Related Research Articles
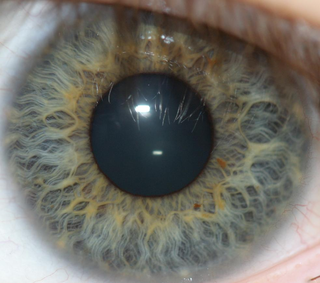
Iris recognition is an automated method of biometric identification that uses mathematical pattern-recognition techniques on video images of one or both of the irises of an individual's eyes, whose complex patterns are unique, stable, and can be seen from some distance. The discriminating powers of all biometric technologies depend on the amount of entropy they are able to encode and use in matching. Iris recognition is exceptional in this regard, enabling the avoidance of "collisions" even in cross-comparisons across massive populations. Its major limitation is that image acquisition from distances greater than a meter or two, or without cooperation, can be very difficult. However, the technology is in development and iris recognition can be accomplished from even up to 10 meters away or in a live camera feed.

A retinal scan is a biometric technique that uses unique patterns on a person's retina blood vessels. It is not to be confused with other ocular-based technologies: iris recognition, commonly called an "iris scan", and eye vein verification that uses scleral veins.

The choroid, also known as the choroidea or choroid coat, is a part of the uvea, the vascular layer of the eye. It contains connective tissues, and lies between the retina and the sclera. The human choroid is thickest at the far extreme rear of the eye, while in the outlying areas it narrows to 0.1 mm. The choroid provides oxygen and nourishment to the outer layers of the retina. Along with the ciliary body and iris, the choroid forms the uveal tract.
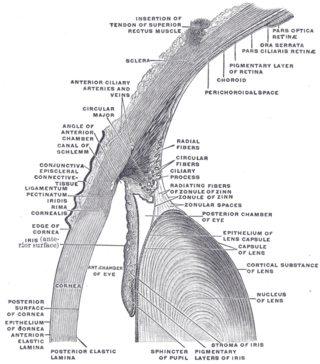
In the anatomy of the eye, the conjunctiva is a thin mucous membrane that lines the inside of the eyelids and covers the sclera. It is composed of non-keratinized, stratified squamous epithelium with goblet cells, stratified columnar epithelium and stratified cuboidal epithelium. The conjunctiva is highly vascularised, with many microvessels easily accessible for imaging studies.

Bionics or biologically inspired engineering is the application of biological methods and systems found in nature to the study and design of engineering systems and modern technology.

The Favaloro University is a private university in the city of Buenos Aires in Argentina. It was founded by surgeon René Favaloro in 1992; it obtained its definitive authorization on October 23, 2003, by decree 963/03 of president Néstor Kirchner. Favaloro did not see his project completely realised, for he committed suicide a few years before completion.

Computer-aided detection (CADe), also called computer-aided diagnosis (CADx), are systems that assist doctors in the interpretation of medical images. Imaging techniques in X-ray, MRI, endoscopy, and ultrasound diagnostics yield a great deal of information that the radiologist or other medical professional has to analyze and evaluate comprehensively in a short time. CAD systems process digital images or videos for typical appearances and to highlight conspicuous sections, such as possible diseases, in order to offer input to support a decision taken by the professional.
Evangelia Micheli-Tzanakou was a professor of biomedical engineering and the Director of Computational Intelligence Laboratories at Rutgers University. Dr. Micheli-Tzanakou was also a Founding Fellow of the American Institute for Medical and Biological Engineering (AIMBE), a Fellow of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), and a Fellow of the New Jersey Academy of Medicine. Dr. Micheli-Tzanakou's areas of interest included neural networks, information processing in the brain, image and signal processing applied to biomedicine, telemedicine, mammography, hearing aids and electronic equivalents of neurons. Dr. Micheli-Tzanakou received international attention in 1974 when she established the first Brain to Computer Interface (BCI) using her algorithm ALOPEX. This method was used in the study of Parkinson's disease. The ALOPEX algorithm has also been applied toward signal processing, image processing, and pattern recognition. Dr. Micheli-Tzanakou died on September 24, 2012, after a long fight with cancer.

Anastasios (Tas) Venetsanopoulos was a professor of electrical and computer engineering at Toronto Metropolitan University in Toronto, Ontario and a professor emeritus with the Edward S. Rogers Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at the University of Toronto. In October 2006, Venetsanopoulos joined what was then Ryerson University and served as the founding vice-president of research and innovation. His portfolio included oversight of the university's international activities, research ethics, Office of Research Services, and Office of Innovation and Commercialization. He retired from that position in 2010, but remained a distinguished advisor to the role. Tas Venetsanopoulos continued to actively supervise his research group at the University of Toronto, and was a highly sought-after consultant throughout his career.
Richard J. Mammone is an American engineer, inventor, entrepreneur and professor. As an inventor, he holds over 15 patents. To date, he has formed four technology companies including SpeakEZ, a firm that specialized in voice recognition technology, and Computed Anatomy Inc., the business that pioneered LASIK eye surgery.
Kayvan Najarian is an Iranian-American scientist, who is a professor in the Department of Computational Medicine and Bioinformatics, Department of Emergency Medicine, and Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor. He is the director of Biomedical and Clinical Informatics (BCIL) University of Michigan in Ann Arbor. Additionally, he is an associate director of Michigan Institute for Data Sciences (MIDAS). He is also serving as an associate director of the MCIRCC's. Kayvan Najarian has over 200 peer-reviewed journal and conference papers, as well as several US and international patents. He is a senior member of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, is a reviewer, referee or member of dozens more committees, journals and councils. He received his B.Sc. in electrical engineering from Sharif University of Technology, his M.Sc. in biomedical engineering from Amirkabir University of Technology, and his Ph.D. in electrical and computer engineering at University of British Columbia.

