The Rights and Resources Initiative (RRI) is a non-governmental organization working to encourage forest tenure and policy reforms and the transformation of the forest economy so that business reflects local development agendas and supports local livelihoods. RRI works at the country, regional and global levels, collaborating on research, advocacy and convening strategic actors.
The RRI Coalition is formed by a group of core partners who work in areas of their regional and thematic expertise. Partners also engage with a wide group of Collaborators who participate in and support RRI activities. The Initiative's 14 partners and 140 plus collaborator organizations are directly engaged in land and forest policy reforms in close to 20 countries throughout Africa, Asia, and Latin America. Together, they are working to encourage greater global commitment and action on pro-poor tenure, policy and market reforms.
This strategic coalition goes beyond the traditional set of international development actors to involve a wide spectrum of organizations, each of which provides a critical perspective in the larger chain of actors necessary to advance change.
The Rights and Resources Initiative was formally established in 2005 by the Coordinating Association of Indigenous and Community Agroforestry in Central America (ACICAFOC), the Center for International Forestry Research (CIFOR), Forest Trends, the Foundation for People and Community Development Papua New Guinea (FPCD), the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), and RECOFTC - The Center for People and Forests. In 2006, the Forest Peoples Programme, HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation, and the World Agroforestry Centre joined as RRI Partners. Civic Response joined in 2007, Federation of Community Forest Users Nepal (FECOFUN) joined in 2008, and the Samdhana Institute joined in January 2009. In late 2010, the Indigenous Peoples' International Centre for Policy Research and Education (Tebtebba) joined, followed by International Forestry Resources and Institutions (IFRI), the Salvadoran Research Program on Development and Environment (PRISMA), and the Centre for Environment and Development (CED) in 2011. The coalition is headquartered in Washington, D.C.
The Green Belt Movement (GBM) is an indigenous, grassroots, non-governmental organization based in Nairobi, Kenya, that takes a holistic approach to development by focusing on environmental conservation, community development and capacity building. Professor Wangari Maathai established the organization in 1977, under the auspices of the National Council of Women of Kenya.

The Center for International Forestry Research (CIFOR) is a non-profit scientific research organization that conducts research on the use and management of forests with a focus on tropical forests in developing countries. CIFOR, which merged with World Agroforestry on Jan. 1, 2019, is the forestry and agroforestry research center of the Consultative Group on International Agricultural Research (CGIAR), a network of 15 research centers around the world that focus on agricultural research for sustainable development, working closely with governments and other partners to help develop evidence-based solutions to problems related to sustainable agriculture and natural resource management.

Forestry laws govern activities in designated forest lands, most commonly with respect to forest management and timber harvesting. Forestry laws generally adopt management policies for public forest resources, such as multiple use and sustained yield. Forest management is split between private and public management, with public forests being sovereign property of the State. Forestry laws are now considered an international affair.
The International Forestry Resources and Institutions (IFRI) Network is a collective of research partners at 12 universities or non-governmental organizations in 11 countries around the world that focus on how institutions and governance arrangements shape forest use and management outcomes. Scholars and policy makers affiliated with IFRI are interested in understanding the role of formal and informal institutions in enhancing livelihoods and adaptive capacity of peoples, conserving biodiversity, and promoting greater sustainability in carbon sequestration. IFRI's goal is to carry out rigorous research that can help policy makers and forest users design and implement improved evidence-based forest policies. IFRI comprises partner collaborating research institutes in North America, Latin America, Asia and Africa. IFRI utilizes the Institutional Analysis and Development (IAD) framework, created at the Workshop in Political Theory and Policy Analysis at Indiana University by Elinor Ostrom and her colleagues.

