
Bodh Gaya is a religious site and place of pilgrimage associated with the Mahabodhi Temple Complex in Gaya district in the Indian state of Bihar. It is famous as it is the place where Gautama Buddha is said to have attained Enlightenment under what became known as the Bodhi Tree. Since antiquity, Bodh Gaya has remained the object of pilgrimage and veneration both for Hindus and Buddhists. In particular, archaeological finds including sculptures show that the site was in use by Buddhists since the Mauryan period.

The Mahabodhi Temple or the Mahābodhi Mahāvihāra, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is an ancient, but rebuilt and restored Buddhist temple in Bodh Gaya, Bihar, India, marking the location where the Buddha is said to have attained enlightenment. Bodh Gaya is 15 km from Gaya and is about 96 km (60 mi) from Patna.

The Bodhi Tree, also called the Mahabodhi Tree, Bo Tree, is a large sacred fig tree located in Bodh Gaya, Bihar, India. Siddhartha Gautama, the spiritual teacher who became known as the Buddha, is said to have attained enlightenment or buddhahood circa 500 BCE under this tree. In religious iconography, the Bodhi Tree is recognizable by its heart-shaped leaves, which are usually prominently displayed.

Gaya is a city, municipal corporation and the administrative headquarters of Gaya district and Magadh division of the Indian state of Bihar. Gaya is 116 kilometres (72 mi) south of Patna and is the state's second-largest city, with a population of 470,839. The city is surrounded on three sides by small, rocky hills, with the Phalgu River on its eastern side.

Munger, formerly spelt as Monghyr, is a twin city and a Municipal Corporation situated in the Indian state of Bihar. It is the administrative headquarters of Munger district and Munger Division. Munger was one of the major cities in Eastern India and undivided Bengal during Mughal period and British Raj. It is one of the major political,cultural,educational and commercial center of Bihar and Eastern India. Munger is situated about 180km from east of capital city Patna, about 480km west of Eastern India's largest city kolkata and 1200km from country's capital New Delhi.
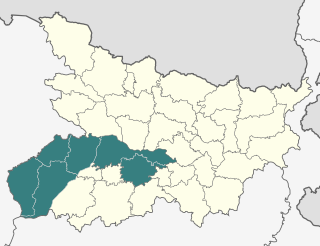
Patna Division is one of the nine administrative units of Bihar, a state in the east of India. Patna is the headquarters of the division. Established in 1829, it is one of the oldest divisions of the state.

Babasaheb Bhimrao Ambedkar Bihar University, formerly Bihar University, popularly known as Dr. B. R. Ambedkar Bihar University (BRABU), is a public university located in Muzaffarpur, Bihar, India. Established in 1960, the university has 38 constituent colleges and 40 affiliated colleges. It offers education from undergraduate to postgraduate and research level, as well as Distance education. It is named after B. R. Ambedkar, social reformer and the architect of Indian Constitution.

The economy of Bihar is one of the fastest-growing in India. It is largely service-based, with a significant share of agricultural and industrial sectors. The GDP of the state was ₹7,45,310 crores at the current market price (2022–23).
Bihar (Hindi: Bihar,, [Bihar] in eastern India is one of the oldest inhabited places in the world with a history going back 3000 years. The rich culture and heritage of Bihar is evident from the innumerable ancient monuments that are dotted all over the state. Bihar is home to many tourist attractions and is visited by large numbers of tourists from all over the world. Around total 6 million tourists visit Bihar every year.
Hinduism is the most followed religion in Bihar, followed by nearly 82.7% of total population as per 2011 Census. Islam is the second-most followed religion which is followed by nearly 16.8% of population. There is also a significant population of Jains and Christians in the state.
Bihar is a state situated in Eastern India. It is surrounded by West Bengal to the east, Uttar Pradesh to the west, Jharkhand to the south and Nepal to the north.

Saran district is one of the thirty-eight districts of Indian state of Bihar. The district, part of Saran Division, is also known as Chhapra district after the headquarters of the district, Chhapra. It is considered as one of the richest Zamindari of Bihar after Raj Darbhanga, Hathwa Raj, Bettiah Raj and Raj Najarganj, Saran Raj.

The Bihar State Milk Co-Operative Federation Ltd is a state government cooperative under the ownership of Ministry of Cooperation, Government of Bihar. It was established in 1983 as a state government cooperative of the Government of Bihar, India. It markets its products under the label "Sudha Dairy". The co-operative facilitates the procurement, processing, and marketing of dairy products. It provides education to the unions on efficient dairy processing, and assists them with animal care including artificial insemination, vaccination, and feeding.
Hindi is the official language of the State of Bihar. Urdu is the second official language in 15 districts of the State. Maithili is a recognized language of the state. However, the majority of the people of Bihar speak one of the Bhojpuri languages, most of which as classified as dialects of Hindi during the census. The major ones are Bhojpuri, Maithili, Magahi and are spoken by large numbers. Maithili is a recognised regional language of India under the Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of India. However speaker numbers for the languages of Bihar are limited because the more educated prefer to speak in Hindi and so return this answer on the census, while many in rural areas and the urban poor, especially the illiterate, list their language as "Hindi" on the census as they regard that as the term for their language. Smaller communities of Bengali and Santali speakers are found in the eastern districts of the state.
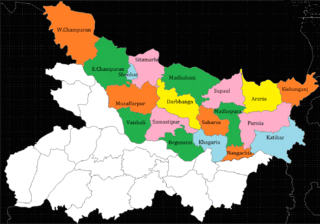
North Bihar is a term used for the region of Bihar, India, which lies north of the Ganga river.
Patna Municipal Corporation or Patna Nagar Nigam, abbr.PMC, is the civic body that governs Patna, the capital of Bihar in India.Municipal Corporation mechanism in India was introduced during British Rule with formation of municipal corporation in Madras (Chennai) in 1688, later followed by municipal corporations in Bombay (Mumbai) and Calcutta (Kolkata) by 1762. Patna Municipal Corporation consists of democratically elected members, is headed by a Mayor, and administers the city's infrastructure, public services, and supplies.

On 7 July 2013 a series of ten bombs exploded in and around the Mahabodhi Temple complex, a UNESCO World Heritage Site in Bodh Gaya, India. Five people, including two Buddhist monks, were injured by the blasts. Three other devices were defused by bomb-disposal squads at a number of locations in Gaya.

Buddha Smriti Park also known as Buddha Memorial Park is an urban park located on Frazer Road near Patna Junction in Patna, India. This park has been designed by Vikram Lall and developed by the Bihar Government to commemorate the 2554th birth anniversary of the Buddha. This park was inaugurated by the 14th Dalai Lama.











