Related Research Articles
Universal access to education is the ability of all people to have equal opportunity in education, regardless of their social class, gender, ethnicity background or physical and mental disabilities. The term is used both in college admission for the middle and lower classes, and in assistive technology for the disabled. Some critics feel that this practice in higher education, as opposed to a strict meritocracy, causes lower academic standards. In order to facilitate the access of education to all, countries have right to education.

The system of education in Uganda has a structure of 7 years of primary education, 6 years of secondary education, and 3 to 5 years of post-secondary education. The government of Uganda recognizes education as a basic human right and continues to strive to provide free primary education to all children in the country. However, issues with funding, teacher training, rural populations, and inadequate facilities continue to hinder the progress of educational development in Uganda. Girls in Uganda are disproportionately discriminated against in terms of education; they face harsher barriers when trying to gain an education and it has left the female population disenfranchised, despite government efforts to close the gap.
Youth participation is the active engagement of young people throughout their own communities. It is often used as a shorthand for youth participation in any many forms, including decision-making, sports, schools and any activity where young people are not historically engaged.

Student voice is "any expression of any learner regarding anything related to education" and describes "the distinct perspectives and actions of young people throughout schools focused on education. Tech educator Dennis Harper writes, "Student voice is giving students the ability to influence learning to include policies, programs, contexts and principles."

Craigie High School (CHS) is a co-educational government funded High school situated in the city of Dundee, Scotland. The school is located within Craigiebank and has been serving the areas of Craigiebank, Douglas and Pitkerro for over 40 years.
Tanbridge House School is a secondary school in Horsham, West Sussex. It is a specialist school of IT, Maths and Science. Its current head master is Mr Jules White who started in January 2008. Previous heads include Ms J Ball, Mr Neil Chapman, Dr Peter Thomas and Ms Maureen Johnson. The school teaches a wide variety of subjects across the curriculum. In 2012 95.7% of students achieved A*-C grades at GCSE. Of those, 79% achieved 5 A*-C including English and Maths.
Modern studies is a subject unique to the Scottish secondary school curriculum. The focus of Modern Studies is to develop learners' knowledge and understanding of contemporary political and social issues in local, Scottish, United Kingdom and international contexts.
Derby Moor Academy, the successor school to Derby Moor Community Sports College Trust, formerly known as Derby Moor Community School, is a secondary school situated on Moorway Lane, Littleover, Derby. It was established in January 2018 when the school converted to Academy status and joined the Spencer Academies Trust. It can also be seen as the successor to Derby School, which closed in 1989, resulting in Derby Moor opening in the same year with a new head teacher and governing body, although the buildings, pupils and most of the teaching staff were the same.
Evolving capacities is the concept in which education, child development and youth development programs led by adults take into account the capacities of the child or youth to exercise rights on their own behalf. It is also directly linked to the right to be heard, requiring adults to be mindful of their responsibilities to respect children's rights, protect them from harm, and provide opportunities so they can exercise their rights. The concept of evolving capacities is employed internationally as a direct alternative to popular concepts of child and youth development.
Multicultural education is a set of educational strategies developed to assist teachers when responding to the many issues created by the rapidly changing demographics of their students. It provides students with knowledge about the histories, cultures, and contributions of diverse groups; it assumes that the future society is pluralistic. It draws on insights from a number of different fields, including ethnic studies and women studies, and reinterprets content from related academic disciplines. It is also viewed as a way of teaching that promotes the principles of inclusion, diversity, democracy, skill acquisition, inquiry, critical thought, value of perspectives, and self-reflection. This method of teaching is found to be effective in promoting educational achievements among immigrants students and is thus attributed to the reform movement behind the transformation of schools.

UNICEF UK, also known as the United Kingdom Committee for UNICEF, is one of 36 UNICEF National Committees based in industrialised countries. The National Committees raise funds for the organisation's worldwide emergency and development work. In 2007, UNICEF UK raised £41.3 million for UNICEF’s work with children worldwide. UNICEF UK also advocates for lasting change for children. For example, it works to change government policies and practices that are detrimental to children’s rights in the UK and internationally.

