
Charles the Bald, also known as Charles II, was a 9th-century king of West Francia (843–877), King of Italy (875–877) and emperor of the Carolingian Empire (875–877). After a series of civil wars during the reign of his father, Louis the Pious, Charles succeeded, by the Treaty of Verdun (843), in acquiring the western third of the empire. He was a grandson of Charlemagne and the youngest son of Louis the Pious by his second wife, Judith.

Charles III, called the Simple or the Straightforward, was the king of West Francia from 898 until 922 and the king of Lotharingia from 911 until 919–923. He was a member of the Carolingian dynasty.

Hugh the Great was the duke of the Franks and count of Paris. He was the most powerful magnate in France.

Lotharingia was a medieval successor kingdom of the Carolingian Empire. It comprised present-day Lorraine (France), Luxembourg, Saarland (Germany), Netherlands, most of Belgium, and Germany west of the Rhine. It was named after King Lothair II, who received this territory as his share of the Kingdom of Middle Francia which his father, Lothair I, had held.

Lothair, sometimes called Lothair II, III or IV, was the penultimate Carolingian king of West Francia, reigning from 10 September 954 until his death in 986.

Judith of Flanders was a Carolingian princess who became Queen of Wessex by two successive marriages and later Countess of Flanders. Judith was the eldest child of the Carolingian emperor Charles the Bald and his first wife, Ermentrude of Orléans. In 856, she married Æthelwulf, King of Wessex. After her husband's death in 858, Judith married his son and successor, Æthelbald. King Ætheldbald died in 860. Both of Judith's first two marriages were childless. Her third marriage was to Baldwin I, Margrave of Flanders, with whom she had several children.
Kingdom of Burgundy was a name given to various states located in Western Europe during the Middle Ages. The historical Burgundy correlates with the border area of France and Switzerland and includes the major modern cities of Geneva and Lyon.
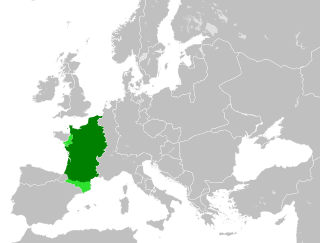
In medieval historiography, West Francia or the Kingdom of the West Franks constitutes the initial stage of the Kingdom of France and extends from the year 843, from the Treaty of Verdun, to 987, the beginning of the Capetian dynasty. It was created from the division of the Carolingian Empire following the death of Louis the Pious, with its neighbor East Francia eventually evolving into the Kingdom of Germany.
The County of Verdun was a sovereign medieval county in the Duchy of Lower Lorraine.
Wigeric or Wideric was a Frankish nobleman and the count of the Bidgau and held the rights of a count within the city of Trier. He received also the advocacy of the Abbey of Saint Rumbold at Mechelen from King Charles the Simple of West Francia. From 915 or 916, he was the count palatine of Lotharingia. He was the founder of the House of Ardennes.

The Prince-Bishopric of Verdun was a state of the Holy Roman Empire. It was located at the western edge of the Empire and was bordered by France, the Duchy of Luxembourg, and the Duchy of Bar. Some time in the late 990s, the suzerainty of the County of Verdun passed from Herman of Ename of the House of Ardenne–Verdun to the Bishopric of Verdun.
Eberhard was the Frankish Duke of Friuli from 846. His name is alternatively spelled Everard, Evrard, Erhard, or Eberard; in Latinized fashion, Everardus, Eberardus, or Eberhardus. He wrote his own name "Evvrardus". He was an important political, military, and cultural figure in the Carolingian Empire during his lifetime. He kept a large library, commissioned works of Latin literature from Lupus Servatus and Sedulius Scottus, and maintained a correspondence with the theologians and church leaders Gottschalk, Rabanus Maurus, and Hincmar.
Count Lambert "the Bearded" was the first person to be described as a count of Leuven in a surviving contemporary record, being described this way relatively late in life, in 1003. He is also the patrilineal ancestor of all the future counts of Leuven and dukes of Brabant until his descendant John III, Duke of Brabant, who died in 1355.
Cunigunda of Sulichgau (893-924) was the daughter of Ermentrude of France, and granddaughter in turn of Louis the Stammerer. In 898 her uncle Charles III gained control as king of the Franks, changing Cunigunda's life for the better.
Ermentrude was a Princess of France in the Middle Ages, named after her grandmother, Queen Ermentrude of Orléans.
Engelram was Chamberlain to Charles the Bald through sometime after 871. He also held the title of count from 853, but it is unclear what his domain was. Nothing is known about his ancestry.
Friderada was a ninth-century noblewoman about whom very little is known. She was probably related to Liudolf, Duke of Saxony. Friderada married at least three times and was the grandmother of Otto, Duke of Lorraine.
The counts of Chiny were part of the nobility of Lotharingia that ruled from the 9th to the 14th century in what is now part of Belgium.
Otto I(Eudes) (died 987), Count of Chiny, perhaps son of Adalbert I the Pious, Count of Vermandois, and Gerberge of Lorraine. Although he probably did not use the title, Otto is regarded as the first Count of Chiny.

Louis IV, called d'Outremer or Transmarinus, reigned as King of West Francia from 936 to 954. A member of the Carolingian dynasty, he was the only son of king Charles the Simple and his second wife Eadgifu of Wessex, daughter of King Edward the Elder of Wessex. His reign is mostly known thanks to the Annals of Flodoard and the later Historiae of Richerus.








