
Coilin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the COIL gene. Coilin got its name from the coiled shape of the CB in which it is found. It was first identified using human autoimmune serum.

Small Cajal body specific RNA 15 is a small nucleolar RNA found in Cajal bodies and believed to be involved in the pseudouridylation of U1 spliceosomal RNA.

Small Cajal body specific RNA 16 is a small nucleolar RNA found in Cajal bodies and believed to be involved in the pseudouridylation of U1 spliceosomal RNA.
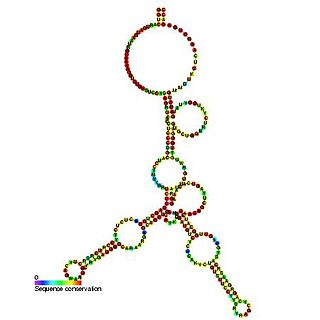
Small Cajal body specific RNA 6 is a small nucleolar RNA found in Cajal bodies and believed to be involved in the pseudouridylation of U5 spliceosomal RNA.

Small Cajal body-specific RNAs (scaRNAs) are a class of small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) that specifically localise to the Cajal body, a nuclear organelle involved in the biogenesis of small nuclear ribonucleoproteins. ScaRNAs guide the modification of RNA polymerase II transcribed spliceosomal RNAs U1, U2, U4, U5 and U12.

H/ACA ribonucleoprotein complex subunit 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the gene DKC1.

PRP31 pre-mRNA processing factor 31 homolog , also known as PRPF31, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the PRPF31 gene.
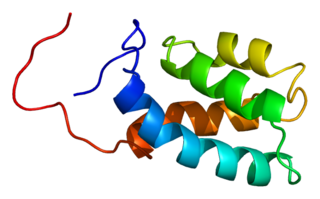
U4/U6 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein Prp3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PRPF3 gene.

Squamous cell carcinoma antigen recognized by T-cells 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SART3 gene.

28S ribosomal protein S12, mitochondrial is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MRPS12 gene.

Gem-associated protein 7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GEMIN7 gene.The gem-associated proteins are those found in the gems of Cajal bodies.

40S ribosomal protein S20 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RPS20 gene.

H/ACA ribonucleoprotein complex subunit 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NHP2 gene.

Zinc finger protein 143 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZNF143 gene.

Protein FRG1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FRG1 gene.

Gem-associated protein 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GEMIN5 gene.

ELL-associated factor 1 is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the EAF1 gene.

Gem-associated protein 8 (Gemin-8) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GEMIN8 gene.
Small Cajal body-specific RNA 26A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SCARNA26A gene.

Mitochondrial ribosomal protein S9 (MRPS9), otherwise known as uS9m, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MRPS9 gene.




