UNICEF Philippines is one of over 190 country offices of the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF). One of the first UNICEF offices established in Asia, it works to uphold the rights of children in the Philippines, including their right to education, healthcare and protection from abuse and exploitation. It also advocates for political change in support of children, and works with partners from the public and private sectors to create change through sustainable programs.

UNICEF Indonesia is one of over 190 national offices of the United Nations Children’s Fund. As one of the first UNICEF offices established in Asia, UNICEF Indonesia has been on the ground since 1948 to uphold the rights of children in the vast archipelago, including their right to an education, healthcare and protection from abuse and exploitation. It also advocates for political change in support of children, and works with partner organizations from the public, charity and private sectors, to effect change.

Youth councils are a form of youth voice engaged in community decision-making. Youth councils exist on local, state, provincial, regional, national, and international levels among governments, non governmental organisations (NGOs), schools, and other entities.
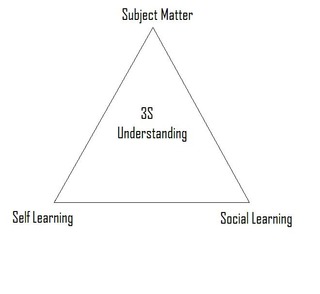
3S Understanding is a curriculum structure that was created by James G. Henderson. 3S Understanding is a mixture of three components that can be diagrammed as a triangle. The three Ss are Subject Matter, Self-learning, and Social Learning.
Children’s rights education is the teaching and practice of children’s rights in schools, educational programmes or institutions, as informed by and consistent with the United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child. When fully implemented, a children's rights education program consists of both a curriculum to teach children their human rights, and framework to operate the school in a manner that respects children's rights. Articles 29 and 42 of the Convention on the Rights of the Child require children to be educated about their rights
Children's rights in Malaysia have progressed since Malaysia acceded to the Convention on the Rights of the Child (CRC) in 1995 and introduced the Child Act in 2001.
Global citizenship education (GCED) is a form of civic learning that involves students' active participation in projects that address global issues of a social, political, economic, or environmental nature. The two main elements of GCE are 'global consciousness'; the moral or ethical aspect of global issues, and 'global competencies', or skills meant to enable learners to participate in changing and developing the world. The promotion of GCE was a response by governments and NGOs to the emergence of supranational institution, regional economic blocs, and the development of information and communications technologies. These have all resulted in the emergence of a more globally oriented and collaborative approach to education. GCE addresses themes such as peace and human rights, intercultural understanding, citizenship education, respect for diversity and tolerance, and inclusiveness.

The Republic of Armenia was admitted into the United Nations on March 2, 1992. Since December 1992 when UN opened its first office in Yerevan, Armenia signed and ratified many international treaties. There are fifteen specialized agencies, programs and funds in the UN Country Team under the supervision of the UN Resident Coordinator. Besides, the World Bank (WB), International Finance Corporation (IFC) and International Monetary Fund (IMF) have offices in the country. The focus was drawn to the attainment of the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) stipulated by the Millennium Declaration adopted during the Millennium Summit in 2000. The MDGs have simulated never before practiced actions to meet the needs of the world's poorest. As the MDG achievement date of December 2015 drew closer a new set of global sustainable development goals was consulted worldwide, to be adopted by the UN General Assembly in September 2015. Armenia was included in the initial group of 50 countries to conduct national consultations on the global Post-2015 development agenda.
Education for Justice is the process of promoting a culture of lawfulness through educational activities at all levels. Education for Justice aims at teaching the next generation about crime prevention, and to better understand and address problems that can undermine the rule of law. It promotes peace and encourages students to actively engage in their communities and future professions. Education for Justice is a basic legal knowledge, in which educational activities at all levels seek to promote understanding of crime prevention, peace, justice, human rights, and problems that can undermine the rule of law. Education reportedly plays a key role in transmitting and sustaining socio-cultural norms and ensuring their continued evolution. As such, governments may seek to strengthen this promotion of a culture of lawfulness through education.