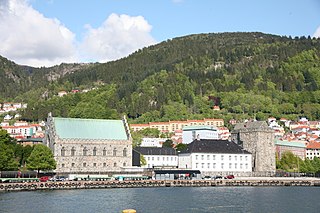Bergen, historically Bjørgvin, is a city and municipality in Vestland county on the west coast of Norway. As of 2022, its population was roughly 289,330. Bergen is the second-largest city in Norway after national capital Oslo. The municipality covers 465 square kilometres (180 sq mi) and is located on the peninsula of Bergenshalvøyen. The city centre and northern neighbourhoods are on Byfjorden, 'the city fjord'. The city is surrounded by mountains, causing Bergen to be called the "city of seven mountains". Many of the extra-municipal suburbs are on islands. Bergen is the administrative centre of Vestland county. The city consists of eight boroughs: Arna, Bergenhus, Fana, Fyllingsdalen, Laksevåg, Ytrebygda, Årstad, and Åsane.

The University Museum of Bergen is a university museum in Bergen, Norway. The museum features material related to anthropology, archaeology, botany, geology, zoology, art, and cultural history.

The Seven Mountains are seven mountains that surround the centre of the city of Bergen in Vestland county, Norway. Bergen is often called 'the city between the seven mountains'.

The Victual Brothers, Vitalien Brothers or Vitalian Brethren were a loosely organized guild of 14th century Germanic privateers. They initially included Mecklenburg nobility, but later became an organisation of commoners, and later evolved into piracy. The guild had a clear historical effect in that era on maritime trade in the North and Baltic Seas. As privateers, they provisioned blockaded locations and otherwise served as a naval contingent on behalf of regional rulers, with clients that included the Queen of Denmark, and rulers of Mecklenburg and East Frisia. As their activities turned to piracy, the aims changed to personal enrichment.
Géde Ollgothach, son of Ollom Fotla, was, according to medieval Irish legend and historical tradition, a High King of Ireland. He succeeded to the throne on the death of his brother Slánoll. His epithet means "possessing a great voice", and the Lebor Gabála Érenn says during his reign all his subjects had voices as sweet as the strings of a zither. He ruled for eight, or twelve, or seventeen years, before being killed by, according to the Lebor Gabála, the otherwise unknown Fíachu son of Fíadchú; according to Geoffrey Keating and the Annals of the Four Masters, by his nephew and successor Fíachu Findoilches, son of Fínnachta. The chronology of Keating's Foras Feasa ar Éirinn dates his reign to 880–863 BC, that of the Annals of the Four Masters to 1241–1231 BC.
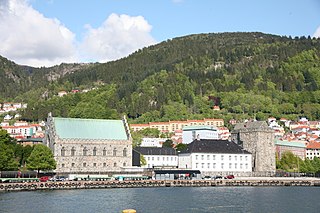
Bergenhus fortress is a fortress located in Bergen, Norway. Located at the entrance of Bergen harbour, the castle is one of the oldest and best preserved stone fortifications in Norway.

The Royal Norwegian Naval Academy is located at Laksevåg in Bergen. It was formally established 27 October 1817 in Frederiksvern. The institution educates officers for the Royal Norwegian Navy.

"Nikolaus" Storzenbecher or "Klaus" Störtebeker was reputed to be leader of a group of privateers known as the Victual Brothers. The Victual Brothers were originally hired during a war between Denmark and Sweden to fight the Danish and supply the besieged Swedish capital Stockholm with provisions. After the end of the war, the Victual Brothers continued to capture merchant vessels for their own account and named themselves "Likedeelers". Recent studies manifest that Störtebeker was not called "Klaus" but "Johann".
Battle of Bergen may refer to:
Koroinen is a district in the Koroinen ward of the city of Turku, in Finland. It is located to the north of the city centre, across the river Aura from the Turku Student Village. Koroinen is mostly non-built-up area, consisting largely of recreational area. The current population of the district is 26.

The Battle of Bergen on 13 April 1759 saw the French army under de Broglie withstand an allied British, Hanoverian, Hessian, Brunswick army under Prince Ferdinand of Brunswick near Frankfurt-am-Main during the Seven Years' War.

Korsholm Castle was a medieval castle in Vaasa, Finland.

In the Baltic Sea region, groups of pirates of Slavic descent lived dating as far back as the 8th to 14th centuries. With some considering them as apart of the orbit of the Viking age labeling them as Vikings either by confused misunderstood identification or the deliberate choice to not distinguish Slavic and Nordic piracy or the religions they may have adhered with prior to Christianization.

Nordnes is a peninsula and neighbourhood in the city centre of Bergen in Vestland county, Norway.

Nygård is a neighbourhood in the city centre of Bergen in Vestland county, Norway. It is located south of the Lille Lungegårdsvannet lake in the city centre and north of the Møhlenpris neighborhood. Grieghallen, St. Jacob's Church, and parts of the University of Bergen are located in Nygård.

Verftet is a neighbourhood of Bergen, Norway. It is located on the Nordnes peninsula. It is the location of Georgernes Verft.

Munkeliv Abbey was a Benedictine abbey located at Nordnes in Bergen, Norway. It was one of the oldest monasteries in Norway, and also one of the wealthiest and best-documented. There are no visible remains today.

Maoklane District is a district of Sétif Province, Algeria.
Cross Link is a proposed fixed link which would connect the municipalities of Øygarden, northern Askøy, and Alver in Vestland county, Norway. The road is planned to give better transport within Nordhordland and from there to Askøy and Øygarden.
Events in the year 1393 in Norway.