Related Research Articles

The Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-9 was the first turbojet fighter developed by Mikoyan-Gurevich in the years immediately after World War II. It used reverse-engineered German BMW 003 engines. Categorized as a first-generation jet fighter, it suffered from persistent problems with engine flameouts when firing its guns at high altitudes due to gun gas ingestion. A number of different armament configurations were tested, but none solved the problem. Several different engines were evaluated, but none were flown, as the prototype of the MiG-15 promised superior performance.

The Yakovlev Yak-38 was Soviet Naval Aviation's only operational VTOL strike fighter aircraft in addition to being its first operational carrier-based fixed-wing aircraft. It was developed specifically for, and served almost exclusively on, the Kiev-class aircraft carriers.

The Yakovlev Yak-141, also known as the Yak-41, is a Soviet supersonic vertical takeoff/landing (VTOL) fighter aircraft designed by Yakovlev. Intended as a replacement for the Yak-38, it was designed as a supersonic fleet defence fighter capable of STOVL/VTOL operating from Soviet carriers. Four prototypes were built before the project's cancellation.

The Yakovlev Yak-36, also known as Izdeliye V, is a Soviet technology demonstrator for a VTOL combat aircraft.

The Sukhoi Su-9 was an early jet fighter built in the Soviet Union shortly after World War II. The design began in 1944 and was intended to use Soviet-designed turbojet engines. The design was heavily influenced by captured German jet fighters and it was subsequently redesigned to use a Soviet copy of a German turbojet. The Su-9 was slower than competing Soviet aircraft and it was cancelled as a result. A modified version with different engines and a revised wing became the Su-11, but this did not enter production either. The Su-13 was a proposal to re-engine the aircraft with Soviet copies of the Rolls-Royce Derwent turbojet as well as to modify it for night fighting, but neither proposal was accepted.

The Yakovlev Yak-15 was a first-generation Soviet turbojet fighter developed by the Yakovlev design bureau (OKB) immediately after World War II. The main fuselage was that of Yakovlev Yak-3 piston-engine fighter modified to mount a reverse-engineered German Junkers Jumo 004 engine. The Yak-15 and the Swedish Saab 21R were the only two jets to be successfully converted from piston-power to enter production. 280 aircraft were built in 1947. Although nominally a fighter, it was mainly used to qualify piston-engine-experienced pilots to fly jets.

The Yakovlev Yak-19 was a prototype Soviet fighter built in the late 1940s. It was the first Soviet aircraft to be equipped with an afterburning turbojet, the Klimov RD-10F that was derived from the German Jumo 004 engine. Only two examples were built as it was rejected for service by the Soviet Air Force.

The Tumansky R-11 is a Soviet Cold War-era turbojet engine.

The Yakovlev Yak-25 was a Soviet military aircraft, an early turbojet-powered fighter aircraft designed by the Yakovlev OKB. The designation was later reused for a different interceptor design. Tasked by the Council of Ministers in a directive issued on 11 March 1947, with producing a straight winged fighter similar to the earlier Yak-19, but powered by a Rolls-Royce Derwent V, OKB-115 swiftly produced the Yak-25, which blazed several trails as the first Soviet fighter with a fully pressurised cockpit, air conditioning, jettisonable canopy, and hydraulic airbrakes on the fuselage amongst other innovations.

The Klimov RD-500 was an unlicensed Soviet copy of the Rolls-Royce Derwent V turbojet that was sold to the Soviet Union in 1947. The Klimov OKB adapted it for Soviet production methods and materials.

