Related Research Articles

Blood glucose monitoring is the use of a glucose meter for testing the concentration of glucose in the blood (glycemia). Particularly important in diabetes management, a blood glucose test is typically performed by piercing the skin to draw blood, then applying the blood to a chemically active disposable 'test-strip'. The other main option is continuous glucose monitoring (CGM). Different manufacturers use different technology, but most systems measure an electrical characteristic and use this to determine the glucose level in the blood. Skin-prick methods measure capillary blood glucose, whereas CGM correlates interstitial fluid glucose level to blood glucose level. Measurements may occur after fasting or at random nonfasting intervals, each of which informs diagnosis or monitoring in different ways.

Agilent Technologies, Inc. is an American global company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, that provides instruments, software, services, and consumables for laboratories. Agilent was established in 1999 as a spin-off from Hewlett-Packard. The resulting IPO of Agilent stock was the largest in the history of Silicon Valley at the time. From 1999 to 2014, the company produced optics, semiconductors, EDA software and test and measurement equipment for electronics; that division was spun off to form Keysight. Since then, the company has continued to expand into pharmaceutical, diagnostics & clinical, and academia & government (research) markets.
A biosensor is an analytical device, used for the detection of a chemical substance, that combines a biological component with a physicochemical detector. The sensitive biological element, e.g. tissue, microorganisms, organelles, cell receptors, enzymes, antibodies, nucleic acids, etc., is a biologically derived material or biomimetic component that interacts with, binds with, or recognizes the analyte under study. The biologically sensitive elements can also be created by biological engineering. The transducer or the detector element, which transforms one signal into another one, works in a physicochemical way: optical, piezoelectric, electrochemical, electrochemiluminescence etc., resulting from the interaction of the analyte with the biological element, to easily measure and quantify. The biosensor reader device connects with the associated electronics or signal processors that are primarily responsible for the display of the results in a user-friendly way. This sometimes accounts for the most expensive part of the sensor device, however it is possible to generate a user friendly display that includes transducer and sensitive element. The readers are usually custom-designed and manufactured to suit the different working principles of biosensors.
Abbott Laboratories is an American multinational medical devices and health care company with headquarters in Green Oaks, Illinois, United States. The company was founded by Chicago physician Wallace Calvin Abbott in 1888 to formulate known drugs; today, it sells medical devices, diagnostics, branded generic medicines and nutritional products. It split off its research-based pharmaceuticals business into AbbVie in 2013.

A glucose meter, also referred to as a "glucometer", is a medical device for determining the approximate concentration of glucose in the blood. It can also be a strip of glucose paper dipped into a substance and measured to the glucose chart. It is a key element of glucose testing, including home blood glucose monitoring (HBGM) performed by people with diabetes mellitus or hypoglycemia. A small drop of blood, obtained from slightly piercing a fingertip with a lancet, is placed on a disposable test strip that the meter reads and uses to calculate the blood glucose level. The meter then displays the level in units of mg/dL or mmol/L.

Danaher Corporation is an American global conglomerate founded in 1984 by brothers Steven and Mitchell Rales. Headquartered in Washington, D.C., the company designs, manufactures, and markets medical, industrial, and commercial products and services. Danaher was among the first companies in North America to adopt Kaizen principles, a Japanese lean manufacturing philosophy of continuous improvement and efficiency. The company held $78.5 billion in assets as of 2024.

QIAGEN N.V. is a German-founded multinational provider of sample and assay technologies for molecular diagnostics, applied testing, academic research, and pharmaceutical research. The company operates in more than 35 offices in over 25 countries. QIAGEN N.V., the global corporate headquarter of the QIAGEN group, is located in Venlo, The Netherlands. The main operative headquarters are located in Hilden, Germany. European, American, Chinese, and Asian-Pacific regional headquarters are located respectively in respectively Hilden, Germany; Germantown, Maryland, United States; Shanghai, China; and Singapore. QIAGEN's shares are listed at the NYSE and at the Frankfurt Stock Exchange in the Prime Standard. Thierry Bernard is the company's Chief Executive Officer (CEO).
Point-of-care testing (POCT), also called near-patient testing or bedside testing, is defined as medical diagnostic testing at or near the point of care—that is, at the time and place of patient care. This contrasts with the historical pattern in which testing was wholly or mostly confined to the medical laboratory, which entailed sending off specimens away from the point of care and then waiting hours or days to learn the results, during which time care must continue without the desired information.
LifeScan, Inc. is a diagnostic systems manufacturer with products focusing on the diabetes market, specifically blood glucose monitoring systems.

Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. is an American-headquartered life science and clinical research company. It is a global supplier of analytical instruments, clinical development solutions, specialty diagnostics, laboratory, pharmaceutical and biotechnology services. Based in Waltham, Massachusetts, Thermo Fisher was formed through the merger of Thermo Electron and Fisher Scientific in 2006. Thermo Fisher Scientific has acquired other reagent, consumable, instrumentation, and service providers, including Life Technologies Corporation (2013), Alfa Aesar (2015), Affymetrix (2016), FEI Company (2016), BD Advanced Bioprocessing (2018), and PPD (2021).
Ortho Clinical Diagnostics is an in vitro diagnostics company that made products and diagnostic equipment for blood testing. Ortho served two primary industries in the medical field: clinical laboratories, by producing platforms and assays that test for a variety of diseases, conditions, and substances; and immunohematology, by providing the means to ensure blood transfusion recipients receive appropriate and compatible blood.

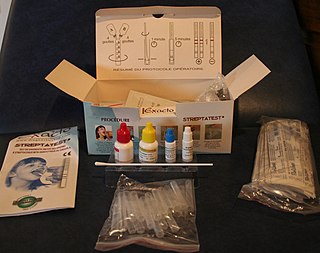
A lateral flow test (LFT), is an assay also known as a lateral flow device (LFD), lateral flow immunochromatographic assay, or rapid test. It is a simple device intended to detect the presence of a target substance in a liquid sample without the need for specialized and costly equipment. LFTs are widely used in medical diagnostics in the home, at the point of care, and in the laboratory. For instance, the home pregnancy test is an LFT that detects a specific hormone. These tests are simple and economical and generally show results in around five to thirty minutes. Many lab-based applications increase the sensitivity of simple LFTs by employing additional dedicated equipment. Because the target substance is often a biological antigen, many lateral flow tests are rapid antigen tests.
Radiometer is a Danish multinational company which develops, manufactures and markets solutions for blood sampling, blood gas analysis, transcutaneous monitoring, immunoassay testing and the related IT management systems. The company was founded in 1935 in Copenhagen, Denmark by Børge Aagaard Nielsen and Carl Schrøder. It has over 3,200 employees and direct representation in more than 32 countries. Corporate headquarters remain in Copenhagen.

Adam Heller is an Israeli American scientist and engineer. He is Chief Science Officer of SynAgile Corp. of Wilson, Wyoming, consults to Abbott Diabetes Care of Alameda, California, and is Ernest Cockrell Sr. Chair Emeritus of Engineering at The University of Texas at Austin. His 1973 paper with James J. Auborn established the feasibility of high energy density, high-voltage, non-rechargeable lithium batteries. Their 3.6-volt lithium thionyl chloride and 3.7-volt lithium sulfuryl chloride batteries remain in use in applications requiring very high energy density and a shelf life of 20 years or more.
QuidelOrtho Corporation is an American manufacturer of diagnostic healthcare products that are sold worldwide.

Alere Inc. was a global manufacturer of rapid point-of-care diagnostic tests. The company was founded in 1991 and was headquartered in Waltham, Massachusetts. As of January 2017, the company had a market capitalization of $3.47 billion with an enterprise value of $5.9 billion. The company was formerly known as Inverness Medical Innovations, Inc. and changed its name to Alere Inc. in 2010.
Bigfoot Biomedical Inc. is a medical technology start-up headquartered in Milpitas, California, founded by a team of people with personal connections to type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
Swiss Precision Diagnostics GmbH is a Swiss medical diagnostic company, that produces Clearblue-branded pregnancy testing equipment.

A continuous glucose monitor (CGM) is a device used for monitoring blood glucose on a continual basis instead of monitoring glucose levels periodically by drawing a drop of blood from a finger. This is known as continuous glucose monitoring. CGMs are used by people who treat their diabetes with insulin, for example people with type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, or other types of diabetes, such as gestational diabetes.

