
The Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) is a regional intergovernmental organization of originally ten post-Soviet republics in Eurasia formed following the dissolution of the Soviet Union. It has an area of 20,368,759 km² and has an estimated population of 239,796,010. The CIS encourages cooperation in economic, political and military affairs and has certain powers to coordinate trade, finance, lawmaking and security. It has also promoted cooperation on cross-border crime prevention.

Berwick-upon-Tweed is a town in the county of Northumberland. It is the northernmost town in England, at the mouth of the River Tweed on the east coast, 2 1⁄2 miles (4 km) south of the Scottish border. Berwick is approximately 56 miles (90 km) east-south east of Edinburgh, 65 miles (105 km) north of Newcastle upon Tyne and 345 miles (555 km) north of London.
The Treaty of Berlin was a treaty, signed on 24 April 1926, under which Germany and the Soviet Union pledged neutrality in the event of an attack on the other by a third party for the next five years. The treaty reaffirmed the German-Soviet Treaty of Rapallo signed in 1922.

The Kuril Islands dispute, also known in Japan as the Northern Territories dispute, is a disagreement between Japan and Russia and also some individuals of the Ainu people over sovereignty of the four southernmost Kuril Islands. The Kuril Islands is a chain of islands that stretch between the Japanese island of Hokkaido at the southern end and the Russian Kamchatka Peninsula at the northern end. The islands separate the Sea of Okhotsk from the Pacific Ocean. The four disputed islands, like other islands in the Kuril chain that are not in dispute, were annexed by the Soviet Union following the Kuril Islands landing operation at the end of World War II. The disputed islands are under Russian administration as the South Kuril District of the Sakhalin Oblast. They are claimed by Japan, which refers to them as its Northern Territories or Southern Chishima, and considers them part of the Nemuro Subprefecture of Hokkaido Prefecture.

The Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic was one of the 15 republics of the Soviet Union which existed from 1940 to 1991. The republic was formed on 2 August 1940 from parts of Bessarabia, a region annexed from Romania on 28 June of that year, and parts of the Moldavian Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic, an autonomous Soviet republic within the Ukrainian SSR.

START I was a bilateral treaty between the United States of America and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) on the reduction and limitation of strategic offensive arms. The treaty was signed on 31 July 1991 and entered into force on 5 December 1994. The treaty barred its signatories from deploying more than 6,000 nuclear warheads atop a total of 1,600 inter-continental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) and bombers. START negotiated the largest and most complex arms control treaty in history, and its final implementation in late 2001 resulted in the removal of about 80 percent of all strategic nuclear weapons then in existence. Proposed by United States President Ronald Reagan, it was renamed START I after negotiations began on the second START treaty.

The Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty was an arms control treaty between the United States and the Soviet Union. US President Ronald Reagan and Soviet General Secretary Mikhail Gorbachev signed the treaty on 8 December 1987. The United States Senate approved the treaty on 27 May 1988, and Reagan and Gorbachev ratified it on 1 June 1988.

The Abkhaz–Georgian conflict involves ethnic conflict between Georgians and the Abkhaz people in Abkhazia, a de facto independent, partially recognized republic. In a broader sense, one can view the Georgian–Abkhaz conflict as part of a geopolitical conflict in the Caucasus region, intensified at the end of the 20th century with the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991.
Territorial changes of the Baltic states refers to the redrawing of borders of Lithuania, Latvia and Estonia after 1940. The three republics, formerly autonomous regions within the former Russian Empire and before that of former Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, gained independence in the aftermath of World War I and the Russian Revolution of 1917. After a two-front independence war fought against both Bolshevist Russian and Baltic German nationalist forces, the countries concluded peace and border treaties with Soviet Russia in 1920. However, with World War II and the occupation and annexation of these republics into the Soviet Union twenty years after their independence, certain territorial changes were made in favour of the Russian SFSR. This has been the source of political tensions after they regained their independence with the dissolution of the Soviet Union. Some of the disputes remain unresolved.
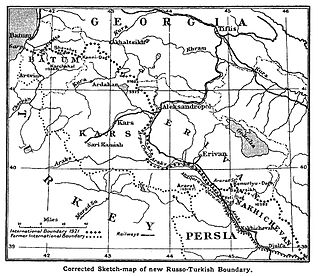
The Treaty of Kars was a peace treaty that established the common borders between Turkey and the three Transcaucasian republics of the Soviet Union. The treaty was signed in the city of Kars on 13 October 1921.

