CAD is a commonly used acronym for computer-aided design.

The XY sex-determination system is the sex-determination system found in humans, most other mammals, some insects (Drosophila), some snakes, and some plants (Ginkgo). In this system, the sex of an individual is determined by a pair of sex chromosomes. Females have two of the same kind of sex chromosome (XX), and are called the homogametic sex. Males have two different kinds of sex chromosomes (XY), and are called the heterogametic sex.

A sex-determination system is a biological system that determines the development of sexual characteristics in an organism. Most organisms that create their offspring using sexual reproduction have two sexes. Occasionally, there are hermaphrodites in place of one or both sexes. There are also some species that are only one sex due to parthenogenesis, the act of a female reproducing without fertilization.

The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes (allosomes) in mammals, including humans, and many other animals. The other is the X chromosome. Y is normally the sex-determining chromosome in many species, since it is the presence or absence of Y that typically determines the male or female sex of offspring produced in sexual reproduction. In mammals, the Y chromosome contains the gene SRY, which by default triggers male development. The DNA in the human Y chromosome is composed of about 59 million base pairs. The Y chromosome is passed only from father to son. With a 30% difference between humans and chimpanzees, the Y chromosome is one of the fastest-evolving parts of the human genome. To date, over 200 Y-linked genes have been identified. All Y-linked genes are expressed and hemizygous except in the cases of aneuploidy such as XYY syndrome or XXYY syndrome.
Ang, ANG or Äng may refer to:

Shoeburyness railway station is the eastern terminus of the London, Tilbury and Southend Railway line, serving the town of Shoeburyness, Essex. It is 39 miles 40 chains (63.57 km) down the main line from London Fenchurch Street via Basildon; the preceding station is Thorpe Bay. Its three-letter station code is SRY.
BMH is a three letter abbreviation that could mean:

46,XX testicular disorders of sex development describes a condition in which individuals with two X chromosomes in each cell, the pattern typically found in females, have a male phenotype appearance. 46,XX testicular disorders of sex development may also be named 46,XX sex reversal, nonsyndromic 46,XX testicular DSD, XX male syndrome, and XX sex reversal.

Testis-determining factor (TDF), also known as sex-determining region Y (SRY) protein, is a DNA-binding protein encoded by the SRY gene that is responsible for the initiation of male sex determination in humans. SRY is an intronless sex-determining gene on the Y chromosome in therians ; mutations in this gene lead to a range of disorders of sex development (DSD) with varying effects on an individual's phenotype and genotype.
The Southern Railway of British Columbia, branded as SRY Rail Link is a Canadian short line railway operating in the southwestern British Columbia. The main facility is the port at Annacis Island with major import of cars, export of forestry products, and other shipments. The railway has interconnections with three Class I railroads, including Canadian Pacific (CP), Canadian National (CN) and Burlington Northern Santa Fe (BNSF). It operates a fleet of 29 locomotives, mostly consisting of EMD GP-9 & SW900 locomotives. It also rosters 5 unique Ex. Canadian National Railway GMD-1 locomotives, and also runs 3 SD38-2 locomotives, and 1 SD38AC. The railroad also operates a fleet 2,000 rail cars, hauling approximately 70,000 carloads per year. It operates around 123 miles (198 km) of track, 62 miles (100 km) of which is mainline track.
WRX is a three-letter abbreviation that may refer to:
XX male syndrome, also known as De la Chapelle syndrome, is a rare congenital intersex condition where an individual with a female genotype has phenotypically male characteristics that can vary among cases. In 90 percent of these individuals, the syndrome is caused by the Y chromosome's SRY gene, which triggers male reproductive development, being accidentally included in the crossing over of genetic information that takes place between the pseudoautosomal regions of the X and Y chromosomes during meiosis in the father. When the X with the SRY gene combines with a normal X from the mother during fertilization, the result is an XX male. Less common are SRY-negative XX males, which can be caused by a mutation in an autosomal or X chromosomal gene. The masculinization of XX males is variable.
SOX genes encode a family of transcription factors that bind to the minor groove in DNA, and belong to a super-family of genes characterized by a homologous sequence called the HMG-box. This HMG box is a DNA binding domain that is highly conserved throughout eukaryotic species. Homologues have been identified in insects, nematodes, amphibians, reptiles, birds and a range of mammals. However, HMG boxes can be very diverse in nature, with only a few amino acids being conserved between species.
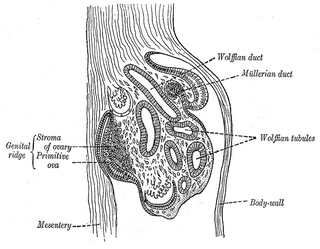
In embryology, the gonadal ridge is the precursor to the gonads. The gonadal ridge initially consists mainly of mesenchyme and cells of underlying mesonephric origin. Once oogonia enter this area they attempt to associate with these somatic cells. Development proceeds and the oogonia become fully surrounded by a layer of cells.
High-Mobility Group or HMG is a group of chromosomal proteins that are involved in the regulation of DNA-dependent processes such as transcription, replication, recombination, and DNA repair.

A sex chromosome, is a chromosome that differs from an ordinary autosome in form, size, and behavior. The human sex chromosomes, a typical pair of mammal allosomes, determine the sex of an individual created in sexual reproduction. Autosomes differ from allosomes because autosomes appear in pairs whose members have the same form but differ from other pairs in a diploid cell, whereas members of an allosome pair may differ from one another and thereby determine sex.
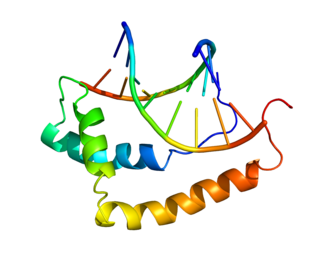
Transcription factor SOX-9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SOX9 gene.

Transcription factor SOX-21 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SOX21 gene. It is a member of the Sox gene family of transcription factors.

A station code is an abbreviation used on railways for railway stations. The codes are most used internally in the business, but can be seen at railway traffic signs and in some time tables.










