
Portland is a city in the U.S. state of Maine. It is the most populous city in the state and the seat of Cumberland County. Portland's population was 68,408 in April 2020. The Greater Portland metropolitan area has a population of approximately 550,000 people. Historically tied to commercial shipping, the marine economy, and light industry, Portland's economy in the 21st century relies mostly on the service sector. The Port of Portland is the second-largest tonnage seaport in the New England area as of 2019.

Deering High School (DHS) is a public high school in Portland, Maine, United States. The school is part of the Portland Public Schools district.

Portland High School is a public high school established in 1821 in Portland, Maine, United States, which educates grades 9–12. The school is part of the Portland Public Schools district, and is one of three high schools in that district, along with Deering High School and Casco Bay High School. It is located at 284 Cumberland Avenue in downtown Portland. Along with its sister school, Deering High School, a family can choose which of the two to send their students to.

The Portland Press Herald is a daily newspaper based in South Portland, Maine, with a statewide readership. The Press Herald mainly serves southern Maine and is focused on the greater metropolitan area of Portland.

The Nathan Clifford School is a former elementary school building at 180 Falmouth Street in Portland, Maine. Built in 1907–09 to a design by John Calvin Stevens and his son John Howard Stevens, it was hailed as a model elementary school by the state, built with up-to-date technology to the latest standards. It was named for Maine politician and jurist Nathan Clifford. The school was closed in 2011, and has been converted to residential use.

Haystack Mountain School of Crafts, commonly called "Haystack," is a craft school located at 89 Haystack School Drive on the coast of Deer Isle, Maine.

Washington High School was a high school in Portland, Oregon, United States, from 1906 to 1981. After fire destroyed the original building, a new building was completed in 1924. The school merged with Monroe High School in 1978 to become Washington-Monroe High School. The school closed shortly after in 1981. A few years later it was used as the Children's Services Center, a multipurpose social service facility that also provided day care and other programs for at risk youth. After that the building was vacant for many years. It was also used for a time as a location for administrative offices for the Portland Public Schools.
Kennedy Park is a neighborhood in East Bayside in downtown Portland, Maine, built around a park, athletic fields, basketball courts, a playground and the Boyd Street Urban Garden.

The Abyssinian Meeting House is a historic church building at 73–75 Newbury Street, in the Munjoy Hill neighborhood of Portland, Maine. Built 1828-1831 by free African-Americans, it is Maine's oldest African-American church building, and the third oldest in the nation. Throughout the years, the Abyssinian was a place for worship and revivals, abolition and temperance meetings, speakers and concerts, the Female Benevolent Society, the Portland Union Anti-Slavery Society and negro conventions, and the black school in Portland from the mid-1840s through the mid-1850s. The building is the only Underground Railroad site in Maine recognized by the National Park Service. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2006.

Walden is an unincorporated community in Lane County, Oregon, United States. It is about 3 miles (5 km) southeast of Cottage Grove, near the confluence of the Row River and Mosby Creek.
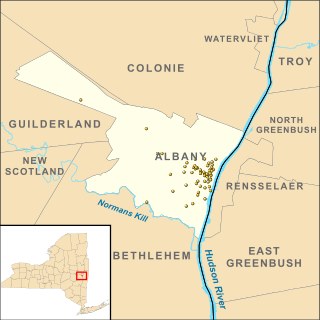
There are 75 properties listed on the National Register of Historic Places in Albany, New York, United States. Six are additionally designated as National Historic Landmarks (NHLs), the most of any city in the state after New York City. Another 14 are historic districts, for which 20 of the listings are also contributing properties. Two properties, both buildings, that had been listed in the past but have since been demolished have been delisted; one building that is also no longer extant remains listed.
Portland, Maine, is home to many neighborhoods.

Mechanics' Hall is a historic building and meeting space at 519 Congress Street in downtown Portland, Maine. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) in 1973 and additional NRHP documentation asserting national significance of the building was approved in 2022. Built in 1857-59 by and for the members of the Maine Charitable Mechanic Association, it is a well-preserved example of Italianate architecture executed in brick and stone, and a landmark of Portland's downtown business and arts district. The building, still owned by MCMA, houses the association's library. The Maine Charitable Mechanic Association was founded in 1815 as a social organization that promoted and supported the skilled trades and their practitioners. Its original members were master craftspeople and entrepreneurs and their apprentices.

Povey Brothers Studio, also known as Povey Brothers Art Glass Works or Povey Bros. Glass Co., was an American producer of stained glass windows based in Portland, Oregon. The studio was active from 1888 to 1928. As the largest and best known art glass company in Oregon, it produced windows for homes, churches, and commercial buildings throughout the West. When the firm was founded in 1888, it was the only creative window firm in Portland, then a city of 42,000 residents.

68 High Street, formerly the Children's Hospital, is a historic colonial revival building in Portland, Maine. Located on the eastern edge of Portland's West End, the building was built in 1909 and was designed by architect Frederick A. Tompson. According to news archives, Drs. Edville Gerhardt Abbott and Harold A. Pingree and Frank W. Lamb founded this worldwide famous children's hospital for disabled children with scoliosis together in 1908. It closed in 1948, with most of the 56 patients at the time being transferred to Maine General Hospital, which was later renamed the Maine Medical Center. It also served as an annex to the Mussey Mansion until the left part of that building was demolished in 1961. It was also owned by the University of Maine system. It housed the University of Maine School of Law from 1962? until 1972, after which was used by the University of Southern Maine as administrative offices.

The Captain Reuben Merrill House is an historic house at 233 West Main Street in Yarmouth, Maine. Built in 1858, it is one of the town's largest and most elaborate 19th-century houses, and is one of three known surviving works of Portland architect Thomas J. Sparrow. It was placed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1974. It is now home to Maine Preservation, a statewide architectural preservation organization.

The Emery School is an historic former school building at 116 Hill Street in Biddeford, Maine. Built in 1912-13 to a design by Miller & Mayo of Portland, it is historically significant for its role the city's education, and architecturally as a fine example of a "modern" elementary school building of the period. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places on November 18, 2011. The building has been converted to residential housing units.

The Loring House Apartments are a senior housing complex at 1125 Brighton Avenue in Portland, Maine. They occupy the buildings of the Portland City Hospital, built in 1902-04 as the city's poor house. The complex was designed by the prominent local firm of F. H. & E. F. Fassett, and was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1985.
The Butler School is an historic schoolhouse turned apartment building in Portland, Maine, United States. Built from 1878-79 at the cost of $8,000, the building served as an elementary school for West End students until 1973. It is located on Pine Street in Andrews Square. It is named for Moses M. Butler, who was mayor from 1877-79. It was designed by local architect Francis H. Fassett in the High Victorian Gothic style; Fassett lived in the neighborhood and also designed many other nearby buildings on the Western Promenade. It was built to replace nearby Brackett Street School and itself was replaced by Howard C. Reiche Community School, which was built a block away on Brackett Street. It did not have a playground until 1945.

















