Related Research Articles

Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are a class of drugs that inhibit the activity of one or both monoamine oxidase enzymes: monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) and monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B). They are best known as highly efficacious anti-depressants, as well as effective therapeutic agents for panic disorder and social phobia. They are particularly effective in treatment-resistant depression and atypical depression. They are also used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease and several other disorders.
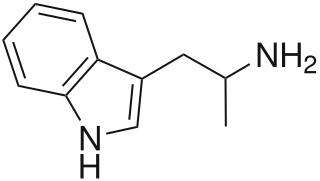
α-Methyltryptamine is a psychedelic, stimulant, and entactogen drug of the tryptamine class. It was originally developed as an antidepressant by workers at Upjohn in the 1960s, and was used briefly as an antidepressant in Russia under the trade name Indopan before being discontinued.

Monoamine neurotransmitters are neurotransmitters and neuromodulators that contain one amino group connected to an aromatic ring by a two-carbon chain (such as -CH2-CH2-). Examples are dopamine, norepinephrine and serotonin.

Phenethylamine (PEA) is an organic compound, natural monoamine alkaloid, and trace amine, which acts as a central nervous system stimulant in humans. In the brain, phenethylamine regulates monoamine neurotransmission by binding to trace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1) and inhibiting vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2) in monoamine neurons. To a lesser extent, it also acts as a neurotransmitter in the human central nervous system. In mammals, phenethylamine is produced from the amino acid L-phenylalanine by the enzyme aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase via enzymatic decarboxylation. In addition to its presence in mammals, phenethylamine is found in many other organisms and foods, such as chocolate, especially after microbial fermentation.

Pethidine, also known as meperidine and sold under the brand name Demerol among others, is a synthetic opioid pain medication of the phenylpiperidine class. Synthesized in 1938 as a potential anticholinergic agent by the German chemist Otto Eisleb, its analgesic properties were first recognized by Otto Schaumann while working for IG Farben, Germany. Pethidine is the prototype of a large family of analgesics including the pethidine 4-phenylpiperidines, the prodines, bemidones and others more distant, including diphenoxylate and analogues.

DET, also known under its chemical name N,N-diethyltryptamine and as T-9, is a psychedelic drug closely related to DMT and 4-HO-DET. However, despite its structural similarity to DMT, its activity is induced by an oral dose of around 50–100 mg, without the aid of MAO inhibitors, and the effects last for about 2–4 hours.
An adrenergic agonist is a drug that stimulates a response from the adrenergic receptors. The five main categories of adrenergic receptors are: α1, α2, β1, β2, and β3, although there are more subtypes, and agonists vary in specificity between these receptors, and may be classified respectively. However, there are also other mechanisms of adrenergic agonism. Epinephrine and norepinephrine are endogenous and broad-spectrum. More selective agonists are more useful in pharmacology.

Isocarboxazid is a non-selective, irreversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine class used as an antidepressant. Along with phenelzine and tranylcypromine, it is one of only three classical MAOIs still available for clinical use in the treatment of psychiatric disorders in the United States, though it is not as commonly employed in comparison to the others.

para-Methoxyphenylpiperazine is a piperazine derivative with stimulant effects which has been sold as an ingredient in "Party pills", initially in New Zealand and subsequently in other countries around the world.

Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and body as both a hormone and neurotransmitter. The name "noradrenaline", derived from Latin roots meaning "at/alongside the kidneys", is more commonly used in the United Kingdom; in the United States, "norepinephrine", derived from Greek roots having that same meaning, is usually preferred. "Norepinephrine" is also the international nonproprietary name given to the drug. Regardless of which name is used for the substance itself, parts of the body that produce or are affected by it are referred to as noradrenergic.

Lobeline is a pyridine alkaloid found in a variety of plants, particularly those in the genus Lobelia, including Indian tobacco, Devil's tobacco, great lobelia, Lobelia chinensis, and Hippobroma longiflora. In its pure form, it is a white amorphous powder which is freely soluble in water.

Etamivan is a respiratory stimulant drug related to nikethamide. It was mainly used in the treatment of barbiturate overdose and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, but has now largely fallen into disuse.

Diclofensine was developed by Hoffmann-La Roche in the 1970s in the search for a new antidepressant. It was found that the (S)-isomer was responsible for activity. Is a stimulant drug which acts as a triple monoamine reuptake inhibitor, primarily inhibiting the reuptake of dopamine and norepinephrine, with affinities (Ki) of 16.8 nM, 15.7 nM, and 51 nM for DAT, NET, and SERT, respectively. It was found to be an effective antidepressant in human trials, with relatively few side effects, but was ultimately dropped from clinical development, possibly due to concerns about its abuse potential.

A monoamine releasing agent (MRA), or simply monoamine releaser, is a drug that induces the release of a monoamine neurotransmitter from the presynaptic neuron into the synapse, leading to an increase in the extracellular concentrations of the neurotransmitter. Many drugs induce their effects in the body and/or brain via the release of monoamine neurotransmitters, e.g., trace amines, many substituted amphetamines, and related compounds.

Substituted phenethylamines are a chemical class of organic compounds that are based upon the phenethylamine structure; the class is composed of all the derivative compounds of phenethylamine which can be formed by replacing, or substituting, one or more hydrogen atoms in the phenethylamine core structure with substituents.
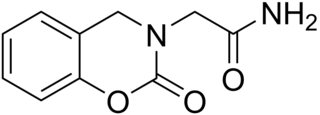
Caroxazone is an antidepressant which was formerly used for the treatment of depression but is now no longer marketed. It acts as a reversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor (RIMA) of both MAO-A and MAO-B subtypes, with five-fold preference for the latter.

Mepiprazole is an anxiolytic drug of the phenylpiperazine group with additional antidepressant properties that is marketed in Spain. It acts as a 5-HT2A and α1-adrenergic receptor antagonist and inhibits the reuptake and induces the release of serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine to varying extents, and has been described as a serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitor (SARI). Controlled clinical trials of mepiprazole in patients with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) were also carried out and suggested some benefits of the drug in relieving symptoms of IBS in some patients. Similarly to other phenylpiperazines like trazodone, nefazodone, and etoperidone, mepiprazole produces mCPP as an active metabolite.
A monoamine reuptake inhibitor (MRI) is a drug that acts as a reuptake inhibitor of one or more of the three major monoamine neurotransmitters serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine by blocking the action of one or more of the respective monoamine transporters (MATs), which include the serotonin transporter (SERT), norepinephrine transporter (NET), and dopamine transporter (DAT). This in turn results in an increase in the synaptic concentrations of one or more of these neurotransmitters and therefore an increase in monoaminergic neurotransmission.
α-Alkyltryptamines are a group of substituted tryptamines which possess an alkyl group, such as a methyl or ethyl group, attached at the alpha carbon, and in most cases no substitution on the amine nitrogen. α-Alkylation of tryptamine makes it much more metabolically stable and resistant to degradation by monoamine oxidase, resulting in increased potency and greatly lengthened half-life. This is analogous to α-methylation of phenethylamine into amphetamine.
Amphetamine type stimulants (ATS) are a group of synthetic drugs that are chemical derivatives of the parent compound alpha-methylphenethylamine, also known as amphetamine. Common ATS includes amphetamine, methamphetamine, ephedrine, pseudoephedrine, 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA), 3,4-methylenedioxyamphetamine (MDA) and 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDEA). ATS when used illicitly has street names including ice, meth, crystal, crank, bennies, and speed. Within the group of amphetamine-type stimulants, there are also prescription drugs including mixed amphetamine salts, dextroamphetamine, and lisdexamfetamine.