Related Research Articles

Interstellar travel is the hypothetical travel of spacecraft between star systems. Due to the vast distances between the Solar System and nearby stars, interstellar travel is not practicable with current propulsion technologies.

Interplanetary spaceflight or interplanetary travel is the crewed or uncrewed travel between stars and planets, usually within a single planetary system. In practice, spaceflights of this type are confined to travel between the planets of the Solar System. Uncrewed space probes have flown to all the observed planets in the Solar System as well as to dwarf planets Pluto and Ceres, and several asteroids. Orbiters and landers return more information than fly-by missions. Crewed flights have landed on the Moon and have been planned, from time to time, for Mars, Venus and Mercury. While many scientists appreciate the knowledge value that uncrewed flights provide, the value of crewed missions is more controversial. Science fiction writers propose a number of benefits, including the mining of asteroids, access to solar power, and room for colonization in the event of an Earth catastrophe.

Spacecraft propulsion is any method used to accelerate spacecraft and artificial satellites. In-space propulsion exclusively deals with propulsion systems used in the vacuum of space and should not be confused with space launch or atmospheric entry.

Voyager 2 is a space probe launched by NASA on August 20, 1977, as a part of the Voyager program. It was launched on a trajectory towards the gas giants Jupiter and Saturn and enabled further encounters with the ice giants Uranus and Neptune. It remains the only spacecraft to have visited either of the ice giant planets, and was the third of five spacecraft to achieve Solar escape velocity, which allowed it to leave the Solar System. Launched 16 days before its twin Voyager 1, the primary mission of the spacecraft was to study the outer planets and its extended mission is to study interstellar space beyond the Sun's heliosphere.

The Voyager program is an American scientific program that employs two interstellar probes, Voyager 1 and Voyager 2. They were launched in 1977 to take advantage of a favorable planetary alignment to explore the two gas giants Jupiter and Saturn and potentially also the ice giants, Uranus and Neptune - to fly near them while collecting data for transmission back to Earth. After Voyager 1 successfully completed its flyby of Saturn and its moon Titan, it was decided to send Voyager 2 on flybys of Uranus and Neptune.

The Pioneer Venus project was part of the Pioneer program consisting of two spacecraft, the Pioneer Venus Orbiter and the Pioneer Venus Multiprobe, launched to Venus in 1978. The program was managed by NASA's Ames Research Center.
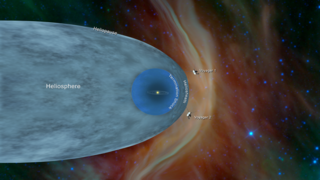
The heliosphere is the magnetosphere, astrosphere, and outermost atmospheric layer of the Sun. It takes the shape of a vast, tailed bubble-like region of space. In plasma physics terms, it is the cavity formed by the Sun in the surrounding interstellar medium. The "bubble" of the heliosphere is continuously "inflated" by plasma originating from the Sun, known as the solar wind. Outside the heliosphere, this solar plasma gives way to the interstellar plasma permeating the Milky Way. As part of the interplanetary magnetic field, the heliosphere shields the Solar System from significant amounts of cosmic ionizing radiation; uncharged gamma rays are, however, not affected. Its name was likely coined by Alexander J. Dessler, who is credited with the first use of the word in the scientific literature in 1967. The scientific study of the heliosphere is heliophysics, which includes space weather and space climate.

Transition Region and Coronal Explorer was a NASA heliophysics and solar observatory designed to investigate the connections between fine-scale magnetic fields and the associated plasma structures on the Sun by providing high-resolution images and observation of the solar photosphere, the transition region, and the solar corona. A main focus of the TRACE instrument is the fine structure of coronal loops low in the solar atmosphere. TRACE is the third spacecraft in the Small Explorer program, launched on 2 April 1998, and obtained its last science image on 21 June 2010, at 23:56 UTC.

The Solar Orbiter (SolO) is a Sun-observing probe developed by the European Space Agency (ESA) with a National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) contribution. Solar Orbiter, designed to obtain detailed measurements of the inner heliosphere and the nascent solar wind, will also perform close observations of the polar regions of the Sun which is difficult to do from Earth. These observations are important in investigating how the Sun creates and controls its heliosphere.

An interstellar probe is a space probe that has left—or is expected to leave—the Solar System and enter interstellar space, which is typically defined as the region beyond the heliopause. It also refers to probes capable of reaching other star systems.

