
Ajmer is one of the major and oldest cities in the Indian state of Rajasthan and the centre of the eponymous Ajmer District. It is located at the centre of Rajasthan. It is also known as heart of Rajasthan. The city was established as Ajayameru by a Chahamana ruler, either Ajayaraja I or Ajayaraja II, and served as their capital until the 12th century CE.

Rajasthan is a state in northwestern India. It covers 342,239 square kilometres (132,139 sq mi) or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the largest Indian state by area and the seventh largest by population. It is on India's northwestern side, where it comprises most of the wide and inhospitable Thar Desert and shares a border with the Pakistani provinces of Punjab to the northwest and Sindh to the west, along the Sutlej-Indus River valley. It is bordered by five other Indian states: Punjab to the north; Haryana and Uttar Pradesh to the northeast; Madhya Pradesh to the southeast; and Gujarat to the southwest. Its geographical location is 23°.3' to 30°.12' North latitude and 69°.30' to 78°.17' East longitude, with the Tropic of Cancer passing through its southernmost tip.

The Pushkar Fair, also called the Pushkar Camel Fair or locally as Kartik Mela or Pushkar ka Mela is an annual multi-day livestock fair and cultural fête held in the town of Pushkar near Ajmer city in Ajmer district in. The fair starts with the Hindu calendar month of Kartik and ends on the Kartik Purnima, which typically overlaps with late October and early November in the Gregorian calendar. In 1998, over 1 million visitors came to Pushkar throughout the year. The Pushkar fair alone attracts over 200,000 visitors.

Pushkar is a temple town, near Ajmer City and headquarters of Pushkar tehsil in the Ajmer district in the Indian state of Rajasthan. It is situated about 10 km (6.2 mi) northwest of Ajmer and about 150 kilometres (93 mi) southwest of Jaipur. It is a pilgrimage site for Hindus and Sikhs. Pushkar has many temples. Most of the temples and ghats in Pushkar are from the 18th century and later, because many temples were destroyed during Muslim conquests in the area. Subsequently, the destroyed temples were rebuilt. The most famous among Pushkar temples is the red spired Brahma Temple. It is considered a sacred city by the Hindus particularly in Shaktism, and meat and eggs consumption are forbidden in the city as are alcohol and drugs. Pushkar is located on the shore of Pushkar Lake, which has many ghats where pilgrims bathe. Pushkar is also significant for its Gurdwaras for Guru Nanak and Guru Gobind Singh. One of the bathing ghats is called Gobind ghat built by the Sikhs in the memory of Guru Gobind Singh.

The Sambhar Salt Lake, India's largest inland salt lake, is located in Sambhar Lake Town, Jaipur district of Rajasthan, India, 80 km (50 mi) southwest of the city of Jaipur and 64 km (40 mi) northeast of Ajmer, Rajasthan. It surrounds the historical Sambhar Lake Town.

Marwar is a region of western Rajasthan state in North Western India. It lies partly in the Thar Desert. The word 'maru' is Sanskrit for desert. In Rajasthani languages, "wad" means a protected area. English translation of the word 'marwar' is the region protected by desert.
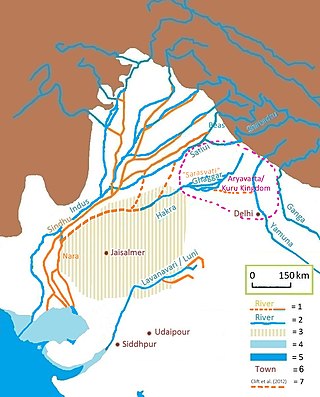
The Luni is the largest river in the Thar Desert of northwest India. It originates in the Pushkar valley of the Aravalli Range, near Ajmer, passes through the southeastern portion of the Thar Desert, and ends in the marshy lands of Rann of Kutch in Gujarat, after travelling a distance of 495 km (308 mi). It is first known as Sagarmati, then after passing Govindgarh, it meets its tributary Sarasvati, which originates from Pushkar Lake and from then on it is called Luni.

Pushkar Lake or Pushkar Sarovar is located in the town of Pushkar near Ajmer city in Ajmer district of the Rajasthan state of western India. Pushkar Lake is a sacred lake of the Hindus. The Hindu scriptures describe it as "Tirtha-Guru" [Thirtha Raj]– the perceptor of pilgrimage sites related to a water-body and relate it to the mythology of the creator-god Brahma, whose most prominent temple stands in Pushkar. The Pushkar Lake finds mention on coins as early as the 4th century BC.

