Related Research Articles

The Roman Empire was the post-Republican state of ancient Rome. It included large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean in Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia, and was ruled by emperors. From the accession of Augustus as the first Roman emperor to the military anarchy of the 3rd century, it was a Principate with Italia as the metropole of its provinces and Rome as its sole capital. The Empire was later ruled by multiple emperors who shared control over the Western and Eastern Roman Empire. The imperial seat moved from Rome to Byzantium; following the collapse of the West in 476, it became its sole capital as Constantinople. The adoption of Christianity as the state church in 380 and the fall of the Western Roman Empire conventionally marks the end of classical antiquity and the beginning of the Middle Ages.

Logudorese Sardinian is one of the two written standards of the Sardinian language, which is often considered one of the most, if not the most conservative of all Romance languages. The orthography is based on the spoken dialects of central northern Sardinia, identified by certain attributes which are not found, or found to a lesser degree, among the Sardinian dialects centered on the other written form, Campidanese. Its ISO 639-3 code is src.
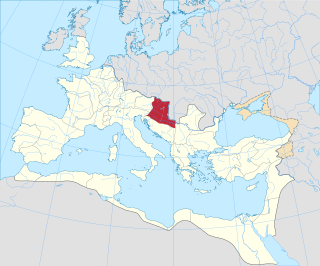
Pannonia was a province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, coterminous westward with Noricum and upper Italy, and southward with Dalmatia and upper Moesia. Pannonia was located in the territory that is now western Hungary, western Slovakia, eastern Austria, northern Croatia, north-western Serbia, northern Slovenia, and northern Bosnia and Herzegovina.
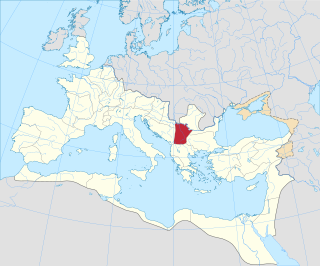
Moesia was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans south of the Danube River, which included most of the territory of modern eastern Serbia, Kosovo, north-eastern Albania, northern parts of North Macedonia, Northern Bulgaria, Romanian Dobruja and small parts of Southern Ukraine.

Līmes is a modern term used primarily for the Germanic border defence or delimiting system of Ancient Rome marking the borders of the Roman Empire, but it was not used by the Romans for that purpose. The term has been extended to refer to the frontier defences in other parts of the empire, such as in the east and in Africa.

Iconography, as a branch of art history, studies the identification, description and interpretation of the content of images: the subjects depicted, the particular compositions and details used to do so, and other elements that are distinct from artistic style. The word iconography comes from the Greek εἰκών ("image") and γράφειν.

Ripuarian or Rhineland Franks were one of the two main groupings of early Frankish people, and specifically it was the name eventually applied to the tribes who settled in the old Roman territory of the Ubii, with its capital at Cologne on the Rhine river in modern Germany. Their western neighbours were the Salii, or "Salian Franks", who were named already in late Roman records, and settled with imperial permission within the Roman Empire in what is today the southern part of the Netherlands, and Belgium, and later expanded their influence into the northern part of France above the Loire river, creating the Frankish empire of Francia.

A rione of Rome is a traditional administrative division of the city of Rome. "Rione" is an Italian term used since the 14th century to name a district of a town. The term was born in Rome, originating from the administrative divisions of the city. The word comes from the Latin word regio ; during the Middle Ages the Latin word became rejones, from which rione comes. Currently, all the rioni are located in Municipio I of Rome.

Sant'Angelo is the 11th rione of Rome, Italy, located in Municipio I. Often written as rione XI - Sant'Angelo, it has a coat of arms with an angel on a red background, holding a palm branch in its left hand. In another version, the angel holds a sword in its right hand and a scale in its left.

Testaccio is the 20th rione of Rome, identified by the initials R. XX, deriving its name from Monte Testaccio. It is located within the Municipio I.

The Art of Painting, also known as The Allegory of Painting, or Painter in his Studio, is a 17th-century oil on canvas painting by Dutch painter Johannes Vermeer. It is owned by the Austrian Republic and is on display in the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna.
Cesare Ripa was an Italian iconographer who worked for Cardinal Anton Maria Salviati as a cook and butler.

Sant'Omobono is a church in Rome at the foot of the Capitoline Hill in rione Ripa.

Italia turrita is the national personification or allegory of Italy, in the appearance of a young woman with her head surrounded by a mural crown completed by towers. It is often accompanied by the Stella d'Italia, from which the so-called Italia turrita e stellata, and by other additional attributes, the most common of which is the cornucopia. The allegorical representation with the towers, which draws its origins from ancient Rome, is typical of Italian civic heraldry, so much so that the wall crown is also the symbol of the cities of Italy.

Kelly Ripa is an American actress and talk show host. Since 2001, she has been the co-host of the syndicated morning talk show Live! with Kelly and Mark in various formats.

Limes Transalutanus is the modern name given to a fortified frontier system of the Roman Empire, built on the western edge of Teleorman's forests in the Roman province of Dacia, modern-day Romania. The frontier was composed of a road following the border, a military stronghold, a three-metre vallum 10–12 metres wide, reinforced with wood palisades on stone walls, and also a ditch. The Transalutanus limes was 235 km long, parallel to Olt river at a distance varying from 5 to 30 km east of the river. The construction was started in 107 under the command of Marcius Turbo, and developed under Iulius Severus (120–126); the final stage of the construction was performed under Septimius Severus.
Cohors [prima] Aurelia Antonina Hemesenorum milliaria [peditata] was a Roman auxiliary infantry regiment. The cohort was stationed in Dacia at castra Micia.

Porto di Ripa Grande was the river port of Rome, just downstream the former Pons Sublicius, where the wares, going up and down the Tiber towards the dock of Fiumicino, were handled. The building of the muraglioni has erased its existence and function, just keeping a trace in the toponymy and in the two ramps giving access to the quay of the river.
The Danubian Limes, or Danube Limes, refers to the Roman military frontier or limes which lies along the River Danube in the present-day German state of Bavaria, in Austria, Slovakia, Hungary, Croatia, Serbia, Bulgaria and Romania.

The Pannonian Limes is that part of the old Roman fortified frontier known as the Danubian Limes that runs for approximately 420 km (260 mi) from the Roman camp of Klosterneuburg in the Vienna Basin in Austria to the castrum in Singidunum (Belgrade) in present-day Serbia. The garrisons of these camps protected the Pannonian provinces against attacks from the north from the time of Augustus (31 BC–14 AD) to the beginning of the 5th century. In places this section of the Roman limes also crossed the river into the territory of the barbarians (Barbaricum).
References
- ↑ Eward, Gibbon (1776–1789). Strahan & Cadell, London. (ed.). The History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire.
See Henry Melvill Gwatkins’ “The Cambridge Medieval History: The Christian Roman Empire and the Foundation of the Teutonic Kingdoms”, 1911. Reference made to Ripa Gothica being ceded by Constantine to his nephew Delmatius.