Related Research Articles

Parallel ATA (PATA), originally AT Attachment, also known as Integrated Drive Electronics (IDE), is a standard interface designed for IBM PC-compatible computers. It was first developed by Western Digital and Compaq in 1986 for compatible hard drives and CD or DVD drives. The connection is used for storage devices such as hard disk drives, floppy disk drives, optical disc drives, and tape drives in computers.
The Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) is a supporting protocol in the Internet protocol suite. It is used by network devices, including routers, to send error messages and operational information indicating success or failure when communicating with another IP address. For example, an error is indicated when a requested service is not available or that a host or router could not be reached. ICMP differs from transport protocols such as TCP and UDP in that it is not typically used to exchange data between systems, nor is it regularly employed by end-user network applications.

Small Computer System Interface is a set of standards for physically connecting and transferring data between computers and peripheral devices, best known for its use with storage devices such as hard disk drives. SCSI was introduced in the 1980s and has seen widespread use on servers and high-end workstations, with new SCSI standards being published as recently as SAS-4 in 2017.
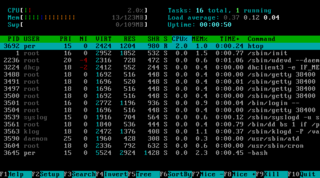
ANSI escape sequences are a standard for in-band signaling to control cursor location, color, font styling, and other options on video text terminals and terminal emulators. Certain sequences of bytes, most starting with an ASCII escape character and a bracket character, are embedded into text. The terminal interprets these sequences as commands, rather than text to display verbatim.
Fibre Channel (FC) is a high-speed data transfer protocol providing in-order, lossless delivery of raw block data. Fibre Channel is primarily used to connect computer data storage to servers in storage area networks (SAN) in commercial data centers.

Atari BASIC is an interpreter for the BASIC programming language that shipped with Atari 8-bit computers. Unlike most American BASICs of the home computer era, Atari BASIC is not a derivative of Microsoft BASIC and differs in significant ways. It includes keywords for Atari-specific features and lacks support for string arrays.
Disk formatting is the process of preparing a data storage device such as a hard disk drive, solid-state drive, floppy disk, memory card or USB flash drive for initial use. In some cases, the formatting operation may also create one or more new file systems. The first part of the formatting process that performs basic medium preparation is often referred to as "low-level formatting". Partitioning is the common term for the second part of the process, dividing the device into several sub-devices and, in some cases, writing information to the device allowing an operating system to be booted from it. The third part of the process, usually termed "high-level formatting" most often refers to the process of generating a new file system. In some operating systems all or parts of these three processes can be combined or repeated at different levels and the term "format" is understood to mean an operation in which a new disk medium is fully prepared to store files. Some formatting utilities allow distinguishing between a quick format, which does not erase all existing data and a long option that does erase all existing data.
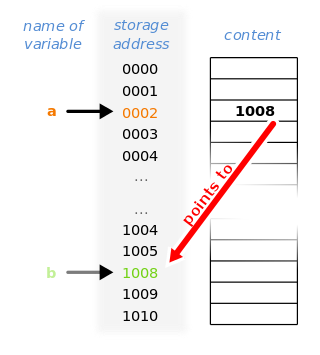
In computer science, a pointer is an object in many programming languages that stores a memory address. This can be that of another value located in computer memory, or in some cases, that of memory-mapped computer hardware. A pointer references a location in memory, and obtaining the value stored at that location is known as dereferencing the pointer. As an analogy, a page number in a book's index could be considered a pointer to the corresponding page; dereferencing such a pointer would be done by flipping to the page with the given page number and reading the text found on that page. The actual format and content of a pointer variable is dependent on the underlying computer architecture.

Self-Monitoring, Analysis, and Reporting Technology is a monitoring system included in computer hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs). Its primary function is to detect and report various indicators of drive reliability, or how long a drive can function while anticipating imminent hardware failures.
In computer storage, a logical unit number, or LUN, is a number used to identify a logical unit, which is a device addressed by the SCSI protocol or by Storage Area Network protocols that encapsulate SCSI, such as Fibre Channel or iSCSI.
In computing, the BIOS parameter block, often shortened to BPB, is a data structure in the volume boot record (VBR) describing the physical layout of a data storage volume. On partitioned devices, such as hard disks, the BPB describes the volume partition, whereas, on unpartitioned devices, such as floppy disks, it describes the entire medium. A basic BPB can appear and be used on any partition, including floppy disks where its presence is often necessary; however, certain filesystems also make use of it in describing basic filesystem structures. Filesystems making use of a BIOS parameter block include FAT12, FAT16, FAT32, HPFS, and NTFS. Due to different types of fields and the amount of data they contain, the length of the BPB is different for FAT16, FAT32, and NTFS boot sectors. Combined with the 11-byte data structure at the very start of volume boot records immediately preceding the BPB or EBPB, this is also called FDC descriptor or extended FDC descriptor in ECMA-107 or ISO/IEC 9293.

Commodore DOS, also known as CBM DOS, is the disk operating system used with Commodore's 8-bit computers. Unlike most other DOSes, which are loaded from disk into the computer's own RAM and executed there, CBM DOS is executed internally in the drive: the DOS resides in ROM chips inside the drive, and is run there by one or more dedicated MOS 6502 family CPUs. Thus, data transfer between Commodore 8-bit computers and their disk drives more closely resembles a local area network connection than typical disk/host transfers.
In computing, a word is the natural unit of data used by a particular processor design. A word is a fixed-sized datum handled as a unit by the instruction set or the hardware of the processor. The number of bits or digits in a word is an important characteristic of any specific processor design or computer architecture.
Key Code Qualifier is an error-code returned by a SCSI device.

Parallel SCSI is the earliest of the interface implementations in the SCSI family. SPI is a parallel bus; there is one set of electrical connections stretching from one end of the SCSI bus to the other. A SCSI device attaches to the bus but does not interrupt it. Both ends of the bus must be terminated.
This timeline of binary prefixes lists events in the history of the evolution, development, and use of units of measure that are germane to the definition of the binary prefixes by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) in 1998, used primarily with units of information such as the bit and the byte.
In Unix-like operating systems, a device file, device node, or special file is an interface to a device driver that appears in a file system as if it were an ordinary file. There are also special files in DOS, OS/2, and Windows. These special files allow an application program to interact with a device by using its device driver via standard input/output system calls. Using standard system calls simplifies many programming tasks, and leads to consistent user-space I/O mechanisms regardless of device features and functions.
SCSI / ATA Translation (SAT) is a set of standards developed by the T10 subcommittee, defining how to communicate with ATA devices through a SCSI application layer. The standard attempts to be consistent with the SCSI architectural model, the SCSI Primary Commands, and the SCSI Block Commands standards.
The Advanced Disc Filing System (ADFS) is a computing file system unique to the Acorn computer range and RISC OS-based successors. Initially based on the rare Acorn Winchester Filing System, it was renamed to the Advanced Disc Filing System when support for floppy discs was added and on later 32-bit systems a variant of a PC-style floppy controller.

The Linux-IOTarget (LIO) is an open-source Small Computer System Interface (SCSI) target implementation included with the Linux kernel.
References
- SCSI Command Reference Manual , Seagate Corp, October 2016.