Related Research Articles
Medical physics deals with the application of the concepts and methods of physics to the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of human diseases with a specific goal of improving human health and well-being. Since 2008, medical physics has been included as a health profession according to International Standard Classification of Occupation of the International Labour Organization.
Gabor Tamas Herman is a Hungarian-American professor of computer science. He is Emiritas Professor of Computer Science at The Graduate Center, City University of New York (CUNY) where he was Distinguished Professor until 2017. He is known for his work on computerized tomography. He is a fellow of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE).
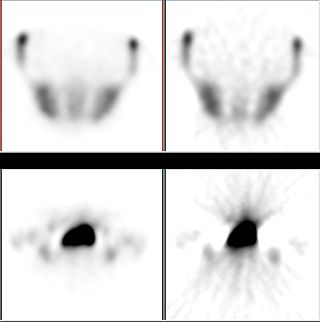
Iterative reconstruction refers to iterative algorithms used to reconstruct 2D and 3D images in certain imaging techniques. For example, in computed tomography an image must be reconstructed from projections of an object. Here, iterative reconstruction techniques are usually a better, but computationally more expensive alternative to the common filtered back projection (FBP) method, which directly calculates the image in a single reconstruction step. In recent research works, scientists have shown that extremely fast computations and massive parallelism is possible for iterative reconstruction, which makes iterative reconstruction practical for commercialization.
Lawrence Alan Shepp was an American mathematician, specializing in statistics and computational tomography.
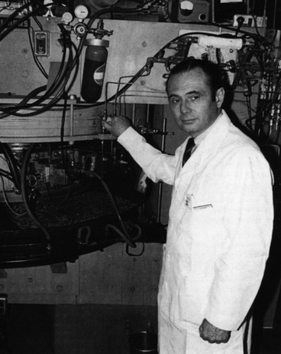
Michel Matthew Ter-Pogossian was an American medical physicist. He was professor of radiology at the Washington University School of Medicine for over 30 years. A pioneer in nuclear medicine, he is best known for his research on the positron emission tomography (PET). He is considered one of its creators and often referred to as the "father of PET."
Michael Edward Phelps is a professor and an American biophysicist. He is known for being one of the fathers of positron emission tomography (PET).
Abass Alavi is an Iranian-American physician-scientist specializing in the field of molecular imaging, most notably in the imaging modality of positron emission tomography (PET). In August 1976, he was part of the team that performed the first human PET studies of the brain and whole body using the radiotracer [18F]Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG). Alavi holds the position of Professor of Radiology and Neurology, as well as Director of Research Education in the Department of Radiology at the University of Pennsylvania. Over a career spanning five decades, he has amassed over 2,300 publications and 60,000 citations, earning an h-index of 125 and placing his publication record in the top percentile of scientists.
The IEEE Marie Sklodowska-Curie Award is a Technical Field Award that was established by the IEEE Board of Directors in 2008. This award may be presented for outstanding contributions to the field of nuclear and plasma sciences and engineering. This award may be presented to an individual, individuals on a team, or up to three multiple recipients. Recipients of this award receive a bronze medal, certificate, and honorarium. This award was presented for the first time in 2011.

Zang-Hee Cho is a South Korean neuroscientist who developed the first Ring-PET scanner and the scintillation detector BGO. More recently, Cho developed the first PET-MRI fusion molecular imaging device for neuro-molecular imaging.

Frank Natterer is a German mathematician. He was born in Wangen im Allgäu, Germany. Natterer pioneered and shaped the field of mathematical methods in imaging including computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and ultrasonic imaging.
Allen Robert Tannenbaum was an American applied mathematician who finished his career as a Distinguished Professor in the Departments of Computer Science and Applied Mathematics & Statistics at the State University of New York at Stony Brook.

