
A bacteriophage, also known informally as a phage, is a virus that infects and replicates within bacteria and archaea. The term was derived from "bacteria" and the Greek φαγεῖν, meaning "to devour". Bacteriophages are composed of proteins that encapsulate a DNA or RNA genome, and may have structures that are either simple or elaborate. Their genomes may encode as few as four genes and as many as hundreds of genes. Phages replicate within the bacterium following the injection of their genome into its cytoplasm.

Streptococcus is a genus of gram-positive coccus or spherical bacteria that belongs to the family Streptococcaceae, within the order Lactobacillales, in the phylum Bacillota. Cell division in streptococci occurs along a single axis, thus when growing they tend to form pairs or chains, which may appear bent or twisted. This differs from staphylococci, which divide along multiple axes, thereby generating irregular, grape-like clusters of cells. Most streptococci are oxidase-negative and catalase-negative, and many are facultative anaerobes.

Escherichia virus T4 is a species of bacteriophages that infect Escherichia coli bacteria. It is a double-stranded DNA virus in the subfamily Tevenvirinae of the family Straboviridae. T4 is capable of undergoing only a lytic life cycle and not the lysogenic life cycle. The species was formerly named T-even bacteriophage, a name which also encompasses, among other strains, Enterobacteria phage T2, Enterobacteria phage T4 and Enterobacteria phage T6.
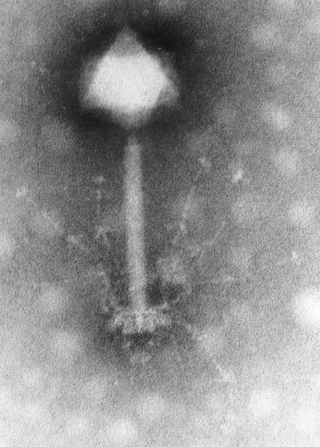
Myoviridae was a family of bacteriophages in the order Caudovirales. The family Myoviridae and order Caudovirales have now been abolished, with the term myovirus now used to refer to the morphology of viruses in this former family. Bacteria and archaea serve as natural hosts. There were 625 species in this family, assigned to eight subfamilies and 217 genera.

Podoviridae was a family of bacteriophage in the order Caudovirales often associated with T-7 like phages. The family and order Caudoviraleshave now been abolished, with the term podovirus now used to refer to the morphology of viruses in this former family. There were 130 species in this family, assigned to 3 subfamilies and 52 genera. This family was characterized by having very short, noncontractile tails. Many former phages in the former family Podoviriade are now classified in the Autographiviridae

Filamentous bacteriophages are a family of viruses (Inoviridae) that infect bacteria, or bacteriophages. They are named for their filamentous shape, a worm-like chain, about 6 nm in diameter and about 1000-2000 nm long. This distinctive shape reflects their method of replication: the coat of the virion comprises five types of viral protein, which are located in the inner membrane of the host bacterium during phage assembly, and these proteins are added to the nascent virion's DNA as it is extruded through the membrane. The simplicity of filamentous phages makes them an appealing model organism for research in molecular biology, and they have also shown promise as tools in nanotechnology and immunology.

Cystovirus is a genus of double-stranded RNA viruses which infects bacteria. It is the only genus in the family Cystoviridae. The name of the group cysto derives from Greek kystis which means bladder or sack. There are seven species in this genus.

Streptococcus mutans is a facultatively anaerobic, gram-positive coccus commonly found in the human oral cavity and is a significant contributor to tooth decay. It is part of the "streptococci", an informal general name for all species in the genus Streptococcus. The microbe was first described by James Kilian Clarke in 1924.

Lysogeny, or the lysogenic cycle, is one of two cycles of viral reproduction. Lysogeny is characterized by integration of the bacteriophage nucleic acid into the host bacterium's genome or formation of a circular replicon in the bacterial cytoplasm. In this condition the bacterium continues to live and reproduce normally, while the bacteriophage lies in a dormant state in the host cell. The genetic material of the bacteriophage, called a prophage, can be transmitted to daughter cells at each subsequent cell division, and later events can release it, causing proliferation of new phages via the lytic cycle.

Bacteriophage T7 is a bacteriophage, a virus that infects bacteria. It infects most strains of Escherichia coli and relies on these hosts to propagate. Bacteriophage T7 has a lytic life cycle, meaning that it destroys the cell it infects. It also possesses several properties that make it an ideal phage for experimentation: its purification and concentration have produced consistent values in chemical analyses; it can be rendered noninfectious by exposure to UV light; and it can be used in phage display to clone RNA binding proteins.
A Bacillus phage is a member of a group of bacteriophages known to have bacteria in the genus Bacillus as host species. These bacteriophages have been found to belong to the families Myoviridae, Siphoviridae, Podoviridae, or Tectiviridae. The genus Bacillus includes the model organism, B. subtilis, and two widely known human pathogens, B. anthracis and B. cereus. Other strains of Bacillus bacteria that phage are known to infect include B. megaterium, B. mycoides, B. pseudomycoides, B. thuringiensis, and B. weihenstephanensis. More than 1,455 bacillus phage have been discovered from many different environments and areas around the world. Only 164 of these phages have been completely sequenced as of December 16, 2021.

