The Cameroon Armed Forces are the military of the Republic of Cameroon. The armed forces number 40,000 personnel in ground, air, and naval forces. There are approximately 40,000 troops in the army across three military regions. Approximately 1,300 troops are part of the Cameroonian Navy, which is headquartered at Douala. Under 600 troops are part of the Air Force. There is an additional 12,500 paramilitary troops that serve as a gendarmerie or reconnaissance role.

British Cameroon or the British Cameroons was a British mandate territory in British West Africa, formed of the Northern Cameroons and Southern Cameroons. Today, the Northern Cameroons forms parts of the Borno, Adamawa and Taraba states of Nigeria, while the Southern Cameroons forms part of the Northwest and Southwest regions of Cameroon.

Kumba is a metropolitan city in the Meme department, Southwest Region, Western Cameroon, commonly referred to as "K-town" colloquially. Kumba is the largest and most developed city in the Meme Department and is increasingly drawing in residents from the local villages such as Mbonge. It is also the largest urban area in the South-West. Kumba has an estimated population of about 400,000 with three quarters of this population being young due to advancement in medicine and lowering infant mortality. The N8 and N16 highways meet at Kumba.

Buea is the capital of the Southwest Region of Cameroon. The city is located in Fako Division, on the eastern slopes of Mount Cameroon, and has a population of about 800.000 inhabitants as of 2023. It has two Government Hotels, the Mountain Hotel and Parliamentarian Flats Hotel located around The Government Residential Area.

Tiko, originally called ‘Keka’ by the Bakweris, is a town and important port in the southwest region of Cameroon. The settlement grew as a market town for Duala fishermen, Bakweri farmers and hunters from Molyko, Bwenga, Bulu and Bokova. The core quarters in Tiko include Streets 1 to 7, Motombolombo, Down Beach, New Quarter, P&T quarters, New Layout, Long Street, Likomba, Golf Club, Mutengene, Ombe. As of 2010, the town is estimated to have a population of 55,914.

The Southern Cameroons was the southern part of the British League of Nations mandate territory of the British Cameroons in West Africa. Since 1961, it has been part of the Republic of Cameroon, where it makes up the Northwest Region and Southwest Region. Since 1994, pressure groups in the territory claim there was no legal document in accordance to UNGA RES 1608(XV) paragraph 5, and are seeking to restore statehood and independence from the Republic. They renamed the British Southern Cameroons as Ambazonia.
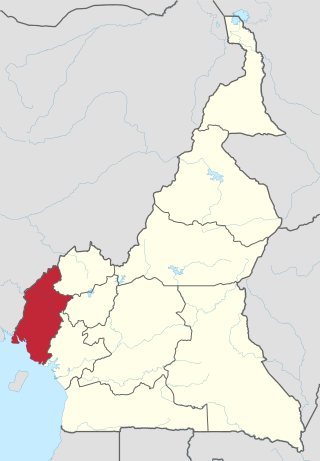
The Southwest Region or South-West Region is a region in Cameroon. Its capital is Buea. As of 2015, its population was 1,553,320. Along with the Northwest Region, it is one of the two Anglophone (English-speaking) regions of Cameroon. Various Ambazonian nationalist and separatist factions regard the Sud-Ouest region as being distinct as a polity from Cameroon.
Mount Cameroon Football Club is a Cameroonian football club based in Buéa. The club was founded in 1997 by Hon. Calvin Foinding. They have competed for more than 12 years in the Cameroon Première Division. Their home stadium is the 3,200 seat Molyko Omnisport Stadium but Mount Cameroon FC also plays its home matches on its own academy "Stade d'Honneur" field.

The Mount Cameroon Race of Hope is an annual, televised footrace held at Mount Cameroon in the Southwest Region of Cameroon in January or February. The 20th edition of the Guinness Mount Cameroon race of hope was scheduled for February 14, 2015. The information was made public in a joint press conference granted by the president of the Cameroon Athletics Federation, Emmanuel Motomby Mbome, and the General manager of Guinness Cameroun, Baker Magunda.