Andreas Mandelis FRSC, FCAE, FAPS, FSPIE, FAAAS, FASME, is a Greek - Canadian physicist who is a professor and researcher in the department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering at the University of Toronto. He is the director of the Center for Advanced Diffusion-Wave and Photoacoustic Technologies (CADIPT). and of the Institute for Advanced Non-Destructive and Non-Invasive Diagnostic Technologies (IANDIT) at the University of Toronto. He is an internationally recognized expert in thermophotonics. and is considered a pioneer in the fields of diffusion-wave, photothermal, and photoacoustic sciences and related technologies. His research interests encompass studies of physical energy conversion processes in condensed and biological matter as they impact instrumentation science and signal generation technologies with applications spanning the development of a wide spectrum of novel instrumentation, measurement and imaging techniques using optical-to-thermal, thermoelastic, electronic, ultrasonic and/or photonic energy conversion high-dynamic-range and high-sensitivity analytical methodologies, leading to advanced non-destructive / non-invasive diagnostic, inspection and monitoring technologies with major focus on advanced dynamic imaging instrumentation for industrial and biomedical applications. He is the inventor of a photothermal imaging radar which can detect tooth decay at an early stage, can detect the onset of cancerous lesions in soft tissues, cracks in teeth and monitor dental structural integrity over time. His research team also pioneered and patented 22 analytical instrumentation and measurement methodologies and metrologies.
Bruce Rosen is an American physicist and radiologist and a leading expert in the area of functional neuroimaging. His research for the past 30 years has focused on the development and application of physiological and functional nuclear magnetic resonance techniques, as well as new approaches to combine functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) data with information from other modalities such as positron emission tomography (PET), magnetoencephalography (MEG) and noninvasive optical imaging. The techniques his group has developed to measure physiological and metabolic changes associated with brain activation and cerebrovascular insult are used by research centers and hospitals throughout the world.

Michael Ira Miller is an American-born biomedical engineer and data scientist, and the Bessie Darling Massey Professor and Director of the Johns Hopkins University Department of Biomedical Engineering. He worked with Ulf Grenander in the field of Computational Anatomy as it pertains to neuroscience, specializing in mapping the brain under various states of health and disease by applying data derived from medical imaging. Miller is the director of the Johns Hopkins Center for Imaging Science, Whiting School of Engineering and codirector of Johns Hopkins Kavli Neuroscience Discovery Institute. Miller is also a Johns Hopkins University Gilman Scholar.
Yuichi Motai is a Japanese researcher, professor, and book author. He serves as director of the Sensory Intelligence Laboratory at Virginia Commonwealth University (VCU) and as an associate professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering. Motai is a past professor at University of Vermont; He was a visiting faculty of Air Force Research Lab at Hanscom MA, and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA.

Peter J. H. Scott FRSC CChem is a British and American chemist and radiochemist who is a professor of radiology, professor of pharmacology and professor of medicinal chemistry, as well as a core member of the Rogel Cancer Center at the University of Michigan in the United States. He is Chief of Nuclear Medicine and director of the University of Michigan Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Center, and runs a research group developing new radiochemistry methodology and novel PET radiotracers.
Audrey K. Ellerbee Bowden is an American engineer and Dorothy J. Wingfield Phillips Chancellor's Faculty Fellow at Vanderbilt University, as well as an Associate Professor of Biomedical Engineering and Electrical Engineering. She is a Fellow of Optica, the American Institute for Medical and Biological Engineering and the International Society for Optics and Photonics (SPIE).

Katherine Whittaker Ferrara is an American engineer who is a professor of radiology at Stanford University. Ferrara has been elected a Fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science, Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers and American Institute for Medical and Biological Engineering.

Hui Cao (曹蕙) is a Chinese-American physicist who is the professor of applied physics, a professor of physics and a professor of electrical engineering at Yale University. Her research interests are mesoscopic physics, complex photonic materials and devices, with a focus on non-conventional lasers and their unique applications. She is an elected member of the US National Academy of Sciences and of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences.

Ge Wang is a medical imaging scientist focusing on computed tomography (CT) and artificial intelligence (AI) especially deep learning. He is the Clark & Crossan Chair Professor of Biomedical Engineering and the Director of the Biomedical Imaging Center at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, Troy, New York, USA. He is known for his employment on CT and AI-based imaging. He is Fellow of American Institute for Medical and Biological Engineering (AIMBE), Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), International Society for Optics and Photonics (SPIE), Optical Society of America (OSA/Optica), American Association of Physicists in Medicine (AAPM), American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS), and National Academy of Inventors (NAI).
References
- ↑ "Dr. Richard Carson, Ph.D. | Neuroinformatics Research Group". nrg.wustl.edu. Retrieved 2022-02-05.
- 1 2 "Richard Carson, PhD". medicine.yale.edu. Retrieved 2022-02-05.
- ↑ anonymous. "Richard Carson Wins IEEE Award". Yale School of Engineering & Applied Science. Retrieved 2022-02-05.