
Amenhotep I, Amenôthes I, or Amenophis I, (,) from Ancient Greek Ἀμένωφις, additionally King Zeserkere, was the second Pharaoh of the 18th Dynasty of Egypt. His reign is generally dated from 1526 to 1506 BC. He was a son of Ahmose I and Ahmose-Nefertari, but had at least two elder brothers, Ahmose-ankh and Ahmose Sapair, and was not expected to inherit the throne. However, sometime in the eight years between Ahmose I's 17th regnal year and his death, his heir apparent died and Amenhotep became crown prince. He then acceded to the throne and ruled for about 21 years. Although his reign is poorly documented, it is possible to piece together a basic history from available evidence. He inherited the kingdom formed by his father's military conquests and maintained dominance over Nubia and the Nile Delta but probably did not attempt to maintain Egyptian power in the Levant. He continued the rebuilding of temples in Upper Egypt and revolutionized mortuary complex design by separating his tomb from his mortuary temple, setting a trend in royal funerary monuments which would persist throughout the New Kingdom. After his death, he was deified as a patron god of Deir el-Medina.

Heqamaatre Ramesses IV was the third pharaoh of the Twentieth Dynasty of the New Kingdom of Ancient Egypt. His name prior to assuming the crown was Amonhirkhopshef. He was the fifth son of Ramesses III and was appointed to the position of crown prince by the twenty-second year of his father's reign when all four of his elder brothers predeceased him. His promotion to crown prince:
is suggested by his appearance in a scene of the festival of Min at the Ramesses III temple at Karnak, which may have been completed by Year 22 [of his father's reign].

Deir el-Bahari or Dayr al-Bahri is a complex of mortuary temples and tombs located on the west bank of the Nile, opposite the city of Luxor, Egypt. This is a part of the Theban Necropolis.

Djedkare Isesi was a pharaoh, the eighth and penultimate ruler of the Fifth Dynasty of Egypt in the late 25th century to mid-24th century BC, during the Old Kingdom. Djedkare succeeded Menkauhor Kaiu and was in turn succeeded by Unas. His relations to both of these pharaohs remain uncertain, although it is often conjectured that Unas was Djedkare's son, owing to the smooth transition between the two.

Qubbet el-Hawa is a site on the western bank of the Nile, opposite Aswan. The name is derived from the dome of the tomb of an Islamic sheikh, but archaeologically, it is usually understood as referring to the site of the tombs of the officials lined up on artificial terraces below the summit of the Nile bank upon which the Islamic tomb stands.

The Autobiography of Harkhuf is a private tomb inscription from ancient Egypt. It is significant in Egyptology as one of the two most important, and the most famous, autobiographical inscriptions of Old Kingdom officials.

Neferkauhor Khuwihapi was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh of the Eighth Dynasty during the early First Intermediate Period, at a time when Egypt was possibly divided between several polities. Neferkauhor was the sixteenth and penultimate king of the Eighth Dynasty and as such would have ruled over the Memphite region. Neferkauhor reigned for little over 2 years and is one of the best attested kings of this period with eight of his decrees surviving in fragmentary condition to this day.

The National Museum of Sudan or Sudan National Museum, abbreviated SNM, is a double storied building constructed in 1955 and established as a museum in 1971. The building and its surrounding gardens house the largest and most comprehensive Nubian archaeological collection in the world including objects from the Paleolithic through to the Islamic period originating from every site of importance in the Sudan.
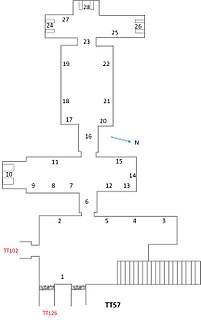
The Theban Tomb TT57 is located in Sheikh Abd el-Qurna. It forms part of the Theban Necropolis, situated on the west bank of the Nile opposite Luxor. The tomb is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian official Khaemhat, who was royal scribe and overseer of double granary, during the reign Amenhotep III. The relief decoration of the tomb is regarded as the best of New Kingdom art.

