
The sartorius muscle is the longest muscle in the human body. It is a long, thin, superficial muscle that runs down the length of the thigh in the anterior compartment.

The femoral artery is a large artery in the thigh and the main arterial supply to the thigh and leg. It enters the thigh from behind the inguinal ligament as the continuation of the external iliac artery.

The femoral triangle is an anatomical region of the upper third of the thigh. It is a subfascial space which appears as a triangular depression below the inguinal ligament when the thigh is flexed, abducted and laterally rotated.

The genitofemoral nerve refers to a human nerve that is found in the abdomen. Its branches, the genital branch and femoral branch supply sensation to the upper anterior thigh, as well as the skin of the anterior scrotum in males and mons pubis in females. The femoral branch is different from the femoral nerve, which also arises from the lumbar plexus.

Inguinal lymph nodes are the lymph nodes in the inguinal region (groin). They are located in the femoral triangle, and are grouped into superficial lymph nodes, and deep lymph nodes. The superficial lymph nodes have three divisions – the superomedial, superolateral, and inferior superficial lymph nodes.
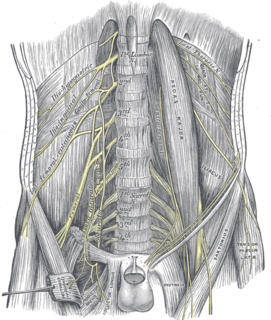
The femoral nerve is a nerve in the thigh that supplies skin on the upper thigh and inner leg, and the muscles that extend the knee.

The lumbar plexus is a web of nerves in the lumbar region of the body which forms part of the larger lumbosacral plexus. It is formed by the divisions of the first four lumbar nerves (L1-L4) and from contributions of the subcostal nerve (T12), which is the last thoracic nerve. Additionally, the ventral rami of the fourth lumbar nerve pass communicating branches, the lumbosacral trunk, to the sacral plexus. The nerves of the lumbar plexus pass in front of the hip joint and mainly support the anterior part of the thigh.

The lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh is a cutaneous nerve that innervates the skin on the lateral part of the thigh.
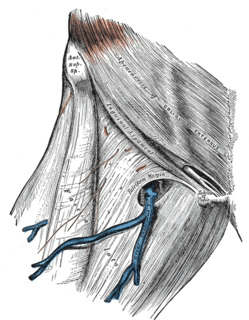
The fascia lata is the deep fascia of the thigh. It encloses the thigh muscles and forms the outer limit of the fascial compartments of thigh, which are internally separated by intermuscular septa. The fascia lata is thickened at its lateral side where it forms the iliotibial tract, a structure that runs to the tibia and serves as a site of muscle attachment.
Femoral hernias occur just below the inguinal ligament, when abdominal contents pass through a naturally occurring weakness in the abdominal wall called the femoral canal. Femoral hernias are a relatively uncommon type, accounting for only 3% of all hernias. While femoral hernias can occur in both males and females, almost all develop in women due to the increased width of the female pelvis. Femoral hernias are more common in adults than in children. Those that do occur in children are more likely to be associated with a connective tissue disorder or with conditions that increase intra-abdominal pressure. Seventy percent of pediatric cases of femoral hernias occur in infants under the age of one.
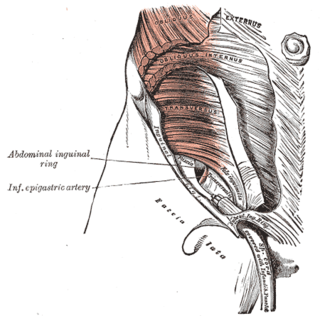
The transversalis fascia is a thin aponeurotic membrane which lies between the inner surface of the transverse abdominal muscle and the parietal peritoneum.

In human anatomy of the leg, the femoral sheath has three compartments. The lateral compartment contains the femoral artery, the intermediate compartment contains the femoral vein, and the medial and smallest compartment is called the femoral canal. The femoral canal contains efferent lymphatic vessels and a lymph node embedded in a small amount of areolar tissue. It is conical in shape and is about 2 cm long.

The iliac fascia is a fascia in the region of the ilium of the pelvis.

The femoral sheath is formed by a prolongation downward, behind the inguinal ligament, of the abdominal fascia, the transverse fascia being continued down in front of the femoral vessels and the iliac fascia behind them. The femoral sheath is contained within the femoral triangle.

The lumboinguinal nerve, also known as the femoral or crural branch of genitofemoral, is a nerve in the abdomen. The lumboinguinal nerve is a branch of the genitofemoral nerve. The "femoral" part supplies skin to the femoral triangle area.
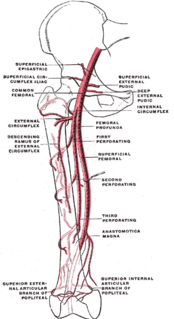
The superficial iliac circumflex artery, the smallest of the cutaneous branches of the femoral artery, arises close to the superficial epigastric artery, and, piercing the fascia lata, runs lateralward, parallel with the inguinal ligament, as far as the crest of the ilium.
The vascular lacuna is the compartment beneath the inguinal ligament which allows for passage of the femoral vessels, lymph vessels and lymph nodes. Its boundaries are the iliopectineal arch, the inguinal ligament, the lacunar ligament, and the superior border of the pubis. The structures found in the vascular lacuna, from medial to lateral, are:
The muscular lacuna is the lateral compartment of the thigh inferior to the inguinal ligament, for the passage of the iliopsoas muscle, the femoral nerve and the lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh; it is separated by the iliopectineal arch from the vascular lacuna.
The Iliopectineal arch is a thickened band of fused iliac fascia and psoas fascia passing from the posterior aspect of the inguinal ligament anteriorly across the front of the femoral nerve to attach to the iliopubic eminence of the hip bone posteriorly. The iliopectinal arch thus forms a septum which subdivides the space deep to the inguinal ligament into a lateral muscular lacuna and a medial vascular lacuna. When a psoas minor muscle is present, its tendon of insertion blends with the iliopectineal arch