Vein matching, also called vascular technology, is a technique of biometric identification through the analysis of the patterns of blood vessels visible from the surface of the skin. Though used by the Federal Bureau of Investigation and the Central Intelligence Agency, this method of identification is still in development and has not yet been universally adopted by crime labs as it is not considered as reliable as more established techniques, such as fingerprinting. However, it can be used in conjunction with existing forensic data in support of a conclusion.
Bir Bhanu is the Marlan and Rosemary Bourns Endowed University of California Presidential Chair in Engineering, the Distinguished Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Cooperative Professor of Computer Science and Engineering, Mechanical Engineering and Bioengineering, at the Marlan and Rosemary Bourns College of Engineering at the University of California, Riverside (UCR). He is the first Founding Faculty of the Marlan and Rosemary Bourns College of Engineering at UCR and served as the Founding Chair of Electrical Engineering from 1/1991 to 6/1994 and the Founding Director of the Center for Research in Intelligent Systems (CRIS) from 4/1998 to 6/2019. He has been the director of Visualization and Intelligent Systems Laboratory (VISLab) at UCR since 1991. He was the Interim Chair of the Department of Bioengineering at UCR from 7/2014 to 6/2016. Additionally, he has been the Director of the NSF Integrative Graduate Education, Research and Training (IGERT) program in Video Bioinformatics at UC Riverside. Dr. Bhanu has been the principal investigator of various programs for NSF, DARPA, NASA, AFOSR, ONR, ARO and other agencies and industries in the areas of object/target recognition, learning and vision, image/video understanding, image/video databases with applications in security, defense, intelligence, biological and medical imaging and analysis, biometrics, autonomous navigation and industrial machine vision.
Thomas Baer is the executive director of the Stanford Photonics Research Center, a consulting professor in the applied physics department and an associate member of the Stem Cell Institute at Stanford University. His current scientific research is focused on developing imaging and biochemical analysis technology for exploring the molecular basis of human developmental biology and neuroscience. He received a B.A. in physics from Lawrence University in 1974, and a Ph.D. in atomic physics from the University of Chicago in 1979, where he studied with Professors Ugo Fano and Isaac Abella. After receiving his Ph.D. he worked with Nobel Laureate John L. Hall at JILA, University of Colorado, performing research on frequency stabilized lasers and ultra-high precision molecular spectroscopy.
Eye vein verification is a method of biometric authentication that applies pattern-recognition techniques to video images of the veins in a user's eyes. The complex and random patterns are unique, and modern hardware and software can detect and differentiate those patterns at some distance from the eyes.
EyeVerify, Inc. is a biometric security technology company based in Kansas City, Missouri owned by Ant Group. Its chief product, Eyeprint ID, provides verification using eye veins and other micro-features in and around the eye. Images of the human eye are used to authenticate mobile device users. EyeVerify licenses its software for use in mobile banking applications, such as those offered by Tangerine Bank, NCR/Digital Insight and Wells Fargo.

Núria López Bigas is a Spanish biologist and research professor with expertise in medical genetics, computational biology, and bioinformatics. She is an ICREA professor at Pompeu Fabra University and she also leads the Biomedical Genomics Research Group at the Institute for Research in Biomedicine in Barcelona, Spain. Her research is focused on developing computational approaches to investigate cancer genomes.

Michael Bronstein is an Israeli computer scientist and entrepreneur. He is a computer science professor at the University of Oxford and scientific director of Aithyra Institute at the Vienna Biocenter in Austria.
Gari David Clifford is a British-American physicist, biomedical engineer, academic, and researcher. He is the Chair of Emory's Department of Biomedical Informatics and a Professor of Biomedical Engineering and Biomedical Informatics at Emory University and Georgia Institute of Technology.
Stephanie A. C. Schuckers is an American electrical engineer and bioengineer specializing in biomedical signal processing, especially focusing on liveness testing for biometrics, with additional research on non-invasive biomedical monitoring. She is Paynter-Krigman Endowed Professor in Engineering Science and director of the Center for Identification Technology Research at Clarkson University.
References
- ↑ "Speakers" . Retrieved 2015-04-12.
- ↑ Stacy, Michael (22 February 2012). "Kansas City startup EyeVerify sees opportunity in the whites of your eyes". Silicon Prairie News. Retrieved 20 February 2014.
- ↑ "Associate Professor Reza Derakhshani earns prestigious award for research" . Retrieved 2015-04-12.
- ↑ "Meet our 8 finalists for Technologist and Designer of the Year" . Retrieved 2015-04-12.
- ↑ "Reza R. Derakhshani, Ph.D." Retrieved 2015-04-12.
- ↑ "Congratulations to the winners of the UMKC Trustee Awards" . Retrieved 2015-04-12.