, at any point after the project begins. This can occur when the scope of a project is not properly defined, documented, or controlled. It is generally considered harmful. It is related to but distinct from feature creep, because feature creep refers to features, and scope creep refers to the whole project.
In project management, float or slack is the amount of time that a task in a project network can be delayed without causing a delay to:
In organizational studies, resource management is the efficient and effective development of an organization's resources when they are needed. Such resources may include the financial resources, inventory, human skills, production resources, or information technology (IT) and natural resources.
Project Management Professional (PMP) is an internationally recognized professional designation offered by the Project Management Institute (PMI). As of 31 July 2020, there are 1,036,368 active PMP-certified individuals and 314 chartered chapters across 214 countries and territories worldwide.
Project portfolio management (PPM) is the centralized management of the processes, methods, and technologies used by project managers and project management offices (PMOs) to analyze and collectively manage current or proposed projects based on numerous key characteristics. The objectives of PPM are to determine the optimal resource mix for delivery and to schedule activities to best achieve an organization’s operational and financial goals, while honouring constraints imposed by customers, strategic objectives, or external real-world factors. Standards for Portfolio Management include Project Management Institute's framework for project portfolio management, Management of Portfolios by Office of Government Commerce and the PfM² Portfolio Management Methodology by the PM² Foundation.

The precedence diagram method (PDM) is a tool for scheduling activities in a project plan. It is a method of constructing a project schedule network diagram that uses boxes, referred to as nodes, to represent activities and connects them with arrows that show the dependencies. It is also called the activity-on-node (AON) method.
Terms of reference (TOR) define the purpose and structures of a project, committee, meeting, negotiation, or any similar collection of people who have agreed to work together to accomplish a shared goal.
In project management, resource leveling is defined by A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge as "A technique in which start and finish dates are adjusted based on resource limitation with the goal of balancing demand for resources with the available supply." Resource leveling problem could be formulated as an optimization problem. The problem could be solved by different optimization algorithms such as exact algorithms or meta-heuristic methods.
A glossary of terms relating to project management and consulting.
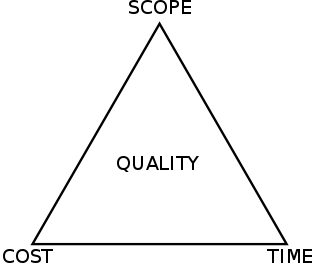
The project management triangle is a model of the constraints of project management. While its origins are unclear, it has been used since at least the 1950s. It contends that:
- The quality of work is constrained by the project's budget, deadlines and scope (features).
- The project manager can trade between constraints.
- Changes in one constraint necessitate changes in others to compensate or quality will suffer.
In project management, scope is the defined features and functions of a product, or the scope of work needed to finish a project. Scope involves getting information required to start a project, including the features the product needs to meet its stakeholders' requirements.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to project management:

Spider Project is a project management software, developed by a company, called Spider Project Team.
Project production management (PPM) is the application of operations management to the delivery of capital projects. The PPM framework is based on a project as a production system view, in which a project transforms inputs into outputs.
References
- ↑ "6.5.2.3 Resource Optimization". A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK® Guide) (6th ed.). Project Management Institute. 2017. p. 720. ISBN 978-1-62825-382-5.
- ↑ Sanghera 2019.
- ↑ Building), CIOB (The Chartered Institute of (2010-11-09). Guide to Good Practice in the Management of Time in Complex Projects. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-1-4443-2961-2.
- ↑ Woodward 1997.
- ↑ Carmichael 2006.
- ↑ Levine 2002.