Related Research Articles

An exon is any part of a gene that will form a part of the final mature RNA produced by that gene after introns have been removed by RNA splicing. The term exon refers to both the DNA sequence within a gene and to the corresponding sequence in RNA transcripts. In RNA splicing, introns are removed and exons are covalently joined to one another as part of generating the mature RNA. Just as the entire set of genes for a species constitutes the genome, the entire set of exons constitutes the exome.

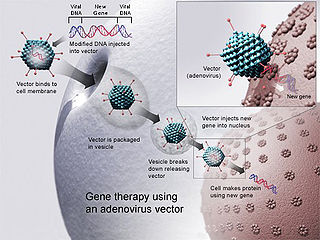
Gene therapy is a medical technology that aims to produce a therapeutic effect through the manipulation of gene expression or through altering the biological properties of living cells.

Interferons are a group of signaling proteins made and released by host cells in response to the presence of several viruses. In a typical scenario, a virus-infected cell will release interferons causing nearby cells to heighten their anti-viral defenses.

An oncogene is a gene that has the potential to cause cancer. In tumor cells, these genes are often mutated, or expressed at high levels.

Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic disorder inherited in an autosomal recessive manner that impairs the normal clearance of mucus from the lungs, which facilitates the colonization and infection of the lungs by bacteria, notably Staphylococcus aureus. CF is a rare genetic disorder that affects mostly the lungs, but also the pancreas, liver, kidneys, and intestine. The hallmark feature of CF is the accumulation of thick mucus in different organs. Long-term issues include difficulty breathing and coughing up mucus as a result of frequent lung infections. Other signs and symptoms may include sinus infections, poor growth, fatty stool, clubbing of the fingers and toes, and infertility in most males. Different people may have different degrees of symptoms.

Small interfering RNA (siRNA), sometimes known as short interfering RNA or silencing RNA, is a class of double-stranded RNA at first non-coding RNA molecules, typically 20–24 base pairs in length, similar to miRNA, and operating within the RNA interference (RNAi) pathway. It interferes with the expression of specific genes with complementary nucleotide sequences by degrading mRNA after transcription, preventing translation. It was discovered in 1998, by Andrew Fire at Carnegie Institution for Science in Washington DC and Craig Mello at University of Massachusetts in Worcester.
Human genetic enhancement or human genetic engineering refers to human enhancement by means of a genetic modification. This could be done in order to cure diseases, prevent the possibility of getting a particular disease, to improve athlete performance in sporting events, or to change physical appearance, metabolism, and even improve physical capabilities and mental faculties such as memory and intelligence. These genetic enhancements may or may not be done in such a way that the change is heritable.

Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a severe type of muscular dystrophy predominantly affecting boys. The onset of muscle weakness typically begins around age four, with rapid progression. Initially, muscle loss occurs in the thighs and pelvis, extending to the arms, which can lead to difficulties in standing up. By the age of 12, most individuals with Duchenne muscular dystrophy are unable to walk. Affected muscles may appear larger due to an increase in fat content, and scoliosis is common. Some individuals may experience intellectual disability, and females carrying a single copy of the mutated gene may show mild symptoms.

Glioblastoma, previously known as glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), is the most aggressive and most common type of cancer that originates in the brain, and has a very poor prognosis for survival. Initial signs and symptoms of glioblastoma are nonspecific. They may include headaches, personality changes, nausea, and symptoms similar to those of a stroke. Symptoms often worsen rapidly and may progress to unconsciousness.

Thymidine kinase is an enzyme, a phosphotransferase : 2'-deoxythymidine kinase, ATP-thymidine 5'-phosphotransferase, EC 2.7.1.21. It can be found in most living cells. It is present in two forms in mammalian cells, TK1 and TK2. Certain viruses also have genetic information for expression of viral thymidine kinases. Thymidine kinase catalyzes the reaction:

Adeno-associated viruses (AAV) are small viruses that infect humans and some other primate species. They belong to the genus Dependoparvovirus, which in turn belongs to the family Parvoviridae. They are small replication-defective, nonenveloped viruses and have linear single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) genome of approximately 4.8 kilobases (kb).

