Further reading
- Chapter 5: The Nuclear Industry's Experience with Standardization, Nuclear Powerplant Standardization: Light Water Reactors, April 1981, Congressional Office of Technology Assessment, NTIS order #PB81-213589
SNUPPS is an acronym standing for Standardized Nuclear Unit Power Plant System. It refers to a 4-loop PWR reactor design produced by Westinghouse in the 1970s. The design was developed for four USA utilities, and plants were built at Callaway and Wolf Creek. The UK plant at Sizewell B was also based on SNUPPS but with significant modifications, such as a passive Emergency Boration System.

A nuclear reactor is a device used to initiate and control a fission nuclear chain reaction or nuclear fusion reactions. Nuclear reactors are used at nuclear power plants for electricity generation and in nuclear marine propulsion. Heat from nuclear fission is passed to a working fluid, which in turn runs through steam turbines. These either drive a ship's propellers or turn electrical generators' shafts. Nuclear generated steam in principle can be used for industrial process heat or for district heating. Some reactors are used to produce isotopes for medical and industrial use, or for production of weapons-grade plutonium. As of 2022, the International Atomic Energy Agency reports there are 422 nuclear power reactors and 223 nuclear research reactors in operation around the world.


A pressurized water reactor (PWR) is a type of light-water nuclear reactor. PWRs constitute the large majority of the world's nuclear power plants. In a PWR, the primary coolant (water) is pumped under high pressure to the reactor core where it is heated by the energy released by the fission of atoms. The heated, high pressure water then flows to a steam generator, where it transfers its thermal energy to lower pressure water of a secondary system where steam is generated. The steam then drives turbines, which spin an electric generator. In contrast to a boiling water reactor (BWR), pressure in the primary coolant loop prevents the water from boiling within the reactor. All light-water reactors use ordinary water as both coolant and neutron moderator. Most use anywhere from two to four vertically mounted steam generators; VVER reactors use horizontal steam generators.

A boiling water reactor (BWR) is a type of light water nuclear reactor used for the generation of electrical power. It is the second most common type of electricity-generating nuclear reactor after the pressurized water reactor (PWR), which is also a type of light water nuclear reactor.

A nuclear meltdown is a severe nuclear reactor accident that results in core damage from overheating. The term nuclear meltdown is not officially defined by the International Atomic Energy Agency or by the United States Nuclear Regulatory Commission. It has been defined to mean the accidental melting of the core of a nuclear reactor, however, and is in common usage a reference to the core's either complete or partial collapse.

A nuclear power plant (NPP) is a thermal power station in which the heat source is a nuclear reactor. As is typical of thermal power stations, heat is used to generate steam that drives a steam turbine connected to a generator that produces electricity. As of September 2023, the International Atomic Energy Agency reported there were 410 nuclear power reactors in operation in 31 countries around the world, and 57 nuclear power reactors under construction.

The Callaway Plant is a nuclear power plant located on 2,767 acres (1,120 ha) in Callaway County, Missouri, near Fulton, Missouri. It began operating on December 19, 1984. The plant, which is the state's only commercial nuclear unit, has one 1,190-megawatt Westinghouse four-loop pressurized water reactor and a General Electric turbine-generator. It is owned by the Ameren Corporation and operated by subsidiary Ameren Missouri. It is one of several Westinghouse reactors built to a design called Standard Nuclear Unit Power Plant System, or SNUPPS.

The Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC) is India's premier nuclear research facility, headquartered in Trombay, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India. It was founded by Homi Jehangir Bhabha as the Atomic Energy Establishment, Trombay (AEET) in January 1954 as a multidisciplinary research program essential for India's nuclear program. It operates under the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE), which is directly overseen by the Prime Minister of India.

The advanced boiling water reactor (ABWR) is a Generation III boiling water reactor. The ABWR is currently offered by GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy (GEH) and Toshiba. The ABWR generates electrical power by using steam to power a turbine connected to a generator; the steam is boiled from water using heat generated by fission reactions within nuclear fuel. Kashiwazaki-Kariwa unit 6 is considered the first Generation III reactor in the world.

