Related Research Articles

Charles Blount, 1st Earl of Devonshire, KG was an English nobleman and soldier who served as Lord Deputy of Ireland under Queen Elizabeth I, and later as Lord Lieutenant of Ireland under King James I.

Hugh O'Neill, was an Irish Gaelic lord, Earl of Tyrone and was later created The Ó Néill Mór, Chief of the Name. O'Neill's career was played out against the background of the Tudor conquest of Ireland, and he is best known for leading a coalition of Irish clans during the Nine Years' War, the strongest threat to the House of Tudor in Ireland since the uprising of Silken Thomas against King Henry VIII.

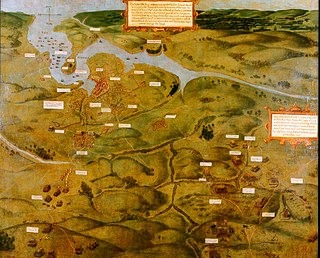
The siege of Kinsale, also known as the battle of Kinsale, was the ultimate battle in England's conquest of Gaelic Ireland, commencing in October 1601, near the end of the reign of Queen Elizabeth I, and at the climax of the Nine Years' War—a campaign by Hugh O'Neill, Hugh Roe O'Donnell and other Irish lords against English rule.
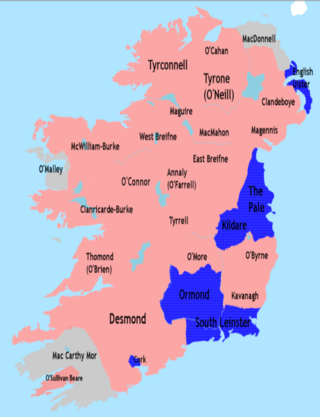
The Nine Years' War, sometimes called Tyrone's Rebellion, took place in Ireland from 1593 to 1603. It was fought between an Irish confederation—led mainly by Hugh O'Neill of Tyrone and Hugh Roe O'Donnell of Tyrconnell—against English rule in Ireland, and was a response to the ongoing Tudor conquest of Ireland. The war began in Ulster and northern Connacht, but eventually engulfed the entire island. The Irish alliance won numerous victories against the English forces in Ireland, such as the Battle of Clontibret (1595) and the Battle of the Yellow Ford (1598), but the English won a pivotal victory against the alliance and their Spanish allies in the siege of Kinsale (1601–02). The war ended with the Treaty of Mellifont (1603). Many of the defeated northern lords left Ireland to seek support for a new uprising in the Flight of the Earls (1607), never to return. This marked the end of Gaelic Ireland and led to the Plantation of Ulster.

The Battle of the Yellow Ford was fought in County Armagh on 14 August 1598, during the Nine Years' War in Ireland. An English army of about 4,000, led by Henry Bagenal, was sent from the Pale to relieve the besieged Blackwater Fort. Marching from Armagh to the Blackwater, the column was routed by a Gaelic Irish army under Hugh O'Neill of Tyrone. O'Neill's forces divided the English column and a large earthwork stalled its advance. Bagenal was killed by an Irish musketeer, and scores of his men were killed and wounded when the English gunpowder wagon exploded. About 1,500 of the English army were killed and 300 deserted. After the battle, the Blackwater Fort surrendered to O'Neill. The battle marked an escalation in the war, as the English Crown greatly bolstered its military forces in Ireland, and many Irish lords who had been neutral joined O'Neill's alliance.

Sir John Norris, or Norreys, of Rycote, Oxfordshire, and of Yattendon and Notley in Berkshire, was an English soldier. The son of Henry Norris, 1st Baron Norreys, he was a lifelong friend of Queen Elizabeth.
Aodh Mag Uidhir, anglicised as Hugh Maguire was Chief of the Name of the Irish clan Maguire and Lord of Fermanagh during the reign of Elizabeth I. He died in battle resisting the Tudor conquest of Ireland as part of the Nine Years War.

The Battle of Clontibret was fought in County Monaghan in May 1595, during the Nine Years' War in Ireland. A column of 1,750 English troops led by Henry Bagenal was ambushed near Clontibret by a larger Gaelic Irish army led by Hugh O'Neill, Earl of Tyrone. The English column had been sent to relieve the besieged English garrison at Monaghan Castle. The English suffered very heavy losses, but a suicidal cavalry charge apparently saved it from destruction. The Irish victory shocked the English and was their first severe setback during the war.

The Battle of Curlew Pass was fought on 15 August 1599 during the campaign of the Earl of Essex in the Nine Years' War, between an English force under Sir Conyers Clifford and a rebel Irish force led by Aodh Ruadh Ó Domhnaill. The English were ambushed and routed while marching through a pass in the Curlew Mountains, near the town of Boyle, in the west of Ireland. The English forces suffered heavy casualties. Losses by allied Irish forces were not recorded but were probably minimal.

The Second Desmond Rebellion (1579–1583) was the more widespread and bloody of the two Desmond Rebellions in Ireland launched by the FitzGerald Dynasty of Desmond in Munster against English rule. The second rebellion began in July 1579 when James FitzMaurice FitzGerald landed in Ireland with a force of Papal troops, triggering an insurrection across the south of Ireland on the part of the Desmond dynasty, their allies, and others who were dissatisfied for various reasons with English government of the country. The rebellion ended with the 1583 death of Gerald FitzGerald, 14th Earl of Desmond, and the defeat of the rebels.
Events from the year 1600 in Ireland.
The Treaty of Mellifont, also known as the Articles of Mellifont, was signed in 1603 and ended the Nine Years' War which took place in the Kingdom of Ireland from 1594 to 1603.
Sir Francis Roe, alias Rooe, was an English-born infantry officer who served in Ireland during the Nine Years' War, obtained grants of land during the Plantation of Ulster, and became a member of the Parliament of Ireland and mayor of Drogheda.
Sir Josias Bodley (1550-1618) was an English military engineer noted for his service in Ireland during the Nine Years' War. Following the end of the war he remained in Ireland where he oversaw the rebuilding of several major forts. In 1609 he was entrusted with the Bodley Survey which mapped out terrain for the Ulster Plantation.

The siege of Enniskillen took place at Enniskillen in Fermanagh, Ireland, in 1594 and 1595, during the Nine Years' War. In February 1594, the English had captured Enniskillen Castle from the Irish after a waterborne assault and massacred the defenders after they surrendered. From May 1594, an Irish army under Hugh Maguire and Cormac MacBaron O'Neill besieged the English garrison in the castle, and in August they defeated an English relief force. A second relief force was allowed to resupply the garrison, but the castle remained cut off. Eventually, in May 1595, the English garrison surrendered to the Irish and were then massacred.

The Battle of the Ford of the Biscuits took place in Fermanagh, Ireland on 7 August 1594, during the Nine Years' War. A column of almost 650 English troops led by Sir Henry Duke was ambushed and defeated by a Gaelic Irish force under Hugh Maguire and Cormac MacBaron O'Neill at the Arney River. The English column had been sent to relieve and resupply Enniskillen Castle, which had been under siege by the Irish since May. The English suffered at least 56 killed and 69 wounded, and were forced to make a hasty retreat.