Related Research Articles
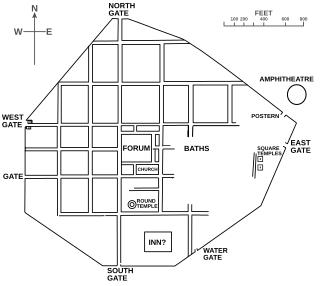
Calleva Atrebatum was an Iron Age oppidum, the capital of the Atrebates tribe. It then became a walled town in the Roman province of Britannia, at a major crossroads of the roads of southern Britain.
Millstones or mill stones are stones used in gristmills, used for triturating, crushing or, more specifically, grinding wheat or other grains. They are sometimes referred to as grindstones or grinding stones.

Viroconium or Uriconium, formally Viroconium Cornoviorum, was a Roman city, one corner of which is now occupied by Wroxeter, a small village in Shropshire, England, about 5 miles (8 km) east-south-east of Shrewsbury. At its peak, Viroconium is estimated to have been the 4th-largest Roman settlement in Britain, a civitas with a population of more than 15,000. The settlement probably lasted until the end of the 7th century or the beginning of the 8th. Extensive remains can still be seen.

Quern-stones are stone tools for hand-grinding a wide variety of materials, especially for various types of grains. They are used in pairs. The lower stationary stone of early examples is called a saddle quern, while the upper mobile stone is called a muller, rubber, or handstone. The upper stone was moved in a back-and-forth motion across the saddle quern. Later querns are known as rotary querns. The central hole of a rotary quern is called the eye, and a dish in the upper surface is known as the hopper. A handle slot contained a handle which enabled the rotary quern to be rotated. They were first used in the Neolithic era to grind cereals into flour.

Julliberrie's Grave, also known as The Giant's Grave or The Grave, is an unchambered long barrow located near to the village of Chilham in the south-eastern English county of Kent. Probably constructed in the fourth millennium BCE, during Britain's Early Neolithic period, today it survives only in a state of ruin.

Sheppard Sunderland Frere, CBE, FSA, FBA was a British historian and archaeologist who studied the Roman Empire. He was a fellow at All Souls College, Oxford.

Malcolm Todd was an English archaeologist. Born in Durham, England, the son of a miner, Todd was educated in classics and classical archaeology at St David's College, Lampeter and Brasenose College, Oxford. He subsequently served as a reader and professor at the University of Nottingham and the University of Exeter respectively. During this time, Todd conducted notable excavations at sites of Roman Britain. He was later principal at Trevelyan College, Durham. Todd retired from Durham in 2000, and subsequently dedicated himself to research and writing. He was the author and editor of several works on the archaeology of Roman Britain and the Germanic peoples in the Migration Period.
Michael Gordon Fulford, is a British archaeologist and academic, specialising in the British Iron Age, Roman Britain and landscape archaeology. He has been Professor of Archaeology at the University of Reading since 1993.
Timothy William Potter was a prominent archaeologist of ancient Italy, as well as of Roman Britain, best known for his focus on landscape archaeology.
Thirlage was a feudal servitude under Scots law restricting manorial tenants in the milling of their grain for personal or other uses. Vassals in a feudal barony were thirled to their local mill owned by the feudal superior. People so thirled were called suckeners and were obliged to pay customary dues for use of the mill and help maintain it.
Euan Wallace MacKie was a British archaeologist and anthropologist. He was a prominent figure in the field of Archaeoastronomy.
Miles Russell, is a British archaeologist best known for his work and publications on the prehistoric and Roman periods and for his appearances in television programmes such as Time Team and Harry Hill's TV Burp.

Folkestone Roman Villa, also referred to as the East Bay Site, is a villa built during the Roman Occupation of Britain, and is located in East Wear Bay near the port town of Folkestone, in Kent, England. The villa is situated on a cliff top overlooking the English Channel, with views of the French coast at Boulogne on a clear day. It is situated near the start of the North Downs Trackway, and the area has been inhabited for thousands of years, with archeological finds in the area and at the villa site dating back to the Mesolithic and Neolithic ages. The villa was built around A. D. 75, and was almost certainly built within the confines of a preexisting Iron Age settlement.
Eszter Bánffy, is a Hungarian prehistorian, archaeologist, and academic. Since 2013, she has been Director of the Romano-Germanic Commission at the German Archaeological Institute. She is also a professor at the Archaeological Institute of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences.
Lindsay Allason-Jones, is a British archaeologist and museum professional specialising in Roman material culture, Hadrian's Wall, Roman Britain, and the presence and role of women in the Roman Empire. She is currently a visiting fellow at Newcastle University.
Mo were stone implements used for grinding wheat in ancient China. It was a rotary quern millstone powered by a hand-operated crank fixed at the top to grind and pulverize grains, wheat, and rice into flour.

Staden is a small hamlet on the southern outskirts of Buxton, Derbyshire, lying between Harpur Hill and Cowdale. It was occupied in Neolithic, Roman and medieval times. Staden is close to the limestone hilltop of Staden Low whose summit is 367 m (1,204 ft) above sea level.
Jodie Lewis is a British archaeologist specialising in the study of prehistory. She is a lecturer at the University of Bradford. She was elected as a Fellow of the Society of Antiquaries of London in 2015. Before joining Bradford in 2022, Lewis lectured at the University of Wales, Bangor, the University of West of England, and the University of Worcester. She is a council member of The Prehistoric Society.
Paul Thomas Bidwell was a British archaeologist specialising in Roman Britain, Roman pottery, Hadrian's Wall and the Roman army in Britain.
References
- ↑ "Our People: Ruth Shaffrey". Oxford Archaeology. Retrieved 20 February 2021.
- ↑ Greene, K. (2008). "Review of: Grinding and Milling: A Study of Romano-British Rotary Querns and Millstones Made from Old Red Sandstone. By R. Shaffrey. British Archaeological Reports British Series 409. Archaeopress, Oxford, 2006. Pp. xi + 175, figs 64, tables 22. Price: £35.00. ISBN 978 1 84171 938 2". Britannia. 39: 409–410. doi:10.3815/006811308785917178.
- ↑ "A14 upgrade: 'Rare' Roman penis carving found in Cambridgeshire". BBC News. 19 February 2021.
- ↑ "Dr Ruth Shaffrey". Society of Antiquaries of London. Retrieved 20 February 2021.