Related Research Articles
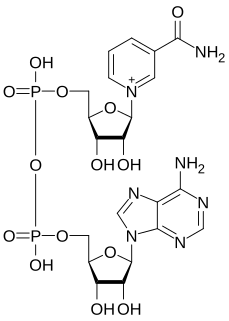
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a coenzyme central to metabolism. Found in all living cells, NAD is called a dinucleotide because it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine nucleobase and the other nicotinamide. NAD exists in two forms: an oxidized and reduced form, abbreviated as NAD+ and NADH (H for hydrogen), respectively.
NR, Nr or nr may refer to:

Zeatin is a cytokinin derived from adenine, which occurs in the form of a cis- and a trans-isomer and conjugates. Zeatin was discovered in immature corn kernels from the genus Zea. It promotes growth of lateral buds and when sprayed on meristems stimulates cell division to produce bushier plants.

Adenylosuccinate lyase deficiency is a rare autosomal recessive metabolic disorder characterized by the appearance of succinylaminoimidazolecarboxamide riboside and succinyladenosine (S-Ado) in cerebrospinal fluid, urine. These two succinylpurines are the dephosphorylated derivatives of SAICA ribotide (SAICAR) and adenylosuccinate (S-AMP), the two substrates of adenylosuccinate lyase (ADSL), which catalyzes an important reaction in the de novo pathway of purine biosynthesis. ADSL catalyzes two distinct reactions in the synthesis of purine nucleotides, both of which involve the β-elimination of fumarate to produce aminoimidazole carboxamide ribotide (AICAR) from SAICAR or adenosine monophosphate (AMP) from S-AMP.
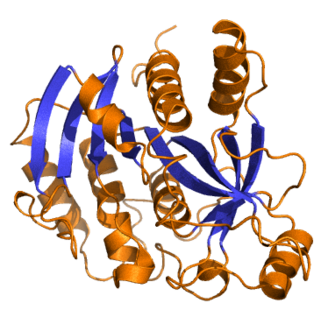
Purine nucleoside phosphorylase, PNP, PNPase or inosine phosphorylase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NP gene. It catalyzes the chemical reaction

Adenylosuccinate lyase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ADSL gene.
In enzymology, an inosine nucleosidase (EC 3.2.2.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
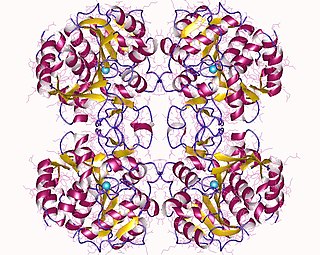
In enzymology, a purine nucleosidase (EC 3.2.2.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an uridine phosphorylase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a ribosylnicotinamide kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Nicotinamide riboside kinase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ITGB1BP3 gene.
Charles Brenner is the chair of the Department of Diabetes & Cancer Metabolism at the Beckman Research Institute of the City of Hope National Medical Center. He is a major contributor to work on nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide metabolism, who discovered the eukaryotic nicotinamide riboside (NR) kinase pathway.
l-Deoxyribose is an organic compound with formula C5H10O4. It is a synthetic monosaccharide, a stereoisomer (mirror image) of the natural compound d-deoxyribose.
SAICA may refer to:
ChromaDex is a dietary supplement and food ingredient company based in Los Angeles, California founded in 1999 that is publicly traded on the NASDAQ.
Nicotinate riboside kinase is an enzyme with systematic name ATP:beta-D-ribosylnicotinate 5-phosphotransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Nicotinamide riboside (NR, SR647) is a pyridine-nucleoside and a form of vitamin B3, functioning as a precursor to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide or NAD+.

Elysium Health is an American manufacturer of dietary supplements based in New York City.

Nicotinamide mononucleotide is a nucleotide derived from ribose, nicotinamide, nicotinamide riboside and niacin. Humans have enzymes that can use NMN to generate nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH). In mice, NMN has been proposed to enter cells via the small intestines within 10 minutes converting to NAD+ through the Slc12a8 transporter. However this observation has been challenged, and remains unsettled.

Vitamin B3, colloquially referred to as niacin, is a vitamin family that includes three forms or vitamers: niacin (nicotinic acid), nicotinamide (niacinamide), and nicotinamide riboside. All three forms of vitamin B3 are converted within the body to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD). NAD is required for human life and people are unable to make it within their bodies without either vitamin B3 or tryptophan. Nicotinamide riboside was identified as a form of vitamin B3 in 2004.