Related Research Articles
Anthroposophy is a spiritual new religious movement which was founded in the early 20th century by the esotericist Rudolf Steiner that postulates the existence of an objective, intellectually comprehensible spiritual world, accessible to human experience. Followers of anthroposophy aim to engage in spiritual discovery through a mode of thought independent of sensory experience. Though proponents claim to present their ideas in a manner that is verifiable by rational discourse and say that they seek precision and clarity comparable to that obtained by scientists investigating the physical world, many of these ideas have been termed pseudoscientific by experts in epistemology and debunkers of pseudoscience.
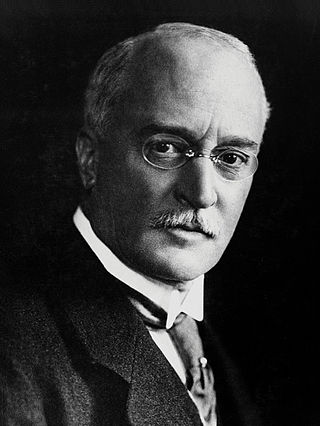
Rudolf Christian Karl Diesel was a German inventor and mechanical engineer who invented the Diesel engine, which burns Diesel fuel; both are named after him.

Rudolf II was Holy Roman Emperor (1576–1612), King of Hungary and Croatia, King of Bohemia (1575–1608/1611) and Archduke of Austria (1576–1608). He was a member of the House of Habsburg.

Rudolf Joseph Lorenz Steiner was an Austrian occultist, social reformer, architect, esotericist, and claimed clairvoyant. Steiner gained initial recognition at the end of the nineteenth century as a literary critic and published works including The Philosophy of Freedom. At the beginning of the twentieth century he founded an esoteric spiritual movement, anthroposophy, with roots in German idealist philosophy and theosophy. His teachings are influenced by Christian Gnosticism. Many of his ideas are pseudoscientific. He was also prone to pseudohistory.

Rudolf I was the first King of Germany from the House of Habsburg. The first of the count-kings of Germany, he reigned from 1273 until his death in 1291.

Rudolf Carnap was a German-language philosopher who was active in Europe before 1935 and in the United States thereafter. He was a major member of the Vienna Circle and an advocate of logical positivism.

Rudolf Ludwig Carl Virchow was a German physician, anthropologist, pathologist, prehistorian, biologist, writer, editor, and politician. He is known as "the father of modern pathology" and as the founder of social medicine, and to his colleagues, the "Pope of medicine".

Rudolf, Crown Prince of Austria was the only son and third child of Emperor Franz Joseph I of Austria and Duchess Elisabeth of Bavaria (Sisi). He was heir apparent to the imperial throne of the Austro-Hungarian Empire from birth. In 1889, he died in a suicide pact with his mistress Baroness Mary Vetsera at the Mayerling hunting lodge. The ensuing scandal made international headlines.

Rudolf Christoph Eucken was a German philosopher. He received the 1908 Nobel Prize in Literature "in recognition of his earnest search for truth, his penetrating power of thought, his wide range of vision, and the warmth and strength in presentation with which in his numerous works he has vindicated and developed an idealistic philosophy of life", after he had been nominated by a member of the Swedish Academy.

In the religion of Theosophy and the spiritual movement called Anthroposophy, the Akashic records are a compendium of all universal events, thoughts, words, emotions, and intent ever to have occurred in the past, present, or future in terms of all entities and life forms, not just human. They are believed by theosophists to be encoded in a non-physical plane of existence known as the mental plane. There is no evidence for the existence of Akashic records, and rigorous scientific research in this field has seen little traction.

Rudolf Khametovich Nureyev was a Soviet-born ballet dancer and choreographer. Nureyev is widely regarded as the greatest male ballet dancer of his generation.

Rudolf Franz Ferdinand Höss was a German SS officer and the commandant of the Auschwitz concentration camp. After the defeat of Nazi Germany and the end of World War II, he was convicted in Poland and executed for war crimes committed on the prisoners of the Auschwitz concentration camp and for his role in the Holocaust.

Puma SE is a German multinational corporation who design and manufacture athletic and casual footwear, apparel, and accessories, headquartered in Herzogenaurach, Bavaria, Germany. Puma is the third largest sportswear manufacturer in the world. The company was founded in 1948 by Rudolf Dassler (1898–1974). In 1924, Rudolf and his brother Adolf "Adi" Dassler had jointly formed the company Gebrüder Dassler Schuhfabrik. The relationship between the two brothers deteriorated until they agreed to split in 1948, forming two separate entities, Adidas and Puma. Following the split, Rudolf originally registered the newly established company as Ruda, but later changed the name to Puma. Puma's earliest logo consisted of a square and beast jumping through a D, which was registered, along with the company's name, in 1948. Puma's shoe and clothing designs feature the Puma logo and the distinctive "Formstrip" which was introduced in 1958.

Rudolf Schenker is a German guitarist, founder and leader of the hard rock band Scorpions. He is the rhythm/lead guitarist, primary songwriter and the sole constant member of the band. He is also the CEO/owner-manager of the Scorpions Musik-Produktions-und Verlagsgesellschaft mbH and owner/founder of the Scorpio-Sound-Studios in Lower Saxony. He is the older brother of Michael Schenker.

The Natural History Museum Vienna is a large natural history museum located in Vienna, Austria.

Adolf "Adi" Dassler was a German cobbler, inventor, and businessman who founded the German sportswear company Adidas. He was also the younger brother of Rudolf Dassler, founder of Puma. Dassler was an innovator in athletic shoe design and one of the early promoters who obtained endorsements from athletes to drive sales of his products. As a result of his concepts, Adi Dassler built the largest manufacturer of sportswear and equipment. At the time of his death, Adidas had 17 factories and annual sales of one billion marks.

Waldorf education, also known as Steiner education, is based on the educational philosophy of Rudolf Steiner, the founder of anthroposophy. Its educational style is holistic, intended to develop pupils' intellectual, artistic, and practical skills, with a focus on imagination and creativity. Individual teachers have a great deal of autonomy in curriculum content, teaching methods, and governance. Qualitative assessments of student work are integrated into the daily life of the classroom, with standardized testing limited to what is required to enter post-secondary education.

Kevin Winston Rudolf is an American singer, songwriter, and record producer. He is best known for his 2008 debut single "Let It Rock", which peaked at number five on the Billboard Hot 100 and received quadruple platinum certification by the Recording Industry Association of America (RIAA). He signed with Birdman's Cash Money Records, an imprint of Universal Republic Records to release the song along with the parent album of which it preceded, In the City (2008). The album received mixed reviews and underperformed commercially at number 94 on the Billboard 200, along with his third album To the Sky (2010), which peaked at number 78. Prior, he released his then-eponymous debut album (2001)—under the name Binocular—through Madonna's record label Maverick.

Rudolf Jeny was a Hungarian football player and manager.
Rudolf Bindig is a German politician who was elected eight times from 1976 to 2005 as a member of the Bundestag for the Social Democratic Party of Germany. From 1996 to 2005 he was also a member of the Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe, of which he was elected a vice-president in 2002.
References
- ↑ "Rudolf Kruspel". Olympedia. Retrieved 18 May 2020.