The AP1000 is a nuclear power plant designed and sold by Westinghouse Electric Company. The plant is a pressurized water reactor with improved use of passive nuclear safety and many design features intended to lower its capital cost and improve its economics.

The water-water energetic reactor (WWER), or VVER is a series of pressurized water reactor designs originally developed in the Soviet Union, and now Russia, by OKB Gidropress. The idea of such a reactor was proposed at the Kurchatov Institute by Savely Moiseevich Feinberg. VVER were originally developed before the 1970s, and have been continually updated. As a result, the name VVER is associated with a wide variety of reactor designs spanning from generation I reactors to modern generation III+ reactor designs. Power output ranges from 70 to 1300 MWe, with designs of up to 1700 MWe in development. The first prototype VVER-210 was built at the Novovoronezh Nuclear Power Plant.

Generation III reactors, or Gen III reactors, are a class of nuclear reactors designed to succeed Generation II reactors, incorporating evolutionary improvements in design. These include improved fuel technology, higher thermal efficiency, significantly enhanced safety systems, and standardized designs intended to reduce maintenance and capital costs. They are promoted by the Generation IV International Forum (GIF).

The Economic Simplified Boiling Water Reactor (ESBWR) is a passively safe generation III+ reactor design derived from its predecessor, the Simplified Boiling Water Reactor (SBWR) and from the Advanced Boiling Water Reactor (ABWR). All are designs by GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy (GEH), and are based on previous Boiling Water Reactor designs.

Since the mid 1980s, the largest source of electricity in France has been nuclear power, with a generation of 379.5 TWh in 2019 and a total electricity production of 537.7 TWh. In 2018, the nuclear share was 71.67%, the highest percentage in the world.
The Mitsubishi advanced pressurized water reactor (APWR) is a generation III nuclear reactor design developed by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) based on pressurized water reactor technology. It features several design enhancements including a neutron reflector, improved efficiency and improved safety systems. It has safety features advanced over the last generation, including a combination of passive and active systems. None are currently under construction.
The three primary objectives of nuclear reactor safety systems as defined by the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission are to shut down the reactor, maintain it in a shutdown condition and prevent the release of radioactive material.

Small modular reactors (SMRs) are a proposed class of nuclear fission reactors, smaller than conventional nuclear reactors, which can be built in one location, then shipped, commissioned, and operated at a separate site. The term SMR refers to the size, capacity and modular construction only, not to the reactor type and the nuclear process which is applied. Designs range from scaled down versions of existing designs to generation IV designs. Both thermal-neutron reactors and fast-neutron reactors have been proposed, along with molten salt and gas cooled reactor models.
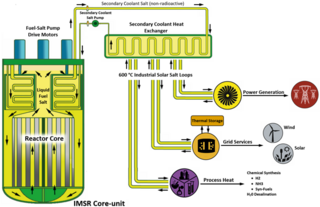
The Integral Molten Salt Reactor (IMSR) is a nuclear power plant design targeted at developing a commercial product for the small modular reactor (SMR) market. It employs molten salt reactor technology which is being developed by the Canadian company Terrestrial Energy. It is based closely on the denatured molten salt reactor (DMSR), a reactor design from Oak Ridge National Laboratory. It also incorporates elements found in the SmAHTR, a later design from the same laboratory. The IMSR belongs to the DMSR class of molten salt reactors (MSR) and hence is a "burner" reactor that employs a liquid fuel rather than a conventional solid fuel; this liquid contains the nuclear fuel and also serves as primary coolant.

The IPHWR-700 is an Indian pressurized heavy-water reactor designed by the NPCIL. It is a Generation III reactor developed from earlier CANDU based 220 MW and 540 MW designs. It can generate 700 MW of electricity. Currently there are 5 units under construction and 10 more units planned, at a cost of ₹1.05 lakh crore (US$13 billion).

The IPHWR is a class of Indian pressurized heavy-water reactors designed by the Bhabha Atomic Research Centre. The baseline 220 MWe design was developed from the CANDU based RAPS-1 and RAPS-2 reactors built at Rawatbhata, Rajasthan. Later the design was based on VVER technology which was scaled to 540 MW and 700 MW designs. Currently there are 17 units of various types operational at various locations in India.