The Indigenous Peoples of Africa Co-ordinating Committee (IPACC) was founded in 1997. It is one of the main trans-national network organizations recognised as a representative of African indigenous peoples in dialogues with governments and bodies such as the UN. As of 2008, IPACC was composed of 150 member organisations in 21 African countries.
The Intellectual Property Issues in Cultural Heritage (IPinCH) Project is a seven-year international research initiative based at Simon Fraser University, in British Columbia, Canada. IPinCH's work explores the rights, values, and responsibilities of material culture, cultural knowledge, and the practice of heritage research. The project is directed by Dr. George P. Nicholas, co-developed with Julie Hollowell and Kelly Bannister and is funded by the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada's (SSHRC) major collaborative research initiatives (MCRI) program.
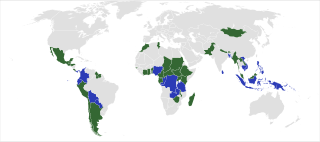
The United Nations Programme on Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation is a collaborative programme of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), created in 2008 in response to the UNFCCC decisions on the Bali Action Plan and REDD at COP-13. It should not be confused with REDD+, a voluntary climate change mitigation approach that has been developed by Parties to the UNFCCC.
The Rainforest Foundation US is a non-profit NGO working in Central and South America. It is one of the first international organizations to support the indigenous peoples of the world's rainforests in their efforts to protect their environment and fulfill their rights to land, life and livelihood.
Reducing emissions from deforestation and forest degradation and the role of conservation, sustainable management of forests and enhancement of forest carbon stocks in developing countries (REDD+) was first negotiated under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) in 2005, with the objective of mitigating climate change through reducing net emissions of greenhouse gases through enhanced forest management in developing countries. Most of the key REDD+ decisions were completed by 2013, with the final pieces of the rulebook finished in 2015.
The Connect U.S. Fund (CUSF) was a Washington, D.C.-based nonprofit that promotes responsible U.S. global engagement in issues like nuclear nonproliferation, human rights, climate change, and development. It was founded in 2004 by several foundations and shut down in 2013. The organization supported grantees and other non-governmental organizations in their efforts to collaborate, engage policy makers, and bring issues to the attention of the media. Its last President was Nancy Soderberg.

The International Day of Forests was established on the 21st day of March, by resolution of the United Nations General Assembly on November 28, 2013. Each year, various events celebrate and raise awareness of the importance of all types of forests, and trees outside forests, for the benefit of current and future generations. Countries are encouraged to undertake efforts to organize local, national, and international activities involving forests and trees, such as tree planting campaigns, on International Day of Forests. The Secretariat of the United Nations Forum on Forests, in collaboration with the Food and Agriculture Organization, facilitates the implementation of such events in collaboration with governments, the Collaborative Partnership on Forests, and international, regional and subregional organizations. International Day of Forests was observed for the first time on March 21, 2013.

Edwin Gariguez is a Filipino religious leader and environmentalist. He was awarded the Goldman Environmental Prize in 2012, for his voicing of protests on behalf of indigenous communities against large scale mining projects in the Philippines. Edwin Gariguez was the former executive secretary of National Secretariat for Social Action (NASSA), the humanitarian, advocacy and social development arm of the Catholic Bishops' Conference of the Philippines (CBCP).

The African Forum for Agricultural Advisory Services (AFAAS), is a continental organization for strengthening Agricultural Extension and Advisory Services (AEAS) in Africa. It operates within the framework of the Comprehensive Africa Agriculture Development Programme (CAADP), a venture of the African Union in the New Partnership for Africa's Development (NEPAD). AFAAS is an autonomous subsidiary of the Forum for Agricultural Research in Africa (FARA).
Runa Foundation is a public, non-profit organization with offices in Brooklyn, NY; Quito, Ecuador; Archidona, Ecuador; and Tarapoto, Peru. Runa Foundation's stated mission is to "create new value for tropical forests that benefit local people and the forest ecosystem". Runa Foundation is a 501(c)3 non-profit corporation registered in the state of Rhode Island.

The Global Landscapes Forum (GLF) is a multi-stakeholder forum dedicated to promoting the landscape approach.
The Hispanic Federation (HF) is a U.S based non-governmental organization focused on supporting Hispanic communities through local, state, and national advocacy. The Federation was founded in New York City in 1990 by a small group of Latino leaders, establishing initiatives to advocate for the interests of the Hispanic community and has expanded to establish programs, and policies in 16 states. The organization's objective is to empower and advance the Hispanic community primarily through service pillars, membership services, advocacy, and community programs. The Federation has formed relationships with a network of 100 Latino grassroots nonprofits, as well as collaborating with organizations, government officials, and private sector partners to enact systemic change related to a variety of socioeconomic issues for Hispanic communities. The Federation has gained national recognition for its work in areas of education, health, immigration, economic empowerment, civic engagement, environment, and organizational development to strengthening Latino institutions to ultimately increase the quality of life within Hispanic communities.