Cyanophages are viruses that infect cyanobacteria, also known as Cyanophyta or blue-green algae. Cyanobacteria are a phylum of bacteria that obtain their energy through the process of photosynthesis. Although cyanobacteria metabolize photoautotrophically like eukaryotic plants, they have prokaryotic cell structure. Cyanophages can be found in both freshwater and marine environments. Marine and freshwater cyanophages have icosahedral heads, which contain double-stranded DNA, attached to a tail by connector proteins. The size of the head and tail vary among species of cyanophages. Cyanophages infect a wide range of cyanobacteria and are key regulators of the cyanobacterial populations in aquatic environments, and may aid in the prevention of cyanobacterial blooms in freshwater and marine ecosystems. These blooms can pose a danger to humans and other animals, particularly in eutrophic freshwater lakes. Infection by these viruses is highly prevalent in cells belonging to Synechococcus spp. in marine environments, where up to 5% of cells belonging to marine cyanobacterial cells have been reported to contain mature phage particles.

Corticovirus is a genus of viruses in the family Corticoviridae. Corticoviruses are bacteriophages; that is, their natural hosts are bacteria. The genus contains two species. The name is derived from Latin cortex, corticis. However, prophages closely related to PM2 are abundant in the genomes of aquatic bacteria, suggesting that the ecological importance of corticoviruses might be underestimated. Bacteriophage PM2 was first described in 1968 after isolation from seawater sampled from the coast of Chile.

Autographiviridae is a family of viruses in the order Caudovirales. Bacteria serve as natural hosts. There are 373 species in this family, assigned to 9 subfamilies and 133 genera.
Phikmvvirus is a genus of viruses that infect bacteria. There are currently 16 species in this genus including the type species Pseudomonas virus phiKMV. Bacteriophage phiKMV and its relatives are known to be highly virulent phages, producing large clear plaques on a susceptible host. The only reported exception is phage LKA1, which yields small plaques surrounded by a halo. While all other P. aeruginosa-specific phikmvviruses use the Type IV pili as primary receptor, LKA1 particles attach to the bacterial lipopolysaccharide layer.
Rauchvirus is a genus of viruses in the order Caudovirales, in the family Podoviridae. Bacteria serve as natural hosts. The genus contains only one species: Bordetella virus BPP1.
Enquatrovirus is a genus of bacteriophages in the order Caudovirales, in the family Podoviridae. Bacteria serve as natural hosts. There is currently only one species in this genus: the type species Escherichia virus N4.
Bacteriophage T12 is a bacteriophage that infects Streptococcus pyogenes bacteria. It is a proposed species of the family Siphoviridae in the order Caudovirales also known as tailed viruses. It converts a harmless strain of bacteria into a virulent strain. It carries the speA gene which codes for erythrogenic toxin A. speA is also known as streptococcal pyogenic exotoxin A, scarlet fever toxin A, or even scarlatinal toxin. Note that the name of the gene "speA" is italicized; the name of the toxin "speA" is not italicized. Erythrogenic toxin A converts a harmless, non-virulent strain of Streptococcus pyogenes to a virulent strain through lysogeny, a life cycle which is characterized by the ability of the genome to become a part of the host cell and be stably maintained there for generations. Phages with a lysogenic life cycle are also called temperate phages. Bacteriophage T12, proposed member of family Siphoviridae including related speA-carrying bacteriophages, is also a prototypic phage for all the speA-carrying phages of Streptococcus pyogenes, meaning that its genome is the prototype for the genomes of all such phages of S. pyogenes. It is the main suspect as the cause of scarlet fever, an infectious disease that affects small children.

Ff phages is a group of almost identical filamentous phage including phages f1, fd, M13 and ZJ/2, which infect bacteria bearing the F fertility factor. The virion is a flexible filament measuring about 6 by 900 nm, comprising a cylindrical protein tube protecting a single-stranded circular DNA molecule at its core. The phage codes for only 11 gene products, and is one of the simplest viruses known. It has been widely used to study fundamental aspects of molecular biology. George Smith and Greg Winter used f1 and fd for their work on phage display for which they were awarded a share of the 2018 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Early experiments on Ff phages used M13 to identify gene functions, and M13 was also developed as a cloning vehicle, so the name M13 is sometimes used as an informal synonym for the whole group of Ff phages.
Mycobacterium virus D29 (D29) is a cluster A mycobacteriophage belonging to the Siphoviridae family of viruses, it was discovered in 1954 by S. Froman. D29 is notable for its ability to infect M. tuberculosis. D29 is a double stranded DNA mycobacteriophage. It is a lytic phage, this means that D29 takes the lytic pathway of infection instead of the lysogenic pathway of infection. There are no human associated diseases associated with mycobacterium virus D29.













