Related Research Articles

The Caribbean Sea is an American mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean in the tropics of the Western Hemisphere. It is bounded by Mexico and Central America to the west and south west, to the north by the Greater Antilles starting with Cuba, to the east by the Lesser Antilles, and to the south by the north coast of South America.

The Norwegian Sea is a marginal sea in the Arctic Ocean, northwest of Norway between the North Sea and the Greenland Sea, adjoining the Barents Sea to the northeast. In the southwest, it is separated from the Atlantic Ocean by a submarine ridge running between Iceland and the Faroe Islands. To the north, the Jan Mayen Ridge separates it from the Greenland Sea.

The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south and is bounded by the continents of Asia and Australia in the west and the Americas in the east.

A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in groups.

In marine geology, a guyot, also known as a tablemount, is an isolated underwater volcanic mountain (seamount) with a flat top more than 200 m (660 ft) below the surface of the sea. The diameters of these flat summits can exceed 10 km (6.2 mi). Guyots are most commonly found in the Pacific Ocean, but they have been identified in all the oceans except the Arctic Ocean.

The Philippine Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean east of the Philippine archipelago, occupying an estimated surface area of 5 million square kilometers. The Philippine Sea Plate forms the floor of the sea. It is bordered by the first island chain to the west, which comprises the Ryukyu Islands in the northwest and Taiwan in the due west, and the Filipino islands of Luzon, Catanduanes, Samar, Leyte and Mindanao to the southwest; by the Japanese islands of Honshu, Shikoku and Kyūshū to the north; by the second island chain to the east, which comprises the Bonin Islands and Iwo Jima in the northeast, the Mariana Islands in the due east, and Halmahera, Palau, Yap and Ulithi in the southeast; and by Indonesia's Morotai Island to the south.
Darwin Mounds is a large field of undersea sand mounds situated off the north west coast of Scotland that were first discovered in May 1998. They provide a unique habitat for ancient deep water coral reefs and were found using remote sensing techniques during surveys funded by the oil industry and steered by the joint industry and United Kingdom government group the Atlantic Frontier Environment Network (AFEN). The mounds were named after the research vessel, itself named for the eminent naturalist and evolutionary theorist Charles Darwin.
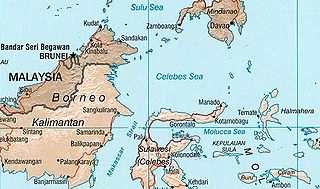
The Celebes Sea of the western Pacific Ocean is bordered on the north by the Sulu Archipelago and Sulu Sea and Mindanao Island of the Philippines, on the east by the Sangihe Islands chain, on the south by Sulawesi's Minahasa Peninsula, and on the west by northern Kalimantan in Indonesia. It extends 420 miles (675 km) north-south by 520 mi (840 km) east-west and has a total surface area of 110,000 square miles (280,000 km2), to a maximum depth of 20,300 feet (6,200 m). South of the Mangkalihat Peninsula, the sea opens southwest through the Makassar Strait into the Java Sea.

Pulley Ridge is a mesophotic coral reef system off the shores of the continental United States. The reef rests on sunken barrier islands and lies 100 miles west of the Tortugas Ecological Reserve and stretches north about 60 miles at depths ranging from 60–80 meters. Pulley Ridge was originally discovered in 1950 during a dredging operation conducted by an academic group from Texas. While well known to fishermen, this remarkable habitat remained undiscovered by scientists until 1999 when the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) and graduate students from the University of South Florida happened upon it. This reef system, like other mesophotic ecosystems, is inhabited by photosynthesizing corals and algae that are adapted to low-light environments. It is habitat for numerous species of bottom fish including Epinephelus morio spawning area.

John Pennekamp Coral Reef State Park is a Florida State Park located on Key Largo in Florida. It includes approximately 70 nautical square miles (240 km²) of adjacent Atlantic Ocean waters. The park is approximately 25 miles in length and extends 3 miles into the Atlantic Ocean. It was the first underwater park in the United States. The park was added to the National Register of Historic Places on April 14, 1972. The primary attractions of the park are the coral reefs and their associated marine life.

