
William Joseph Hardee was a career U.S. Army and Confederate States Army officer. For the U.S. Army, he served in the Second Seminole War and in the Mexican–American War, where he was captured and exchanged. In the American Civil War, he sided with the South and became a general. Hardee served in the Western Theater and quarreled sharply with two of his commanding officers, Braxton Bragg and John Bell Hood. He served in the Atlanta Campaign of 1864 and the Carolinas Campaign of 1865, where he surrendered with General Joseph E. Johnston to William Tecumseh Sherman in April. Hardee's writings about military tactics were widely used on both sides in the conflict.

Skirmishers are light infantry or light cavalry soldiers deployed as a vanguard, flank guard or rearguard to screen a tactical position or a larger body of friendly troops from enemy advances. They are usually deployed in a skirmish line, an irregular open formation that is much more spread out in depth and in breadth than a traditional line formation. Their purpose is to harass the enemy by engaging them in only light or sporadic combat to delay their movement, disrupt their attack, or weaken their morale. Such tactics are collectively called skirmishing.
William Henry Gilham was an American soldier, teacher, chemist, and author. A member of the faculty at Virginia Military Institute, in 1860, he wrote a military manual which was still in modern use 145 years later. He served in the Confederate Army during the American Civil War, and became president of Southern Fertilizing Company in Richmond after the War.

The Springfield Model 1861 was a Minié-type rifled musket used by the United States Army and Marine Corps during the American Civil War. Commonly referred to as the "Springfield". It was the most widely used Union Army shoulder weapon during the Civil War, favored for its range, accuracy, and reliability.
A rifled musket, rifle musket, or rifle-musket is a type of firearm made in the mid-19th century. Originally the term referred only to muskets that had been produced as a smoothbore weapon and later had their barrels replaced with rifled barrels. The term later included rifles that directly replaced, and were of the same design overall as, a particular model of smoothbore musket.

The Hardee hat, also known as the Model 1858 Dress Hat and sometimes nicknamed the "Jeff Davis", was the regulation dress hat for enlisted men in the Union Army during the American Civil War. The Hardee hat was also worn by Confederate soldiers.

Line infantry was the type of infantry that composed the basis of European land armies from the late 17th century to the mid-19th century. Maurice of Nassau and Gustavus Adolphus are generally regarded as its pioneers, while Turenne and Montecuccoli are closely associated with the post-1648 development of linear infantry tactics. For both battle and parade drill, it consisted of two to four ranks of foot soldiers drawn up side by side in rigid alignment, and thereby maximizing the effect of their firepower. By extension, the term came to be applied to the regular regiments "of the line" as opposed to light infantry, skirmishers, militia, support personnel, plus some other special categories of infantry not focused on heavy front line combat.

Field artillery in the American Civil War refers to the artillery weapons, equipment, and practices used by the Artillery branch to support the infantry and cavalry forces in the field. It does not include siege artillery, use of artillery in fixed fortifications, or coastal or naval artillery. Nor does it include smaller, specialized artillery classified as small arms.

The infantry in the American Civil War comprised foot-soldiers who fought primarily with small arms and carried the brunt of the fighting on battlefields across the United States. The vast majority of soldiers on both sides of the Civil War fought as infantry and were overwhelmingly volunteers who joined and fought for a variety of reasons. Early in the war, there was great variety in how infantry units were organized and equipped - many copied famous European formations such as the Zouaves - but as time progressed there was more uniformity in their arms and equipment.

The city of Winchester, Virginia, and the surrounding area, were the site of numerous battles during the American Civil War, as contending armies strove to control the lower Shenandoah Valley. Winchester changed hands more often than any other Confederate city.
The M1841 Mississippi rifle is a muzzle-loading percussion rifle used in the Mexican–American War and the American Civil War.

The Richmond rifle was a rifled musket produced by the Richmond Armory in Richmond, Virginia, for use by the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War.

The 5th Arkansas Infantry, also called the Fighting Fifth (1861–1865) was a Confederate Army infantry regiment organized in Arkansas to serve for the Confederate States of America during the American Civil War. It served throughout the war in the western theater, seeing action in the Kentucky, Tennessee and Georgia campaigns. Following its depletion in numbers the regiment was consolidated several times with other Arkansas regiments, finally merging in 1865 into the 1st Arkansas Consolidated Infantry Regiment. Another Arkansas unit also had the designation 5th Arkansas, the 5th Regiment, Arkansas State Troops which participated in the Battle of Wilson's Creek, but was never transferred to Confederate Service. There is no connection between the two units.
During the American Civil War, an assortment of small arms found their way onto the battlefield. Though the muzzleloader percussion cap rifled musket was the most numerous weapon, being standard issue for the Union and Confederate armies, many other firearms, ranging from the single-shot breech-loading Sharps and Burnside rifles to the Spencer and the Henry rifles - two of the world's first repeating rifles - were issued by the hundreds of thousands, mostly by the Union. The Civil War brought many advances in firearms technology, most notably the widespread use of rifled barrels.
The Lorenz rifle was an Austrian rifle used in the mid 19th century. It was used in the Second Italian War of Independence in 1859 and the Austro-Prussian War in 1866, and also featured prominently in the American Civil War.

A sharpshooter is one who is highly proficient at firing firearms or other projectile weapons accurately. Military units composed of sharpshooters were important factors in 19th-century combat. Along with "marksman" and "expert", "sharpshooter" is one of the three marksmanship badges awarded by the United States Army and the United States Marine Corps. The United States Navy and the United States Coast Guard use a ribbon with an attached "S" device to note a sharpshooter qualification.

The 7th Arkansas Volunteer Infantry (1861−1865) was a Confederate Army infantry regiment during the American Civil War. Organized mainly from companies, including several prewar volunteer militia companies, raised in northeastern Arkansas, the regiment was among the first transferred to Confederate service, and spent virtually the entire war serving east of the Mississippi River. After the unit sustained heavy casualties in the Battle of Shiloh and the Kentucky Campaign, the unit spent most of the rest of the war field consolidated with the 6th Arkansas Infantry Regiment to form the 6th/7th Arkansas Infantry Regiment.
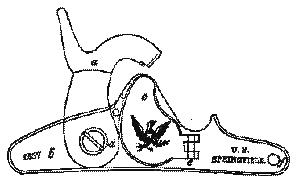
The Springfield Model 1855 was a rifled musket widely used in the American Civil War. It exploited the advantages of the new conical Minié ball, which could be deadly at over 1,000 yards (910 m). It was a standard infantry weapon for Union and Confederates alike, until the Springfield Model 1861 supplanted it, obviating the use of the insufficiently weather resistant Maynard tape primer.

William Stephen Walker was a Confederate States Army brigadier general during the American Civil War. He was born in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, but was raised by Robert J. Walker, his uncle, who was a Secretary of the Treasury and U.S. Senator. Walker served as a first lieutenant in the United States Army during the Mexican–American War from 1847 to 1848. He was discharged in 1848. Walker rejoined the army as captain in the 1st U.S. Cavalry Regiment on March 3, 1855, and served until he resigned on May 1, 1861. Walker was wounded in the left arm and lost his left foot during the Battle of Ware Bottom Church during the Overland Campaign. After the war, he lived at Atlanta, Georgia.