The Tumansky R-15 is an axial flow, single shaft turbojet with an afterburner. Its best known use is on the Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-25.
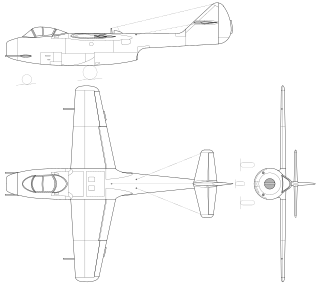
The Lavochkin La-150, was designed by the Lavochkin design bureau (OKB) in response to a 1945 order to build a single-seat jet fighter using a single German turbojet. By this time both the Americans and British, as well as the Germans, had already flown jet fighters and the single Soviet jet engine under development was not yet ready for production. The design was completed quickly, but the construction of the five flying prototypes was protracted by the factory's inexperience in building metal aircraft. The aircraft made its first flight in September 1946, but proved to require extensive modifications to meet the Soviet Air Forces' requirements. These took so long to make and test that the aircraft was essentially obsolete by the time that they were completed. Even one variant with a much more powerful engine was inferior to other aircraft that the OKB had under development and all work was terminated in 1947.

Yakovlev Yak-50 was an early experimental turbojet interceptor aircraft designed in 1948 by the Yakovlev OKB in the USSR. The aircraft was essentially a stretched version of the Yakovlev Yak-30 (1948), with a more powerful engine and greater wing sweep. The Yak-50 is perhaps most significant as the first Yakovlev aircraft equipped with velosipednoye (bicycle) landing gear, a trademark of later Yakovlev designs. The Yak-50 designation was later reused for a propeller-driven aerobatic and trainer aircraft.
The Yakovlev Yak-33 was a vertical takeoff and landing supersonic multi-purpose aircraft family, studied in the early 1960s, with variants of a basic design used to fulfill different roles, in a similar fashion to the Yak-25, Yak-27, Yak-28 family.

The Lavochkin La-152,, and its variants, was a jet fighter prototype designed and manufactured by the Lavochkin Design Bureau (OKB) shortly after the end of World War II. Derived from the Lavochkin La-150, the 152 used several different engines, but the program was canceled as other fighters with more powerful engines and swept wings showed more promise.
The Lyulka TR-1 was a turbojet designed by Arkhip Lyulka and produced by his Lyulka design bureau. It was the first indigenous Soviet jet engine.

The Yakovlev Yak-1000 was a Soviet supersonic technology demonstrator intended to evaluate the aerodynamic layout and field performance of the cropped delta wing discussed in captured German documents in combination with the new Lyulka AL-5 turbojet. The tandem undercarriage proved to be unsatisfactory and there were serious flight stability problems related to the delta wing, enough so that it never flew after an accident during taxiing tests.

The Yakovlev Yak-140 was a Soviet prototype lightweight supersonic fighter developed during the 1950s. The prototype was completed in 1954, but it was denied authorization to enter flight testing and the program was cancelled in 1956.
The Mikoyan-Gurevich I-350, was a Soviet Cold War-era experimental fighter aircraft. It was the first Soviet aircraft able to maintain supersonic speed.
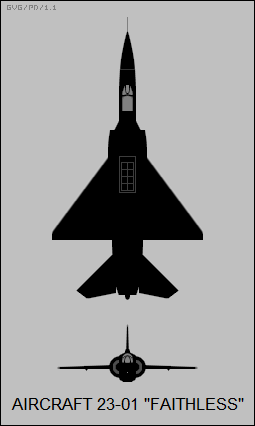
The Mikoyan-Gurevich 23-01, aka Izdeliye 92 and (erroneously) Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-23PD, NATO reporting name Faithless, was a 1960s STOL fighter / attack aircraft, designed in the USSR, to fulfil a requirement for ground-attack and fighter aircraft able to operate from short runways.
References
- 1 2 3 4 Gordon, Yefim; Dmitry; Sergey Komissarov (2005). OKB Yakovlev . Hinkley: Midland Publishing. pp. 334-342. ISBN 1-85780-203-9.
- 1 2 3 “Engine” No. 4/2007 // Alexander Nikolaev “We take off vertically!”
- ↑ “Wings of the Motherland” No. 9/2001 // Vyacheslav Zayarin, Konstantin Udalov “The Concept of the Universal Vertical