Elizabeth and Middleton Reefs Marine National Park Reserve is a former Marine protected area consisting of waters around Elizabeth and Middleton Reefs located at the south-eastern end of the Coral Sea Islands, an Australian territory in the Coral Sea. It was incorporated into the new Lord Howe Commonwealth Marine Reserve in December 2012. The two reefs also form a Ramsar site, having been listed as Ramsar Site 1223, on 21 October 2002, under the Ramsar Convention as a wetland of international importance.

The Miami Terrace Reef is a coral reef off the coast of Florida stretching from South Miami to Boca Raton, in the Atlantic Ocean. It lies in depths of 650 to 2,000 feet on top of a geological formation known as the Miami Terrace, a 40-mile (65 km) long shelf about 15 miles (24 km) off shore. Much of the platform remains unexplored, and new portions of the reef are still being discovered. University of Miami researchers discovered new reef sites there in December 2005.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and introduction to Oceanography.

The habitat of deep-water corals, also known as cold-water corals, extends to deeper, darker parts of the oceans than tropical corals, ranging from near the surface to the abyss, beyond 2,000 metres (6,600 ft) where water temperatures may be as cold as 4 °C (39 °F). Deep-water corals belong to the Phylum Cnidaria and are most often stony corals, but also include black and horny corals and soft corals including the Gorgonians. Like tropical corals, they provide habitat to other species, but deep-water corals do not require zooxanthellae to survive.

The Florida Reef is the only living coral barrier reef in the continental United States. It is the third largest coral barrier reef system in the world. It lies a few miles seaward of the Florida Keys, is about 4 miles wide and extends 270 km (170 mi) from Fowey Rocks just east of Soldier Key to just south of the Marquesas Keys. The barrier reef tract forms a great arc, concentric with the Florida Keys, with the northern end, in Biscayne National Park, oriented north-south and the western end, south of the Marquesas Keys, oriented east-west. The rest of the reef outside Biscayne National Park lies within John Pennekamp Coral Reef State Park and the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary. Isolated coral patch reefs occur northward from Biscayne National Park as far north as Stuart, in Martin County. Coral reefs are also found in Dry Tortugas National Park west of the Marquesas Keys. There are more than 6,000 individual reefs in the system. The reefs are 5,000 to 7,000 years old, having developed since sea levels rose following the Wisconsinan glaciation.

Marine habitats are habitats that support marine life. Marine life depends in some way on the saltwater that is in the sea. A habitat is an ecological or environmental area inhabited by one or more living species. The marine environment supports many kinds of these habitats.

Redbird Reef is an artificial reef located in the Atlantic Ocean, off the coast of Slaughter Beach, Delaware, 16 miles (25.7 km) east of the Indian River Inlet.

Siderastrea radians, also known as the lesser starlet coral or the shallow-water starlet coral, is a stony coral in the family Siderastreidae. It is found in shallow parts of the western Atlantic Ocean as small, solid mounds or encrusting sheets.

Pterois is a genus of venomous marine fish, commonly known as lionfish, native to the Indo-Pacific. Also called zebrafish, firefish, turkeyfish, tastyfish or butterfly-cod, it is characterized by conspicuous warning coloration with red, white, creamy, or black bands, showy pectoral fins, and venomous spiky fin rays. Pterois radiata, Pterois volitans, and Pterois miles are the most commonly studied species in the genus. Pterois species are popular aquarium fish. P. volitans and P. miles are recent and significant invasive species in the west Atlantic, Caribbean Sea and Mediterranean Sea.

The Amazon Reef, or Amazonian Reef, is an extensive coral and sponge reef system, located in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of French Guiana and northern Brazil. It is one of the largest known reef systems in the world, with scientists estimating its length at over 1,000 kilometres, and its area as over 9,300 km2 (3,600 sq mi). Publication of its discovery was released in April 2016, following an oceanographic study of the region in 2012. Evidence of a large structure near the delta of the Amazon River dated from as early as the 1950s.
References
- 1 2 Huffington Post Scientists discover giant deep-sea coral reef off Atlantic coast, August 25, 2018