Related Research Articles
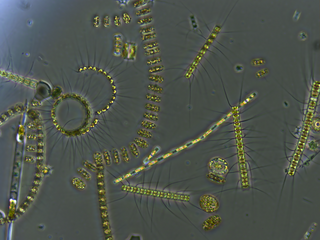
Phytoplankton are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words φυτόν, meaning 'plant', and πλαγκτός, meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'.
The mesopelagiczone, also known as the middle pelagic or twilight zone, is the part of the pelagic zone that lies between the photic epipelagic and the aphotic bathypelagic zones. It is defined by light, and begins at the depth where only 1% of incident light reaches and ends where there is no light; the depths of this zone are between approximately 200 to 1,000 meters below the ocean surface.
High-nutrient, low-chlorophyll (HNLC) regions are regions of the ocean where the abundance of phytoplankton is low and fairly constant despite the availability of macronutrients. Phytoplankton rely on a suite of nutrients for cellular function. Macronutrients are generally available in higher quantities in surface ocean waters, and are the typical components of common garden fertilizers. Micronutrients are generally available in lower quantities and include trace metals. Macronutrients are typically available in millimolar concentrations, while micronutrients are generally available in micro- to nanomolar concentrations. In general, nitrogen tends to be a limiting ocean nutrient, but in HNLC regions it is never significantly depleted. Instead, these regions tend to be limited by low concentrations of metabolizable iron. Iron is a critical phytoplankton micronutrient necessary for enzyme catalysis and electron transport.
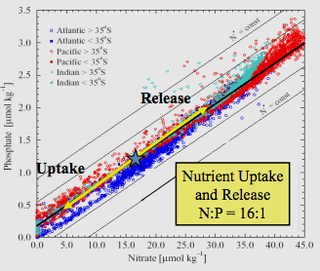
The Redfield ratio or Redfield stoichiometry is the consistent atomic ratio of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus found in marine phytoplankton and throughout the deep oceans.

Iron fertilization is the intentional introduction of iron-containing compounds to iron-poor areas of the ocean surface to stimulate phytoplankton production. This is intended to enhance biological productivity and/or accelerate carbon dioxide sequestration from the atmosphere. Iron is a trace element necessary for photosynthesis in plants. It is highly insoluble in sea water and in a variety of locations is the limiting nutrient for phytoplankton growth. Large algal blooms can be created by supplying iron to iron-deficient ocean waters. These blooms can nourish other organisms.

Sallie Watson "Penny" Chisholm is an American biological oceanographer at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. She is an expert in the ecology and evolution of ocean microbes. Her research focuses particularly on the most abundant marine phytoplankton, Prochlorococcus, that she discovered in the 1980s with Rob Olson and other collaborators. She has a TED talk about their discovery and importance called "The tiny creature that secretly powers the planet".

Ocean color is the branch of ocean optics that specifically studies the color of the water and information that can be gained from looking at variations in color. The color of the ocean, while mainly blue, actually varies from blue to green or even yellow, brown or red in some cases. This field of study developed alongside water remote sensing, so it is focused mainly on how color is measured by instruments.

Pyrocystis fusiformis is a non-motile, tropical, epipelagic, marine dinoflagellate, reaching lengths of up to 1 millimetre (0.039 in). P. fusiformis display bioluminescence when disturbed or agitated. In coastal marine waters, this dinoflagellate causes glowing effects after dark. P. fusiformis was first described in the Proceedings of the Royal Society of London in 1876.

Bacterioplankton refers to the bacterial component of the plankton that drifts in the water column. The name comes from the Ancient Greek word πλανκτος, meaning "wanderer" or "drifter", and bacterium, a Latin term coined in the 19th century by Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg. They are found in both seawater and freshwater.

A planktivore is an aquatic organism that feeds on planktonic food, including zooplankton and phytoplankton. Planktivorous organisms encompass a range of some of the planet's smallest to largest multicellular animals in both the present day and in the past billion years; basking sharks and copepods are just two examples of giant and microscopic organisms that feed upon plankton. Planktivory can be an important mechanism of top-down control that contributes to trophic cascades in aquatic and marine systems. There is a tremendous diversity of feeding strategies and behaviors that planktivores utilize to capture prey. Some planktivores utilize tides and currents to migrate between estuaries and coastal waters; other aquatic planktivores reside in lakes or reservoirs where diverse assemblages of plankton are present, or migrate vertically in the water column searching for prey. Planktivore populations can impact the abundance and community composition of planktonic species through their predation pressure, and planktivore migrations facilitate nutrient transport between benthic and pelagic habitats.
Bigelow Laboratory for Ocean Sciences, founded in 1974, is an independent, non-profit oceanography research institute. The Laboratory's research ranges from microbial oceanography to the large-scale biogeochemical processes that drive ocean ecosystems and health of the entire planet.
William Li is a Canadian biological oceanographer who did research on marine picoplankton, marine macroecology, ocean surveys of plankton from measurements of flow cytometry, and detection of multi-annual ecological change in marine phytoplankton.

The North Atlantic Aerosols and Marine Ecosystems Study (NAAMES) was a five-year scientific research program that investigated aspects of phytoplankton dynamics in ocean ecosystems, and how such dynamics influence atmospheric aerosols, clouds, and climate. The study focused on the sub-arctic region of the North Atlantic Ocean, which is the site of one of Earth's largest recurring phytoplankton blooms. The long history of research in this location, as well as relative ease of accessibility, made the North Atlantic an ideal location to test prevailing scientific hypotheses in an effort to better understand the role of phytoplankton aerosol emissions on Earth's energy budget.

Trevor Charles Platt was a British and Canadian biological oceanographer who was distinguished for his fundamental contributions to quantifying primary production by phytoplankton at various scales of space and time in the ocean.
Clarice Morel Yentsch is a scientist, author, education and museum professional, and community benefactor. As a scientist, she pioneered the use of flow cytometry to investigate marine phytoplankton and co-founded Bigelow Laboratory for Ocean Sciences.
Mary Wilcox Silver is Professor Emerita at the University of California Santa Cruz. Silver is known for research on marine snow and harmful algal blooms, setting the stage for woman conducting research in the field, and for mentoring and teaching of graduate and undergraduate students.
Mary Jane Perry is an American oceanographer known for the use of optics to study marine phytoplankton.
Colleen Beckmann Mouw is an associate professor at the University of Rhode Island known for her work on phytoplankton ecology and increasing retention of women in oceanography.
Patricia Ana Matrai is a marine scientist known for her work on the cycling of sulfur. She is a senior research scientist at Bigelow Laboratory for Ocean Sciences.
Shubha Platt, known professionally as Shubha Sathyendranath, is a marine scientist known for her work on marine optics and remote sensing of ocean colour. She is the 2021 recipient of the A.G. Huntsman Award for Excellence in the Marine Sciences.
References
- 1 2 Andersen, Robert A. (2011-09-01). "Robert Guillard Celebrates 90Th Birthday". Limnology and Oceanography Bulletin. 20 (3): 54–58. doi: 10.1002/lob.201120353 . ISSN 1539-6088.
- ↑ "Remembering Robert Guillard: Renowned Scientist, Treasured Friend - Bigelow Laboratory for Ocean Sciences". www.bigelow.org. Retrieved 2019-12-04.
- ↑ Guillard, Robert R. L.; Ryther, John H. (1962-04-01). "Studies of marine planktonic diatoms: i. cyclotella nana hustedt, and detonula confervacea (cleve) gran". Canadian Journal of Microbiology. 8 (2): 229–239. doi:10.1139/m62-029. ISSN 0008-4166. PMID 13902807.