The Space Sciences Laboratory (SSL) is an Organized Research Unit (ORU) of the University of California, Berkeley. Founded in 1959, the laboratory is located in the Berkeley Hills above the university campus. It has developed and continues to develop many projects in the space sciences, including the search for extraterrestrial life (SETI@home). The laboratory have built instruments to fly on more than 100 satellites and flown more than 150 balloons to "measure electric fields, auroral x-rays, hard x-rays and gamma rays, cosmic rays and the cosmic microwave background." The lab has also built and flown two dozen rockets to measure "auroral particles, UV emissions, and solar flare nuclei." It currently has projects categorized into planetary projects, geospace projects, solar and heliophysics projects, astrophysics and exoplanets projects, which are accompanied by a missions operations system, an engineering division and an information lab.

International Ultraviolet Explorer, was the first space observatory primarily designed to take ultraviolet (UV) electromagnetic spectrum. The satellite was a collaborative project between NASA, the United Kingdom's Science and Engineering Research Council and the European Space Agency (ESA), formerly European Space Research Organisation (ESRO). The mission was first proposed in early 1964, by a group of scientists in the United Kingdom, and was launched on 26 January 1978, 17:36:00 UTC aboard a NASA Thor-Delta 2914 launch vehicle. The mission lifetime was initially set for 3 years, but in the end, it lasted 18 years, with the satellite being shut down in 1996. The switch-off occurred for financial reasons, while the telescope was still functioning at near original efficiency.

CHIPS was a NASA Explorer program satellite. It was launched on 12 January 2003 from Vandenberg Air Force Base aboard a Delta II with the larger satellite ICESat, and had an intended mission duration of one year. CHIPS was the second of NASA's University Explorer (UNEX) mission class. It performed spectroscopy from 90 to 250 Angstrom extreme ultraviolet (EUV) light.

Interstellar Boundary Explorer is a NASA satellite in Earth orbit that uses energetic neutral atoms (ENAs) to image the interaction region between the Solar System and interstellar space. The mission is part of NASA's Small Explorer program and was launched with a Pegasus-XL launch vehicle on 19 October 2008.

Hinode, formerly Solar-B, is a Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency Solar mission with United States and United Kingdom collaboration. It is the follow-up to the Yohkoh (Solar-A) mission and it was launched on the final flight of the M-V rocket from Uchinoura Space Center, Japan on 22 September 2006 at 21:36 UTC. Initial orbit was perigee height 280 km, apogee height 686 km, inclination 98.3 degrees. Then the satellite maneuvered to the quasi-circular Sun-synchronous orbit over the day/night terminator, which allows near-continuous observation of the Sun. On 28 October 2006, the probe's instruments captured their first images.

Space research is scientific study carried out in outer space, and by studying outer space. From the use of space technology to the observable universe, space research is a wide research field. Earth science, materials science, biology, medicine, and physics all apply to the space research environment. The term includes scientific payloads at any altitude from deep space to low Earth orbit, extended to include sounding rocket research in the upper atmosphere, and high-altitude balloons.

EQUULEUS is a nanosatellite of the 6U CubeSat format that will measure the distribution of plasma that surrounds the Earth (plasmasphere) to help scientists understand the radiation environment in that region. It will also demonstrate low-thrust trajectory control techniques, such as multiple lunar flybys, within the Earth-Moon region using water steam as propellant. The spacecraft was designed and developed jointly by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) and the University of Tokyo.
NASA's Solar Terrestrial Probes program (STP) is a series of missions focused on studying the Sun-Earth system. It is part of NASA's Heliophysics Science Division within the Science Mission Directorate.

SOLRAD 4 was a solar X-rays, ultraviolet, and electronic surveillance satellite. Developed by the United States Navy's United States Naval Research Laboratory (USNRL), it was the fourth in both the SOLRAD and the GRAB programs.
References
- 1 2 Hatfield, Miles (2021-04-15). "SHIELDS Up! NASA Rocket to Survey Our Solar System's Windshield". NASA. Retrieved 2021-12-18.
- ↑ Nikzad, S. (2019-12-01). "High Performance Ultraviolet Detectors for Suborbital, CubeSat, and Flagship Missions". AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts. 2019: P43G–3530. Bibcode:2019AGUFM.P43G3530N.
- ↑ Elizabeth Howell (2021-04-20). "Small NASA rocket will study boundary of interstellar space". Space.com. Retrieved 2021-12-18.