The Belovezha Accords are accords forming the agreement that declared the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) as effectively ceasing to exist and established the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) in its place as a successor entity. It was signed at the state dacha near Viskuli in Belovezhskaya Pushcha on December 8, 1991, by the leaders of three of the four republics-signatories of the Treaty on the Creation of the USSR – Russian President Boris Yeltsin and First Deputy Prime Minister of RSFSR/Russian Federation Gennady Burbulis, Ukrainian President Leonid Kravchuk and Ukrainian Prime Minister Vitold Fokin, Belarusian Parliament Chairman Stanislav Shushkevich and Prime Minister of Belarus Vyacheslav Kebich. The original accord could not be found as of 2013.

Relations between the Soviet Unionand Japan between the Communist takeover in 1917 and the collapse of Communism in 1991 tended to be hostile. Japan had sent troops to counter the Bolshevik presence in Russia's Far East during the Russian Civil War, and both countries had been in opposite camps during World War II and the Cold War. In addition, territorial conflicts over the Kuril Islands and South Sakhalin were a constant source of tension. These, with a number of smaller conflicts, prevented both countries from signing a peace treaty after World War II, and even today matters remain unresolved.

Japan–Russia relations refers to the international relations between Japan and the Russian Federation. Relations between Russia and Japan are the continuation of the relationship of Japan with the Soviet Union from 1917 to 1991, and with the Russian Empire from 1855 to 1917. Historically, the two countries had cordial relations until a clash of territorial ambitions in the Manchuria region of northeastern China led to the Russo–Japanese War in 1904, ending in a Japanese victory which contributed to the weakening of the monarchy in Russia. Japan would later intervene in the Russian Civil War from 1918 until 1922, sending troops to the Russian Far East and Siberia. That was followed by border conflicts between the new Soviet Union and the Empire of Japan throughout the 1930s. The two countries signed a nonaggression pact in 1941, although the Soviet government declared war on Japan anyway in August 1945, invading of the Japanese puppet state of Manchukuo as well as seizing the Kuril chain of islands just north of Japan. The two countries ended their formal state of war with the Soviet–Japanese Joint Declaration of 1956, but as of February 2019 have not resolved this territorial dispute over ownership of the Kurils.

The Sino-Soviet conflict of 1929 was an armed conflict between the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics and Chinese warlord Zhang Xueliang of the Republic of China over the Chinese Eastern Railway.

Russia is the largest and most important partner for Belarus both in the political and economic fields. The Treaty on Equal Rights of Citizens between Belarus and Russia was signed in December 1998, covering employment, and access to medical care and education. The two countries constitute the supranational Union State.
Afghanistan–Russia relations are the relations between the nations of Afghanistan and Russia. These relations are independent of the "Great Game" which consists of Russian–British confrontations over Afghanistan since 1840. On February 28, 1921, Afghanistan and Soviet Russia signed a Friendship Treaty. The Soviet Union was the first country to recognize Afghanistan's independence following the Third Anglo-Afghan War in 1919.
The War of Laws was the series of conflicts between the central government of the Soviet Union, and the governments of the Russian Federation and other constituent republics during the so-called "parade of sovereignties" in the last years of the USSR (1989–1991), which eventually contributed to the dissolution of the union. When Soviet premier Mikhail Gorbachev and the Communist Party of the Soviet Union decided to formally release their control of Soviet Socialist Republics, the individual governments began to reassert their own sovereignty and dominance in their respective areas. This included making their own laws separate from the USSR and refusing to pay taxes to the Moscow government. This worsened the Soviet Union's economic disintegration, and was a major factor in its 1991 collapse.

Relevant events began regarding the Baltic states and the Soviet Union when, following Bolshevist Russia's conflict with the Baltic states—Lithuania, Latvia and Estonia—several peace treaties were signed with Russia and its successor, the Soviet Union. In the late 1920s and early 1930s, the Soviet Union and all three Baltic States further signed non-aggression treaties. The Soviet Union also confirmed that it would adhere to the Kellogg–Briand Pact with regard to its neighbors, including Estonia and Latvia, and entered into a convention defining "aggression" that included all three Baltic countries.

The Treaty on the Creation of the USSR officially created the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union. It de jure legalised a union of several Soviet republics that had existed since 1919 and created a new centralised federal government where key functions were centralised in Moscow.
