Emmanuel Mbela Lifafa Endeley, OBE was a Cameroonian politician who led Southern Cameroonian representatives out of the Eastern Nigerian House of Assembly in Enugu and negotiated the creation of the autonomous region of Southern Cameroons in 1954.
The Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Bamenda is the Metropolitan See of the ecclesiastical province of Bamenda in Cameroon. It was by the Bull Tametsi Christianarum of 13 August 1970, that Pope Paul VI erected the Diocese of Bamenda with territory detached from the Diocese of Buea. On 18 March 1982 Pope John Paul II created, by the Bull Eo Magis Ecclesia Catholica, the Archdiocese of Bamenda, the Ecclesiastical Province of Bamenda and erected the Diocese of Kumbo with territory detached from the Diocese of Bamenda. Bamenda was by the same bull made into the Metropolitan See of the Ecclesiastical Province with Buea and Kumbo as its Suffragans. Mamfe was later created into a diocese with territory detached from Buea. So Bamenda has 3 Suffragan Sees - Buea, Kumbo and Mamfe. As of Nov 2013 there are 35 Parishes in Bamenda divided into 6 Deaneries - NJINIKOM, MANKON, WIDIKUM, BAMBUI, WUM and NDOP.
The mass media in Cameroon includes independent outlets. The nation has only one national newspaper, which is state owned.

University of Buea (UB) is found in Molyko, Buea, in the southwest region of Cameroon. It was founded as a university centre in 1985 and became a full-fledged university in 1992, following a government decree that re-organized state universities in the country. It is regarded as the best university in Cameroon and is one of two English speaking universities in Cameroon, alongside the University of Bamenda, which follow the British system of education. It serves citizens from both anglophone and francophone regions of Cameroon and from neighboring countries such as Nigeria and Equatorial Guinea.
Babanki, or Kejom, is a Bantoid language that is spoken by the Babanki people of the Western Highlands of Cameroon.

The University of Bamenda (UBa) is an Anglophone university in Bamenda, NorthWestern Cameroon.

Silicon Mountain is a nickname coined to represent the technology ecosystem (cluster) in the Mountain area of Cameroon, with its epicenter in Buea. The name refers to Mount Fako. Silicon Mountain is currently home to tech startups and a growing community of developers, designers, business professionals as well as universities such as the University of Buea, Catholic University Institute of Buea, Saint Monica University and many others. This region occupies the entire Fako Division of the South West Region of Cameroon. The phrase originally was the de facto reference to the Buea Tech Community popularized during local tech community meetups such as BarCamp Cameroon 2013, Google I/O Extended Buea 2015 and the Kamer Design Meetups; but has eventually come to refer to the community of developers, creatives, organizers, business professionals, universities in the area.

The Cameroon General Certificate of Education (GCE) Board is the official body in charge of organizing end-of-year examinations for candidates writing the GCE O and A Levels. The Main Office is located in Buea, Southwest Region (Cameroon), and the Current interim Registrar is Bernadette Ndi. The Cameroon GCE board was established in 1993 as a public examination body supervised by Cameroon ministry of secondary education in Yaoundé.

The Anglophone Crisis, also known as the Ambazonia War, is an ongoing armed conflict in the English-speaking Northwest and Southwest regions of Cameroon, between the Cameroonian government and separatist rebel groups, part of the long-standing Anglophone problem. Following the suppression of 2016–17 protests by Cameroonian authorities, separatists in the Anglophone regions launched a guerrilla campaign and later proclaimed independence. Within two months, the government of Cameroon declared war on the separatists and sent its army into the Anglophone regions.
This is a timeline of the Anglophone Crisis during 2018.
Mile 16, also known as Bolifamba and Bolifamba Mile 16, is a locality in the Buea Municipality of the Fako Division, South West Region of Cameroon.





