Choroideremia is a rare, X-linked recessive form of hereditary retinal degeneration that affects roughly 1 in 50,000 males. The disease causes a gradual loss of vision, starting with childhood night blindness, followed by peripheral vision loss and progressing to loss of central vision later in life. Progression continues throughout the individual's life, but both the rate of change and the degree of visual loss are variable among those affected, even within the same family.
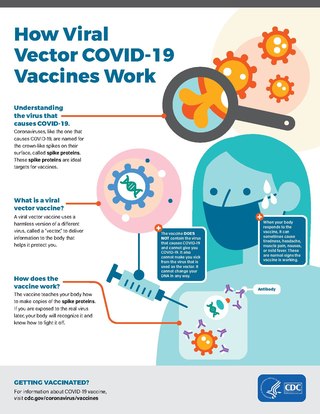
Viral vectors are modified viruses designed to deliver genetic material into cells. This process can be performed inside an organism or in cell culture. Viral vectors have widespread applications in basic research, agriculture, and medicine.

KRAS is a gene that provides instructions for making a protein called K-Ras, a part of the RAS/MAPK pathway. The protein relays signals from outside the cell to the cell's nucleus. These signals instruct the cell to grow and divide (proliferate) or to mature and take on specialized functions (differentiate). It is called KRAS because it was first identified as a viral oncogene in the KirstenRAt Sarcoma virus. The oncogene identified was derived from a cellular genome, so KRAS, when found in a cellular genome, is called a proto-oncogene.

40S ribosomal protein S27, also known as metallopan-stimulin 1 or MPS-1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RPS27 gene. Metallopanstimulin is a zinc finger protein proposed to be involved DNA repair as well as oncogenesis.

Otoferlin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the OTOF gene. It is involved in vesicle membrane fusion, and mutations in the OTOF gene are associated with a genetic form of deafness.

Nelotanserin is a drug developed by Arena Pharmaceuticals which acts as an inverse agonist on the serotonin receptor subtype 5-HT2A and was under development for the treatment of insomnia. It was shown to be effective and well tolerated in clinical trials, but development was halted in December 2008 because the substance did not meet the trial's effectiveness endpoints. Research continues on newer analogues which may potentially be more successful.

Interferon lambda 3 encodes the IFNL3 protein. IFNL3 was formerly named IL28B, but the Human Genome Organization Gene Nomenclature Committee renamed this gene in 2013 while assigning a name to the then newly discovered IFNL4 gene. Together with IFNL1 and IFNL2, these genes lie in a cluster on chromosomal region 19q13. IFNL3 shares ~96% amino-acid identity with IFNL2, ~80% identity with IFNL1 and ~30% identity with IFNL4.
Gene therapy for osteoarthritis is the application of gene therapy to treat osteoarthritis (OA). Unlike pharmacological treatments which are administered locally or systemically as a series of interventions, gene therapy aims to establish sustained therapeutic effect after a single, local injection.

CRISPR gene editing standing for "Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats" is a genetic engineering technique in molecular biology by which the genomes of living organisms may be modified. It is based on a simplified version of the bacterial CRISPR-Cas9 antiviral defense system. By delivering the Cas9 nuclease complexed with a synthetic guide RNA (gRNA) into a cell, the cell's genome can be cut at a desired location, allowing existing genes to be removed and/or new ones added in vivo.
References
- ↑ Costa-Verdera, Helena; Collaud, Fanny; Riling, Christopher R.; Sellier, Pauline; Nordin, Jayme M. L.; Preston, G. Michael; Cagin, Umut; Fabregue, Julien; Barral, Simon; Moya-Nilges, Maryse; Krijnse-Locker, Jacomina; van Wittenberghe, Laetitia; Daniele, Natalie; Gjata, Bernard; Cosette, Jeremie; Abad, Catalina; Simon-Sola, Marcelo; Charles, Severine; Li, Mathew; Crosariol, Marco; Antrilli, Tom; Quinn, William J.; Gross, David A.; Boyer, Olivier; Anguela, Xavier M.; Armour, Sean M.; Colella, Pasqualina; Ronzitti, Giuseppe; Mingozzi, Federico (4 November 2021). "Hepatic expression of GAA results in enhanced enzyme bioavailability in mice and non-human primates". Nature Communications. 12 (1): 6393. Bibcode:2021NatCo..12.6393C. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-26744-4 . ISSN 2041-1723. PMC 8568898 . PMID 34737297.
- ↑ Philippidis, Alex (1 March 2023). "Magenta Halts Development, Pursues Strategic Alternatives After Patient Death". Human Gene Therapy. 34 (5–6): 177–179. doi:10.1089/hum.2023.29236.bfs. PMID 36944087. S2CID 257664969.