
Peppermint is a hybrid mint, a cross between watermint and spearmint. Indigenous to Europe and the Middle East, the plant is now widely spread and cultivated in many regions of the world. It is occasionally found in the wild with its parent species.

An essential oil is a concentrated hydrophobic liquid containing volatile chemical compounds from plants. Essential oils are also known as volatile oils, ethereal oils, aetheroleum, or simply as the oil of the plant from which they were extracted, such as oil of clove. An essential oil is "essential" in the sense that it contains the "essence of" the plant's fragrance—the characteristic fragrance of the plant from which it is derived. The term "essential" used here does not mean indispensable or usable by the human body, as with the terms essential amino acid or essential fatty acid, which are so called because they are nutritionally required by a given living organism.

Thymol (also known as 2-isopropyl-5-methylphenol, IPMP) is a natural monoterpenoid phenol derivative of p-Cymene, C10H14O, isomeric with carvacrol, found in oil of thyme, and extracted from Thymus vulgaris (common thyme), Ajwain and various other kinds of plants as a white crystalline substance of a pleasant aromatic odor and strong antiseptic properties. Thymol also provides the distinctive, strong flavor of the culinary herb thyme, also produced from T. vulgaris.

Cedrus deodara, the deodar cedar, Himalayan cedar, or deodar/ devdar/ devadar/ devadaru, is a species of cedar native to the western Himalayas in Eastern Afghanistan, Northern Pakistan, and India, Southwestern Tibet, and Western Nepal occurring at 1,500–3,200 m (4,921–10,499 ft) altitude.

Rhodiola rosea is a perennial flowering plant in the family Crassulaceae. It grows naturally in wild Arctic regions of Europe, Asia, and North America, and can be propagated as a groundcover. Rhodiola rosea has been used in traditional medicine for several disorders, notably including treatment of anxiety and depression. As of 2019, there is no high-quality randomized or clinical controlled trails adequately assessing its effectiveness for treating "physical fatigue and mild to moderate depression and/or mental fatigue", for "enhancing physical endurance and performance" or "evaluating [its] adaptogenic properties". The United States Food and Drug Administration has issued several warnings to manufacturers of R. rosea dietary supplements for making false health claims about its safety and efficacy.

Citrus bergamia, the bergamot orange, is a fragrant citrus fruit the size of an orange, with a yellow or green color similar to a lime, depending on ripeness.

Rosewood refers to any of a number of richly hued timbers, often brownish with darker veining, but found in many different hues.
Carvacrol, or cymophenol, C6H3(CH3)(OH)C3H7, is a monoterpenoid phenol. It has a characteristic pungent, warm odor of oregano.

Eucalyptol is a monoterpenoid. A colorless liquid, it is a bicyclic ether. Eucalyptol has a fresh mint-like smell and a spicy, cooling taste. It is insoluble in water, but miscible with organic solvents. Eucalyptol makes up 90% of eucalyptus oil. Eucalyptol forms crystalline adducts with hydrohalic acids, o-cresol, resorcinol, and phosphoric acid. Formation of these adducts is useful for purification.

Caryophyllene, more formally (−)-β-caryophyllene, is a natural bicyclic sesquiterpene that is a constituent of many essential oils, especially clove oil, the oil from the stems and flowers of Syzygium aromaticum (cloves), the essential oil of Cannabis sativa, rosemary, and hops. It is usually found as a mixture with isocaryophyllene and α-humulene, a ring-opened isomer. Caryophyllene is notable for having a cyclobutane ring, as well as a trans-double bond in a 9-membered ring, both rarities in nature.
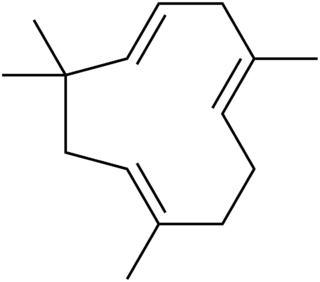
Humulene, also known as α-humulene or α-caryophyllene, is a naturally occurring monocyclic sesquiterpene (C15H24), containing an 11-membered ring and consisting of 3 isoprene units containing three nonconjugated C=C double bonds, two of them being triply substituted and one being doubly substituted. It was first found in the essential oils of Humulus lupulus (hops), from which it derives its name. Humulene is an isomer of β-caryophyllene, and the two are often found together as a mixture in many aromatic plants.
Eucalyptus oil is the generic name for distilled oil from the leaf of Eucalyptus, a genus of the plant family Myrtaceae native to Australia and cultivated worldwide. Eucalyptus oil has a history of wide application, as a pharmaceutical, antiseptic, repellent, flavouring, fragrance and industrial uses. The leaves of selected Eucalyptus species are steam distilled to extract eucalyptus oil.

Juniperus phoenicea, the Phoenicean juniper or Arâr, is a juniper found throughout the Mediterranean region, from Morocco and Portugal east to Italy, Turkey and Egypt, south on the mountains of Lebanon, the Palestine region and in western Saudi Arabia near the Red Sea, and also on Madeira and the Canary Islands. It mostly grows at low altitudes close to the coast, but reaches 2,400 metres (7,900 ft) altitude in the south of its range in the Atlas Mountains. It is the vegetable symbol of the island of El Hierro.

Libidibia ferrea, formerly Caesalpinia ferrea, and commonly known as pau ferro, Jucá, Brazilian ironwood, morado, or leopard tree, is a tree found in Brazil and Bolivia.
Rosewood refers to a number of richly hued timbers. Rosewood may also refer to:

Kaempferia galanga, commonly known as kencur, aromatic ginger, sand ginger, cutcherry, or resurrection lily, is a monocotyledonous plant in the ginger family, and one of four plants called galangal. It is found primarily in open areas in Indonesia, southern China, Taiwan, Cambodia, and India, but is also widely cultivated throughout Southeast Asia.

Aniba is an American neotropical flowering plant genus in the family Lauraceae. They are present in low and mountain cloud forest in Caribbean islands, Central America, and northern to central South America.

Aniba rosaeodora, also known as pau-rosa, is a species of Magnoliid tree in the family Lauraceae. Although sometimes wrongly referred to as rosewood this name is totally misleading; it is no tree of the genus Dalbergia. It grows in parts of the tropical rainforest of South America. It is an endangered species that sees exploitation for its essential oil.

Magnoliids are a group of flowering plants. Until recently, the group included about 9,000 species, including magnolias, nutmeg, bay laurel, cinnamon, avocado, black pepper, tulip tree and many others. That group is characterized by trimerous flowers, pollen with one pore, and usually branching-veined leaves.

