COVID-19 rapid antigen tests or RATs, also frequently called COVID-19 lateral flow tests or LFTs, are rapid antigen tests used to detect SARS-CoV-2 infection (COVID-19). They are quick to implement with minimal training, cost a fraction of other forms of COVID-19 testing, and give users a result within 5–30 minutes. RATs have been used in several countries as part of mass testing or population-wide screening approaches. Many RATs can be used for self-testing, in which an individual "collects their own specimen… and interpret[s] their test result themselves".
References
- ↑ 2 of the other projects (which concerned Dutch elm disease and metabolic engineering) had been sold or spun off, and the rest scrapped.
- ↑ Douglas, Craig M. (11 August 2008). "Boston's barbarian?". Boston Business Journal. Retrieved 28 December 2017.
Sign In Required
- 1 2 3 4 5 Pederson, Jay; Grant, Tina (2004). "Inverness Medical Innovations, Inc". International Directory of Company Histories. St. James Press. Retrieved 5 June 2020.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Isenberg, Daniel (2006). Inverness Medical Innovations--Born Global (A). Harvard Business School Publishing.
- 1 2 "Ron Zwanziger: Executive Profile & Biography". Bloomberg. May 11, 2001. Retrieved December 28, 2017.
- ↑ Worthless, Impossible and Stupid: How Contrarian Entrepreneurs Create and Capture Extraordinary Value. Harvard Business Review Press. 2013. p. 25. ISBN 978-1-4221-8699-2 . Retrieved December 28, 2017.
- 1 2 Heller, Adam; Feldman, Ben (2008). "Electrochemical Glucose Sensors and Their Applications in Diabetes Management". Chemical Reviews. 108 (7): 2482–2505. doi:10.1021/cr068069y. PMID 18465900.
- ↑ Bond, Alan (2002). Broadening Electrochemical Horizons: Principles and Illustration of Voltammetric and Related Techniques. Oxford University Press.
- ↑ "Abbott Laboratories to Buy Medisense for $876 Million". The New York Times. 30 March 1996. Retrieved 28 December 2017.
- 1 2 3 Cyran, Robert (January 1, 2016). "Strategy of Alere Board Paid Off With Buyout by Abbott". The New York Times. Retrieved December 28, 2017.
- ↑ "Alere chief executive Ron Zwanziger resigns, effective immediately - The Boston Globe". bostonglobe.com. Retrieved 28 December 2017.
- ↑ "Alere Inc. CEO Zwanziger, Other Top Executives Resign In Overhaul". BioSpace. July 2, 2014. Retrieved December 28, 2017.
- ↑ "Alere's' Ex-CEO plans $3.82 billion offer for health company". www.ohio.com. December 28, 2017. Retrieved December 28, 2017.
- ↑ "J&J acquires Inverness unit - May 23, 2001". money.cnn.com. Retrieved 28 December 2017.
- ↑ "Inverness wins Biosite with bid of $1.68 billion". sandiegouniontribune.com. Retrieved 1 January 2018.
- ↑ "Actress, Activist and PSI Ambassador Debra Messing and HRH Crown Princess Mette-Marit of Norway Present 2012 Impact Awards". PRWeb. Population Services International. 26 July 2012. Retrieved 4 July 2020.[ dead link ]
- ↑ Ignorance, Out of (27 October 2017). "Abbott's Inviting New Allure". seekingalpha.com. Retrieved 28 December 2017.
- ↑ Pederson, Amanda (24 October 2022). "The Biggest Mistake Abbott Didn't Make". Medical Device and Diagnostic Industry. Retrieved 14 September 2024.
- ↑ "Who We Are". LumiraDx. Retrieved 12 May 2020.
- ↑ "QuotedData's morning briefing 2 November 2023". QuotedData. 2 November 2023. Retrieved 21 November 2023.
- ↑ Mirasol, Feliza (4 January 2024). "Roche to Acquire Point-of-Care Technology from LumiraDx in $350 Million Deal". BioPharm International. Retrieved 22 January 2024.
- ↑ Gates, Bill. "New tools for COVID testing". YouTube. Retrieved 22 January 2024.
- ↑ Brümmer, Lukas E.; Katzenschlager, Stephan; Gaeddert, Mary; Erdmann, Christian; Schmitz, Stephani; Bota, Marc; Grilli, Maurizio; Larmann, Jan; Weigand, Markus A.; Pollock, Nira R.; Macé, Aurélien; Carmona, Sergio; Ongarello, Stefano; Sacks, Jilian A.; Denkinger, Claudia M. (12 August 2021). "Accuracy of novel antigen rapid diagnostics for SARS-CoV-2: A living systematic review and meta-analysis". PLOS Medicine. 18 (8): e1003735. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1003735 . ISSN 1549-1676. PMC 8389849 . PMID 34383750.