Related Research Articles
An economic indicator is a statistic about an economic activity. Economic indicators allow analysis of economic performance and predictions of future performance. One application of economic indicators is the study of business cycles. Economic indicators include various indices, earnings reports, and economic summaries: for example, the unemployment rate, quits rate, housing starts, consumer price index, Inverted yield curve, consumer leverage ratio, industrial production, bankruptcies, gross domestic product, broadband internet penetration, retail sales, price index, and changes in credit conditions.

Principal component analysis (PCA) is a linear dimensionality reduction technique with applications in exploratory data analysis, visualization and data preprocessing.
The City of Maribyrnong is a local government area within the metropolitan area of Melbourne, Australia. It comprises the inner western suburbs between 5 and 10 kilometres from Melbourne city centre. It was formed in 1994 from the merger of the City of Footscray and parts of the City of Sunshine. In June 2018, Maribyrnong had a population of 91,387.

Bangholme is a suburb in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia, 31 km (19 mi) south-east of Melbourne's Central Business District, located within the City of Greater Dandenong local government area. Bangholme recorded a population of 749 at the 2021 census.

Hackett is an inner north suburb of Canberra, the capital city of Australia. Located approximately 4.5 km north-east of the central business district, Hackett is adjacent to Watson, Dickson and Ainslie. It is bounded by Antill Street and Philip Avenue, and the Mount Majura Nature Reserve to the east. Hackett has a neighbourhood oval, and shopping centre.

Secret Harbour is an outer southern suburb of Perth, the capital city of Western Australia, located within the City of Rockingham on the Indian Ocean coast at Comet Bay. Despite its name, Secret Harbour does not have a harbour. The name results from a failed marina development and was approved in 1984.
Alfred Cove was an electoral district of the Legislative Assembly of Western Australia. It was located in Perth's southern suburbs, and named after the riverside suburb of Alfred Cove.

Churchlands is a Legislative Assembly electorate in the state of Western Australia. Churchlands is named for the western suburb of Churchlands, which falls within its borders, and was created at the 1994 redistribution, replacing the seat of Floreat which had existed since 1968.

Nedlands is a Legislative Assembly electorate in the state of Western Australia. Nedlands is named for the inner western Perth suburb of Nedlands, which falls within its borders.

Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS) is an Australian government agency that collects and analyses statistics on economic, population, environmental, and social issues to advise the government.
The Carstairs index is an index of deprivation used in spatial epidemiology to identify Socio-economic confounding.
The Indices of deprivation 2004 is a deprivation index at the small area level, created by the British Department for Communities and Local Government(DCLG).

Poverty is measured in different ways by different bodies, both governmental and nongovernmental. Measurements can be absolute, which references a single standard, or relative, which is dependent on context. Poverty is widely understood to be multidimensional, comprising social, natural and economic factors situated within wider socio-political processes. The capabilities approach argues that capturing the perceptions of poor people is fundamental to understanding poverty.
Income segregation is the separation of various classes of people based on their income. For example, certain people cannot get into country clubs because of insufficient funds. Another example of income segregation in a neighborhood would be the schools, facilities and the characteristics of a population. Income segregation can be illustrated in countries such as the United States, where racial segregation is a major cause of income inequality.
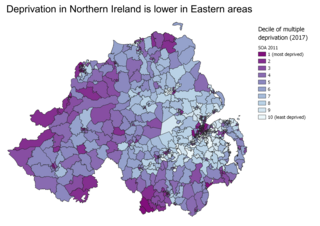
Indices of multiple deprivation (IMD) are widely-used datasets within the UK to classify the relative deprivation of small areas. Multiple components of deprivation are weighted with different strengths and compiled into a single score of deprivation.

Home ownership in Australia is considered a key cultural icon, and part of the Australian tradition known as the Great Australian Dream of "owning a detached house on a fenced block of land." Home ownership has been seen as creating a responsible citizenry; according to a former Premier of Victoria: "The home owner feels that he has a stake in the country, and that he has something worth working for, living for, fighting for."
Blue Mountain Heights is a residential locality in the Toowoomba Region, Queensland, Australia. In the 2016 census, Blue Mountain Heights had a population of 929 people.
Prince Henry Heights is a residential locality on the outskirts of Toowoomba in the Toowoomba Region, Queensland, Australia. In the 2021 census, Prince Henry Heights had a population of 600 people.

Redwood is a rural locality on the outskirts of Toowoomba in the Toowoomba Region, Queensland, Australia. In the 2016 census, Redwood had a population of 170 people.

Rockville is a residential locality in the Toowoomba Region, Queensland, Australia. In the 2021 census, Rockville had a population of 3,204 people.
References
- ↑ "Socio-Economic Indexes for Areas (SEIFA), Australia". 2021 Census. Australian Bureau of Statistics. 27 April 2023. Retrieved 30 August 2023.
- 1 2 3 "Socio-Economic Indexes for Areas (SEIFA): Technical Paper". Australian Bureau of Statistics. 27 April 2023. Retrieved 30 August 2023.
- ↑ "Socio-Economic Indexes for Areas (SEIFA), Australia". 2021 Census. Australian Bureau of Statistics. 27 April 2023. Retrieved 30 August 2023.