Related Research Articles

The gravitational constant is an empirical physical constant involved in the calculation of gravitational effects in Sir Isaac Newton's law of universal gravitation and in Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity. It is also known as the universal gravitational constant, the Newtonian constant of gravitation, or the Cavendish gravitational constant, denoted by the capital letter G.

The Cavendish Laboratory is the Department of Physics at the University of Cambridge, and is part of the School of Physical Sciences. The laboratory was opened in 1874 on the New Museums Site as a laboratory for experimental physics and is named after the British chemist and physicist Henry Cavendish. The laboratory has had a huge influence on research in the disciplines of physics and biology.

Otto Robert Frisch was an Austrian-born British physicist who worked on nuclear physics. With Otto Stern and Immanuel Estermann he first measured the magnetic moment of the proton. With Lise Meitner he advanced the first theoretical explanation of nuclear fission and first experimentally detected the fission by-products. Later, with his collaborator Rudolf Peierls he designed the first theoretical mechanism for the detonation of an atomic bomb in 1940.
In physics, a time projection chamber (TPC) is a type of particle detector that uses a combination of electric fields and magnetic fields together with a sensitive volume of gas or liquid to perform a three-dimensional reconstruction of a particle trajectory or interaction.

The Frisch–Peierls memorandum was the first technical exposition of a practical nuclear weapon. It was written by expatriate German-Jewish physicists Otto Frisch and Rudolf Peierls in March 1940 while they were both working for Mark Oliphant at the University of Birmingham in Britain during World War II.
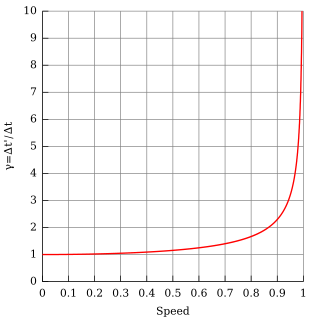
Time dilation as predicted by special relativity is often verified by means of particle lifetime experiments. According to special relativity, the rate of a clock C traveling between two synchronized laboratory clocks A and B, as seen by a laboratory observer, is slowed relative to the laboratory clock rates. Since any periodic process can be considered a clock, the lifetimes of unstable particles such as muons must also be affected, so that moving muons should have a longer lifetime than resting ones. A variety of experiments confirming this effect have been performed both in the atmosphere and in particle accelerators. Another type of time dilation experiments is the group of Ives–Stilwell experiments measuring the relativistic Doppler effect.

Neutron detection is the effective detection of neutrons entering a well-positioned detector. There are two key aspects to effective neutron detection: hardware and software. Detection hardware refers to the kind of neutron detector used and to the electronics used in the detection setup. Further, the hardware setup also defines key experimental parameters, such as source-detector distance, solid angle and detector shielding. Detection software consists of analysis tools that perform tasks such as graphical analysis to measure the number and energies of neutrons striking the detector.
Haroon Ahmed FREng, is a British Pakistani scientist in specialising the fields of microelectronics and electrical engineering. He is Emeritus Professor of Microelectronics at the Cavendish Laboratory, the Physics Department of the University of Cambridge, Honorary Fellow of Corpus Christi College, Cambridge, and Fellow of the Royal Academy of Engineering.

Sir Alfred Brian Pippard, FRS, was a British physicist. He was Cavendish Professor of Physics from 1971 until 1982 and an Honorary Fellow of Clare Hall, Cambridge, of which he was the first President.

The Wendelstein 7-X reactor is an experimental stellarator built in Greifswald, Germany, by the Max Planck Institute for Plasma Physics (IPP), and completed in October 2015. Its purpose is to advance stellarator technology: though this experimental reactor will not produce electricity, it is used to evaluate the main components of a future fusion power plant; it was developed based on the predecessor Wendelstein 7-AS experimental reactor.
Eugene Theodore Booth, Jr. was an American nuclear physicist. He was a member of the historic Columbia University team which made the first demonstration of nuclear fission in the United States. During the Manhattan Project, he worked on gaseous diffusion for isotope separation. He was the director of the design, construction, and operation project for the 385-Mev synchrocyclotron at the Nevis Laboratories, the scientific director of the SCALANT Research Center, and dean of graduate studies at Stevens Institute of Technology. Booth was the scientific director of the SCALANT Research Center, in Italy.
TASSO was a particle detector at the PETRA particle accelerator at the German national laboratory DESY. The TASSO collaboration is best known for having discovered the gluon, the mediator of the strong interaction and carrier of the color charge. Four TASSO scientists, Paul Söding, Bjørn Wiik, Günter Wolf and Sau Lan Wu, were awarded the High Energy and Particle Physics Prize from the European Physical Society (EPS) in 1995. A special prize was also awarded to the TASSO collaboration, as well as the JADE, MARK J and PLUTO collaborations, in recognition of their combined work on the gluon as the "definite existence emerged gradually from the results of the TASSO collaboration and the other experiments working at PETRA, JADE, MARK J and PLUTO". TASSO took data from 1978 to 1986 and discovered the gluon in 1979.
Stopping and Range of Ions in Matter (SRIM) is a group of computer programs which calculate interactions between ions and matter; the core of SRIM is a program called Transport of Ions in Matter (TRIM). SRIM is popular in the ion implantation research and technology community, and also used widely in other branches of radiation material science.
Christine Tullis Hunter Davies is a professor of physics at the University of Glasgow.
Mark H. Shapiro is a professor, emeritus of physics at California State University, Fullerton. Shapiro holds an A.B. degree in physics from the University of California, Berkeley; and, M.S. and Ph.D. degrees in physics from the University of Pennsylvania. He received his Ph.D. from the University of Pennsylvania in 1966.
Erwin Gabathuler was a particle physicist from Northern Ireland.
The polarized targets are used as fixed targets in scattering experiments. In high energy physics they are used to study the nucleon spin structure of simple nucleons like protons, neutrons or deuterons. In deep inelastic scattering the hadron structure is probed with electrons, muons or neutrinos. Using a polarized high energy muon beam, for example, on a fixed target with polarized nucleons it is possible to probe the spin dependent part of the structure functions.
Richard John Eden was a British theoretical physicist who researched quantum field theory, nuclear theory and S-matrix theory in the 1950s and 1960s.
Alexander Wu Chao is a Taiwanese-American physicist, specializing in accelerator physics.
Henry Winston Newson was an American physical chemist and nuclear physicist, known for his research on nuclear resonances and as one of the co-inventors of the control system used in nuclear reactors.
References
- ↑ "Cambridge Physics - Sweepnik". Cambridge Physics, part of the Cavendish Laboratory Educational Outreach website for schools and the public. Archived from the original on 20 June 2006. Retrieved 16 December 2008.
- ↑ Davies, D. J. M.; Frisch, O. R.; Street, G. S. B. (1970-05-30). "Sweepnik: A fast semi-automatic track-measuring machine". Nuclear Instruments and Methods. 82: 54–60. Bibcode:1970NucIM..82...54D. doi:10.1016/0029-554X(70)90325-3. ISSN 0029-554X.
- ↑ "Cavendish Laboratory : The Sweepnik plate analyser for high energy particle tracks in about 1970". Cambridge Digital Library. Retrieved 2024-08-14.
- ↑ Davies, D J M; Street, G S B; Frisch, O R (1970). "SWEEPNIK II, an improved track measuring machine" (PDF). International Conference on Data-Handling Systems in High-Energy Physics. p. 285-292. doi:10.5170/CERN-1970-021-V-1.285.