Related Research Articles

Quality control (QC) is a process by which entities review the quality of all factors involved in production. ISO 9000 defines quality control as "a part of quality management focused on fulfilling quality requirements".

Cost accounting is defined by the Institute of Management Accountants as "a systematic set of procedures for recording and reporting measurements of the cost of manufacturing goods and performing services in the aggregate and in detail. It includes methods for recognizing, allocating, aggregating and reporting such costs and comparing them with standard costs". Often considered a subset of managerial accounting, its end goal is to advise the management on how to optimize business practices and processes based on cost efficiency and capability. Cost accounting provides the detailed cost information that management needs to control current operations and plan for the future.
The theory of constraints (TOC) is a management paradigm that views any manageable system as being limited in achieving more of its goals by a very small number of constraints. There is always at least one constraint, and TOC uses a focusing process to identify the constraint and restructure the rest of the organization around it. TOC adopts the common idiom "a chain is no stronger than its weakest link". That means that organizations and processes are vulnerable because the weakest person or part can always damage or break them, or at least adversely affect the outcome.

Lean manufacturing is a method of manufacturing goods aimed primarily at reducing times within the production system as well as response times from suppliers and customers. It is closely related to another concept called just-in-time manufacturing. Just-in-time manufacturing tries to match production to demand by only supplying goods that have been ordered and focus on efficiency, productivity, and reduction of "wastes" for the producer and supplier of goods. Lean manufacturing adopts the just-in-time approach and additionally focuses on reducing cycle, flow, and throughput times by further eliminating activities that do not add any value for the customer. Lean manufacturing also involves people who work outside of the manufacturing process, such as in marketing and customer service.
Six Sigma (6σ) is a set of techniques and tools for process improvement. It was introduced by American engineer Bill Smith while working at Motorola in 1986.
Design for Six Sigma (DFSS) is a collection of best-practices for the development of new products and processes. It is sometimes deployed as an engineering design process or business process management method. DFSS originated at General Electric to build on the success they had with traditional Six Sigma; but instead of process improvement, DFSS was made to target new product development. It is used in many industries, like finance, marketing, basic engineering, process industries, waste management, and electronics. It is based on the use of statistical tools like linear regression and enables empirical research similar to that performed in other fields, such as social science. While the tools and order used in Six Sigma require a process to be in place and functioning, DFSS has the objective of determining the needs of customers and the business, and driving those needs into the product solution so created. It is used for product or process design in contrast with process improvement. Measurement is the most important part of most Six Sigma or DFSS tools, but whereas in Six Sigma measurements are made from an existing process, DFSS focuses on gaining a deep insight into customer needs and using these to inform every design decision and trade-off.
The Personal Software Process (PSP) is a structured software development process that is designed to help software engineers better understand and improve their performance by bringing discipline to the way they develop software and tracking their predicted and actual development of the code. It clearly shows developers how to manage the quality of their products, how to make a sound plan, and how to make commitments. It also offers them the data to justify their plans. They can evaluate their work and suggest improvement direction by analyzing and reviewing development time, defects, and size data. The PSP was created by Watts Humphrey to apply the underlying principles of the Software Engineering Institute's (SEI) Capability Maturity Model (CMM) to the software development practices of a single developer. It claims to give software engineers the process skills necessary to work on a team software process (TSP) team.

In materials science, work hardening, also known as strain hardening, is the strengthening of a metal or polymer by plastic deformation. Work hardening may be desirable, undesirable, or inconsequential, depending on the context.

Operations management is concerned with designing and controlling the production of goods and services, ensuring that businesses are efficient in using resources to meet customer requirements.
In process improvement efforts, defects per million opportunities or DPMO is a measure of process performance. It is defined as
Lean government refers to the application of Lean Manufacturing principles and methods to both identify and then implement the most efficient, value added way to provide government services. Government agencies have found that when Lean is implemented, they see an improved understanding of how their own processes work, that it facilitates the quick identification and implementation of improvements and that it builds a culture of continuous improvement.
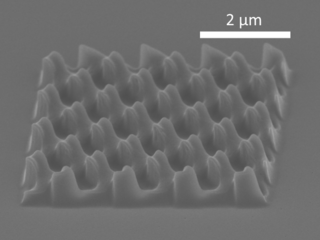
Nanoimprint lithography (NIL) is a method of fabricating nanometer-scale patterns. It is a simple nanolithography process with low cost, high throughput and high resolution. It creates patterns by mechanical deformation of imprint resist and subsequent processes. The imprint resist is typically a monomer or polymer formulation that is cured by heat or UV light during the imprinting. Adhesion between the resist and the template is controlled to allow proper release.
Muda is a Japanese word meaning "futility", "uselessness", or "wastefulness", and is a key concept in lean process thinking such as in the Toyota Production System (TPS), denoting one of three types of deviation from optimal allocation of resources. The other types are known by the Japanese terms mura ("unevenness") and muri ("overload"). Waste in this context refers to the wasting of time or resources rather than wasteful by-products and should not be confused with waste reduction.
The process capability index, or process capability ratio, is a statistical measure of process capability: the ability of an engineering process to produce an output within specification limits. The concept of process capability only holds meaning for processes that are in a state of statistical control. This means it cannot account for deviations which are not expected, such as misaligned, damaged, or worn equipment. Process capability indices measure how much "natural variation" a process experiences relative to its specification limits, and allows different processes to be compared to how well an organization controls them. Somewhat counterintuitively, higher index values indicate better performance, with zero indicating high deviation.
Autonomation describes a feature of machine design to effect the principle of jidoka (自働化)(じどうか jidouka), used in the Toyota Production System (TPS) and lean manufacturing. It may be described as "intelligent automation" or "automation with a human touch". This type of automation implements some supervisory functions rather than production functions. At Toyota, this usually means that if an abnormal situation arises, the machine stops and the worker will stop the production line. It is a quality control process that applies the following four principles:
- Detect the abnormality.
- Stop.
- Fix or correct the immediate condition.
- Investigate the root cause and install a countermeasure.

Value-stream mapping, also known as material- and information-flow mapping, is a lean-management method for analyzing the current state and designing a future state for the series of events that take a product or service from the beginning of the specific process until it reaches the customer. A value stream map is a visual tool that displays all critical steps in a specific process and easily quantifies the time and volume taken at each stage. Value stream maps show the flow of both materials and information as they progress through the process.
A lean laboratory is one which is focused on processes, procedures, and infrastructure that deliver results in the most efficient way in terms of cost, speed, or both. Lean laboratory is a management and organization process derived from the concept of lean manufacturing and the Toyota Production System (TPS). The goal of a lean laboratory is to reduce resource usage and costs while improving productivity, staff morale, and laboratory-driven outcomes.
Lean Six Sigma is a process improvement approach that uses a collaborative team effort to improve performance by systematically removing operational waste and reducing process variation. It combines Lean Management and Six Sigma to increase the velocity of value creation in business processes.
Lean enterprise is a practice focused on value creation for the end customer with minimal waste and processes. The term has historically been associated with lean manufacturing and Six Sigma due to lean principles being popularized by Toyota in the automobile manufacturing industry and subsequently the electronics and internet software industries.
First-pass yield (FPY), also known as throughput yield (TPY), is defined as the number of units coming out of a process divided by the number of units going into that process over a specified period of time.
References
- ↑ "Rolled Throughput Yield". Lean Six Sigma Articles. Lean Sigma Corporation. 5 June 2013. Retrieved 19 September 2013.
- ↑ "Rolled Throughput Yield (RTY)". Six-sigma-material.com. Retrieved 2012-06-22.