
The Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution is a private, nonprofit research and higher education facility dedicated to the study of marine science and engineering.

The Channel Islands National Marine Sanctuary is a sanctuary off the coast of Santa Barbara and Ventura counties in Southern California 350 miles south of San Francisco and 95 miles north of Los Angeles. It was designated in 1980 by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.

Sir Alister Clavering Hardy was an English marine biologist, an expert on marine ecosystems spanning organisms from zooplankton to whales. He had the artistic skill to illustrate his books with his own drawings, maps, diagrams, and paintings.

A research vessel is a ship or boat designed, modified, or equipped to carry out research at sea. Research vessels carry out a number of roles. Some of these roles can be combined into a single vessel but others require a dedicated vessel. Due to the demanding nature of the work, research vessels may be constructed around an icebreaker hull, allowing them to operate in polar waters.

NOAAS Ronald H. Brown is a Thomas G. Thompson-class blue-water research vessel of the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, she is NOAA's only Global-Class research ship.
The Naval Oceanographic Office (NAVOCEANO), located at John C. Stennis Space Center in south Mississippi, is an echelon IV component of the Naval Meteorology and Oceanography Command (NMOC) and comprises approximately 1,000 civilian, military and contract personnel responsible for providing oceanographic products and services to all elements within the Department of Defense.
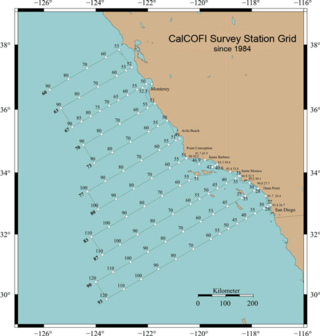
CalCOFI is a multi-agency partnership formed in 1949 to investigate the collapse of the sardine population off California. The organization's members are from NOAA Fisheries Service, Scripps Institution of Oceanography, and California Department of Fish and Wildlife. The scope of this research has evolved into the study of marine ecosystems off California and the management of its fisheries resources. In 2004, the CalCOFI survey area became one of 26 Long Term Ecological Research Network (LTER) research sites. This time-series of oceanographic and fisheries data allows scientists to assess the human impact and effects of climate change on the coastal ocean ecosystem. CalCOFI hydrographic and biological data, publications, and web information are distributed for use without restriction under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License.

YWAM Liberty is the former L'Astrolabe, a French icebreaking research vessel which was used to supply the Dumont d'Urville research station in Antarctica. The vessel made regular voyages between Hobart and the Dumont D'Urville research station for fifteen years and was replaced by a new icebreaker bearing the same name in 2017.

The Continuous Plankton Recorder (CPR) Survey is one of the longest running marine biological monitoring programmes in the world. Started in 1931 by Sir Alister Hardy and Sir Cyril Lucas, the Survey provides marine scientists and policy-makers with measures of plankton communities, coupled with ocean physical, biological and chemical observations, on a pan-oceanic scale. The Survey is a globally recognised leader on the impacts of environmental change on the health of our oceans.

The Australian Continuous Plankton Recorder (AusCPR) survey is a joint project of the CSIRO and the Australian Antarctic Division, DEWHA, to monitor plankton communities as a guide to the health of Australia's oceans.

USS Mobjack (AVP-27/AGP-7) was a motor torpedo boat tender in commission in the United States Navy from 1943 to 1946. She saw service in the Pacific theater during the latter portion of World War II.
A video plankton recorder (VPR) is towed underwater video microscope system, which photographs small to fine-scale structure of plankton, from 50 micrometers and up to a few centimeters in size. A VPR consists of five general components: cameras, strobe, additive sensor and flight control, underwater platform and interface software for plankton identification.
Fishery Oceanographic Research Vessel Sagar Sampada is an Indian research vessel that is equipped to carry out multidisciplinary research in oceanography, marine biology and fishery science. This is the unique facility of the country equipped to undertake oceanography and fisheries (demersal) in the same platform. The vessel is currently managed and operated by the Centre for Marine Living Resources & Ecology (CMLRE), Kochi, a research institute attached to the Ministry of Earth Sciences, Government of India, and is operated from Kochi. FORV Sagar Sampada is a platform for interdisciplinary expeditions in and around the Indian Exclusive Economic Zone, and in International waters with participation from various institutions, from India and abroad.

NOAAS David Starr Jordan (R444)) was an American fisheries research vessel in commission in the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) from 1970 to 2010. She previously was in the United States Fish and Wildlife Service's Bureau of Commercial Fisheries fleet from 1966 to 1970 as US FWS David Starr Jordan.

NOAAS Pisces is an American fisheries and oceanographic research vessel in commission in the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) fleet since 2009.
The North South Atlantic Training Transect (NoSoAT) is a program developed by the Alfred Wegener Institute (AWI), the Strategic Marine Alliance for Research and Training (SMART), and the Partnership for Observation of the Global Oceans (POGO) to further the education and practical training of postgraduate students in climate and marine sciences. Each year, about 30 students are selected through a rigorous application process to join a voyage from Bremerhaven, Germany to Cape Town, South Africa aboard the RV Polarstern. The month-long course provides students with relevant lectures and projects, including hands-on training with atmospheric and oceanographic equipment, and instruction on data processing and analysis.

NOAAS George B. Kelez, previously NOAAS George B. Kelez, was an American research vessel in commission in the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) fleet from 1972 to 1980. Prior to her NOAA career, she operated under the United States Fish and Wildlife Service′s Bureau of Commercial Fisheries from 1962 to 1970 as US FWS George B. Kelez and the National Marine Fisheries Service from 1970 to 1972 as NOAAS George B. Kelez.

JDSAkashi(AGS-5101) was an oceanographic research ship of Japan Maritime Self-Defense Force (JMSDF) in the late 1960s.

US FWS Hugh M. Smith was an American fisheries science research vessel in commission from 1949 to 1959 in the fleet of the United States Department of the Interior's Fish and Wildlife Service. She was among the first U.S. fisheries science vessels to explore the central Pacific Ocean in search of commercially valuable populations of fish.
Carin Jessica Ashjian is an American biological oceanographer who is an associate scientist at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution. She studies how the physical environment influences the distribution of plankton in the Beaufort Sea.
















