
The Ronkonkoma Moraine, in the geography of Long Island, forms the southern of two ridges along Long Island's "backbone." [1]

The Ronkonkoma Moraine, in the geography of Long Island, forms the southern of two ridges along Long Island's "backbone." [1]
The Ronkonkoma Moraine, a terminal moraine, predates the Harbor Hill Moraine (which reached Long Island during the Wisconsin Glacial Episode); the Harbor Hill Moraine cut through the Ronkonkoma Moraine's western portions. [2]
The Ronkonkoma Moraine and the Harbor Hill Moraine intersect at Lake Success in western Nassau County. [2] Today, the moraine is most prominent in Suffolk County, where it traverses the center of Long Island and forms the South Fork. [3]

A moraine is any accumulation of unconsolidated debris, sometimes referred to as glacial till, that occurs in both currently and formerly glaciated regions, and that has been previously carried along by a glacier or ice sheet. It may consist of partly rounded particles ranging in size from boulders down to gravel and sand, in a groundmass of finely-divided clayey material sometimes called glacial flour. Lateral moraines are those formed at the side of the ice flow, and terminal moraines are those formed at the foot, marking the maximum advance of the glacier. Other types of moraine include ground moraines and medial moraines.

Farmingville is a hamlet and census-designated place (CDP) in the Suffolk County town of Brookhaven, New York, United States. The population was 15,481 at the 2010 census.

Holtsville is a hamlet and census-designated place (CDP) in Suffolk County, on Long Island, in New York, United States. The population was 19,714 at the 2010 census.

The Ice Age Trail is a National Scenic Trail stretching 1,200 miles (1,900 km) in the state of Wisconsin in the United States. The trail is administered by the National Park Service, and is constructed and maintained by private and public agencies including the Ice Age Trail Alliance, a non-profit and member-volunteer based organization with local chapters. It became an official unit of the National Park System in 2023.

Islip is a town in Suffolk County, New York, United States, on the South Shore of Long Island. The population was 335,543 at the 2010 census, making it the fourth most populous city or town in the New York metropolitan area.
The Wisconsin glaciation, also called the Wisconsin glacial episode, was the most recent glacial period of the North American ice sheet complex, peaking more than 20,000 years ago. This advance included the Cordilleran Ice Sheet, which nucleated in the northern North American Cordillera; the Innuitian ice sheet, which extended across the Canadian Arctic Archipelago; the Greenland ice sheet; and the massive Laurentide Ice Sheet, which covered the high latitudes of central and eastern North America. This advance was synchronous with global glaciation during the last glacial period, including the North American alpine glacier advance, known as the Pinedale glaciation. The Wisconsin glaciation extended from about 75,000 to 11,000 years ago, between the Sangamonian Stage and the current interglacial, the Holocene. The maximum ice extent occurred about 25,000–21,000 years ago during the last glacial maximum, also known as the Late Wisconsin in North America.

A kettle is a depression or hole in an outwash plain formed by retreating glaciers or draining floodwaters. The kettles are formed as a result of blocks of dead ice left behind by retreating glaciers, which become surrounded by sediment deposited by meltwater streams as there is increased friction. The ice becomes buried in the sediment and when the ice melts, a depression is left called a kettle hole, creating a dimpled appearance on the outwash plain. Lakes often fill these kettles; these are called kettle hole lakes. Another source is the sudden drainage of an ice-dammed lake and when the block melts, the hole it leaves behind is a kettle. As the ice melts, ramparts can form around the edge of the kettle hole. The lakes that fill these holes are seldom more than 10 m (33 ft) deep and eventually fill with sediment. In acidic conditions, a kettle bog may form but in alkaline conditions, it will be kettle peatland.

The North Shore of Long Island is the area along the northern coast of New York's Long Island bordering Long Island Sound. Known for its extreme wealth and lavish estates, the North Shore exploded into affluence at the turn of the 20th century, earning it the nickname the Gold Coast. Historically, this term refers to the affluent coastline neighborhoods of the towns of North Hempstead and Oyster Bay in Nassau County and Huntington in Suffolk County. Some definitions may also include the parts of Smithtown that face the Sound. The region is also largely coextensive with the Gold Coast region of Long Island, though this region excludes Smithtown, as the easternmost Gold Coast mansion is the Geissler Estate, located just west of Indian Hills Country Club in the Fort Salonga section of Huntington.
As part of New England, Connecticut has undergone much geologic change shaped by plate tectonics, volcanism, and glacial activity.

A terminal moraine, also called an end moraine, is a type of moraine that forms at the terminal (edge) of a glacier, marking its maximum advance. At this point, debris that has accumulated by plucking and abrasion, has been pushed by the front edge of the ice, is driven no further and instead is deposited in an unsorted pile of sediment. Because the glacier acts very much like a conveyor belt, the longer it stays in one place, the greater the amount of material that will be deposited. The moraine is left as the marking point of the terminal extent of the ice.

New York's 1st congressional district is a congressional district for the United States House of Representatives in eastern Long Island. It includes the eastern two-thirds of Suffolk County, including the northern portion of Brookhaven, as well as the entirety of the towns of Huntington, Smithtown, Riverhead, Southold, Southampton, East Hampton, and Shelter Island. The district encompasses extremely wealthy enclaves such as the Hamptons, middle class suburban towns such as Selden, Centereach, and Lake Grove, working-class towns such as Riverhead and rural farming communities such as Mattituck and Jamesport on the North Fork. The district currently is represented by Republican Nick LaLota.

New York's 2nd congressional district is a congressional district for the United States House of Representatives along the South Shore of Long Island, New York. It includes southwestern Suffolk County and a small portion of southeastern Nassau County. The district is currently represented by Republican Andrew Garbarino.

Ronkonkoma is a major railroad station and transportation hub along the Main Line of the Long Island Rail Road in Ronkonkoma, New York. The station is the eastern terminus of the Ronkonkoma Branch and the western terminus of the Greenport Branch, and it also serves the adjacent Long Island MacArthur Airport.

Jayne's Hill, also known as High Hill, West Hills, Oakley's Hill, and Janes Hill, is the highest point on Long Island, New York with an elevation of between 387 feet (118 m) and 400.9 feet (122.2 m) above sea level. It is situated on the Harbor Hill moraine, a terminal moraine that makes up the northern spine of Long Island, in West Hills County Park in Suffolk County, a little more than a mile to the north of Melville.

Long Island is in southeastern New York, United States, separated from the rest of the state by the East River and from Connecticut by Long Island Sound. Long Island contains four counties, of which the western two are boroughs of New York City, and the other two are mainly suburban.

Bald Hill, located in the hamlet of Farmingville, New York, part of the Town of Brookhaven, is one of the highest areas of elevation on Long Island. The highest elevation in the Bald Hill area is 331 feet (101 m). Though local residents often claim it to be the highest point on Long Island, that honor actually belongs to Jayne's Hill in the Town of Huntington at 401 feet (122 m). Also, nearby Telescope Hill, about 0.8 miles (1.3 km) WSW, is slightly higher at 334 feet (102 m). Bald Hill in Brookhaven should also not be confused with Bald Hill in Riverhead.
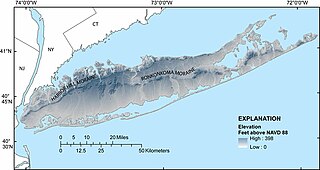
The Harbor Hill Moraine, in the geography of Long Island, forms the northern of two ridges along the "backbone" of Long Island.

Lake Success is a kettle lake in Lake Success, in Nassau County, on Long Island, in New York, United States.