Maia was the wet nurse of the ancient Egyptian pharaoh Tutankhamun in the 14th century BC. Her rock-cut tomb was discovered in the Saqqara necropolis in 1996.

Heqaib, also Hekaib or Hekayeb, was an ancient Egyptian nomarch of the 1st nomos of Upper Egypt under king Pepi II Neferkare, towards the end of the 6th Dynasty. He was also an officer in charge of military expeditions in Nubia.
Heqaib (III) was an Ancient Egyptian local governor at Elephantine. He lived at the end of the 12th Dynasty around 1800 BC. He hold the titles governor and overseer of priests of Khnum, lord of the cataracts.

Shemay was an ancient Egyptian official and later vizier toward the end of the 8th Dynasty during the First Intermediate Period, mainly known for being the beneficiary of most of the Coptos Decrees. His career has been interpreted as a glaring sign of the extreme weakness of the central power, forced to bestow great privileges to maintain the loyalty of powerful local governors. Shemay is buried in a mudbrick mastaba just south of Coptos.

Sarenput I was an ancient Egyptian official during the reign of pharaoh Senusret I of the 12th Dynasty.

Sarenput II, also called Nubkaurenakht was an ancient Egyptian nomarch during the reign of pharaohs Senusret II and Senusret III of the 12th Dynasty.

Djefaihapi was an ancient Egyptian official during the reign of pharaoh Senusret I of the 12th Dynasty. In literature, his name is found written in many other variants such as Hepzefa, Hapidjefa, Hapdjefai, and Djefaihap.

Idy was an important Ancient Egyptian official in the Eighth Dynasty, at the beginning of the First Intermediate Period. He was the son of Shemay, who is also known from several monuments and decrees from Koptos. His mother was the king's daughter Nebet. Idy appears on many royal decrees found at Koptos. There he bears the important title of a vizier, but was also overseer of Upper Egypt and overseer of priest and count. The decrees are dated under king Neferkauhor and Neferirkare. One decree is addressed to Shemay and dates under Neferkauhor. It reports the appointment of Idy to the overseer of Upper Egypt. A second one mentions affairs in the temple of Min at Koptos. In a third decree Idy bears the titles of a vizier. In the decree, the king protects the statues and the funerary cult of Idy. The decree is dated under king Neferirkare, who was the successor of Neferkauhor. It seems that Idy took over many positions that his father hold before.
Djehutyhotep, also called Paitsy, was a Nubian official under Hatshepsut and Thutmosis III. He was chief of Teh-khet and was therefore a governor ruling a region in Lower Nubia for the Egyptian state. In the New Kingdom, Egyptian kings had conquered Lower Nubia. To secure control over the new region they appointed people of the local elite as governors. Teh-khet was a Nubian region that covered about Debeira and Serra. The local governors here formed a family, while the governor proper hold the title chief of Teh-khet. Djehutyhotep's father Ruiu was also chief of Teh-khet. His mother was called Runia. His wife Tenetnub. His brother Amenemhat was also chief of Teh-khet and followed Djehutyhotep in office.
Ruiu was a Nubian official at the beginning of the 18th Dynasty. He was chief of Teh-khet and was, therefore, a governor ruling a region in Lower Nubia for the Egyptian state. In the New Kingdom, Egyptian kings had conquered Lower Nubia. To secure control over the new region they appointed people of the local elite as governors. Teh-khet was a Nubian region that covered about Debeira and Serra. The local governors here formed a family, while the governor proper hold the title chief of Teh-khet.
Ishemai was an ancient Egyptian official at the end of the Old Kingdom, around 2150 BC. He is mainly known from his rock cut tomb found at the Qubbet el-Hawa. Ishemai had several titles, including royal sealer, sole friend, lector priest and great overlord of the king.














