The topic of this article may not meet Wikipedia's general notability guideline .(December 2021) |
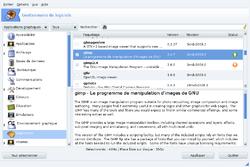
rpmdrake is a graphical interface to urpmi, which permits the installation of software packages. It is provided as part of Mandriva Linux, Mageia and ROSA for package installation.
The application is written in gtk2-perl, and allows:
- updating lists of packages available from configured installation media (CDs, websites, or network shares)
- visualization of dependencies for one or more packages
- installation and un-installation of packages to and from the operating system
rpmdrake is free software, available under the GNU General Public License, version 2. [1]
urpmi was developed by Guillaume Cottenceau, then by Rafael Garcia-Suarez, then by Thierry Vignaud, first at Mandriva, then at Mageia (see , ).