The Banas is a river which lies entirely within the state of Rajasthan in western India. It is a tributary of the Chambal River, itself a tributary of the Yamuna, which in turn merges into the Ganga. The Banas is approximately 512 kilometres in length.

Ajmer district is a district in the Indian state of Rajasthan. It is part of the Ajmer division–one of the ten administrative divisions of Rajasthan. The city of Ajmer is the district headquarters. The district is situated in the center of Rajasthan, and is bounded by Didwana Kuchaman district to the north, Jaipur Rural and Dudu to the north-east, Tonk to the east, Kekri and Beawar to the south, and Nagaur to the west. It has an area of 8,481 km2 (3,275 sq mi), and a population of 2,583,052.

Nagaur District is one of the 50 districts of the state of Rajasthan in western India. Panchayati Raj was introduced here. It is the fifth largest district in Rajasthan and the area of the district is 17,718 km2 (6,841 sq mi). The city of Nagaur is the district headquarters.

The Drishadvati River is a river hypothesized by Indologists to identify the route of the Vedic river Saraswati and the state of Brahmavarta. According to Manusmriti, the Brahmavarta, where the Rishis composed the Vedas and other Sanskrit texts of the Vedic religion, was at the confluence of the Saraswati and Drishadvati rivers during the Vedic period.

Gangapur City is a city and a municipal council located in Gangapur district in the Indian state of Rajasthan. It is the administrative headquarters of Gangapur district. It is famous for its Sweet Cuisine Kheermohan and newly built Kushalgarh Baba Shyam Temple.

Rajendra Singh is an Indian water conservationist and environmentalist from Alwar district, Rajasthan in India. Also known as "waterman of India", he won the Magsaysay Award in 2001 and Stockholm Water Prize in 2015. He runs an NGO called 'Tarun Bharat Sangh' (TBS), which was founded in 1975. The NGO based in village hori-Bhikampura in Thanagazi tehsil, near Sariska Tiger Reserve, has been instrumental in fighting the slow bureaucracy, mining lobby and has helped villagers take charge of water management in their semi-arid area as it lies close to Thar Desert, through the use of johad, rainwater storage tanks, check dams and other time-tested as well as path-breaking techniques. Starting from a single village in 1985, over the years TBS helped build over 8,600 johads and other water conservation structures to collect rainwater for the dry seasons, has brought water back to over 1,000 villages and revived five rivers in Rajasthan, Arvari, Ruparel, Sarsa, Bhagani and Jahajwali. He is one of the members of the National Ganga River Basin Authority (NGRBA) which was set up in 2009, by the Government of India as an empowered planning, financing, monitoring and coordinating authority for the Ganges (Ganga), in exercise of the powers conferred under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986. In the UK he is a founder member of an NGO called the Flow Partnership which aims to counter the negative effects of soil erosion and flooding.

The Arvari River, which originates in Aravalli range, is a small river flowing through the Alwar District of Rajasthan, India. It has a total length of 45 km (28 mi) and a total basin area of 492 km2 (190 sq mi). Downstream of the Sainthal Sagar dam on Arvari, the Arvari river meets Sarsa River to become the Sanwan River. The Sanwan meets the Tildah and Banganga rivers to converge with the Gambhir. Gambhir then converges with the Yamuna in Mainpuri district of Uttar Pradesh, Yamuna converges with Ganges at Triveni Sangam in Prayagraj.

Rajasthan is one of the most popular tourist destinations in India, for both domestic and international tourists. Rajasthan attracts tourists for its historical forts, palaces, art and culture with its slogan "Padharo Mhare Desh " The capital city, Jaipur, also known as Pink City, is a very popular tourist destination and is a part of the Golden Triangle. The Walled City of Jaipur is only the second Indian city to be recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage Site, after Ahmedabad.

Bisalpur Dam is a gravity dam on the Banas River near Bisalpur in Tonk district, Rajasthan, India. The dam was completed in 1999 for the purpose of irrigation and water supply.
The term Rajasthani Muslims is usually used to signify Muslims from the state of Rajasthan in the north-western part of India and speak Hindi, Urdu and Sindhi languages.
The Mentha River also known Mendha river is a river in the northwestern region of India. It originates from Manoharpura hills, located in Jaipur District, and flows through the Sikar District & Nagore District before eventually emptying into Sambhar Lake. The river follows a northward course, contributing to the freshwater inflow of the lake.

Naga Pahar(en:Snake Mountain), is a significant geographical and spiritual landmark located between the towns of Pushkar and Ajmer in the Indian state of Rajasthan. This mountain holds cultural and mythological importance, intertwined with legends and beliefs that have been passed down through generations.
















