
Omar Hassan Ahmad al-Bashir is a Sudanese former military officer and politician who served as the seventh head of state of Sudan under various titles from 1989 until 2019, when he was deposed in a coup d'état. He was subsequently incarcerated, tried and convicted on multiple corruption charges. He came to power in 1989 when, as a brigadier general in the Sudanese Army, he led a group of officers in a military coup that ousted the democratically elected government of prime minister Sadiq al-Mahdi after it began negotiations with rebels in the south. He was elected three times as president in elections that have been under scrutiny for electoral fraud. In 1992, al-Bashir founded the National Congress Party, which remained the dominant political party in the country until 2019. In March 2009, al-Bashir became the first sitting head of state to be indicted by the International Criminal Court (ICC), for allegedly directing a campaign of mass killing, rape, and pillage against civilians in Darfur. On 11 February 2020, the Sudanese government announced that it had agreed to hand over al-Bashir to the ICC for trial.
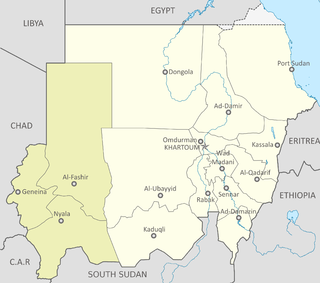
Darfur is a region of western Sudan. Dār is an Arabic word meaning "home [of]" – the region was named Dardaju while ruled by the Daju, who migrated from Meroë c. 350 AD, and it was renamed Dartunjur when the Tunjur ruled the area. Darfur was an independent sultanate for several hundred years until it was incorporated into Sudan by Anglo-Egyptian forces in 1916. As an administrative region, Darfur is divided into five federal states: Central Darfur, East Darfur, North Darfur, South Darfur and West Darfur. Because of the War in Darfur between Sudanese government forces and the indigenous population, the region has been in a state of humanitarian emergency and genocide since 2003. The factors include religious and ethnic rivalry, and the rivalry between farmers and herders.

The Baggāra or Chadian Arabs are a nomadic confederation of people of mixed Arab and Arabized indigenous African ancestry, inhabiting a portion of the Sahel mainly between Lake Chad and the Nile river near south Kordofan, numbering over six million. They are known as Baggara and Abbala in Sudan, and as Shuwa Arabs in Cameroon, Nigeria and Western Chad. The term Shuwa is said to be of Kanuri origin.
The Janjaweed are a Sudanese Arab militia group that operate in Sudan, particularly Darfur, and eastern Chad. Using the United Nations definition, the Janjaweed comprise Sudanese Arab tribes, the core of whom are from the Abbala background with significant recruitment from the Baggara people. This UN definition may not necessarily be accurate, as instances of members from other tribes have been noted.

Kordofan is a former province of central Sudan. In 1994 it was divided into three new federal states: North Kordofan, South Kordofan and West Kordofan. In August 2005, West Kordofan State was abolished and its territory divided between North and South Kordofan States, as part of the implementation of the Comprehensive Peace Agreement between the Government of Sudan and the Sudan People's Liberation Movement. West Kordofan was reestablished in July 2013.
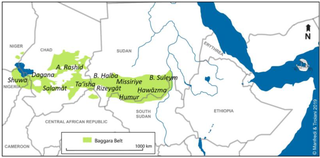
Ta'isha, or Ta'aisha, or Taaisha, one of a series of Arabic-speaking groups collectively called Baggara "cattle people", who live in Sudan, across southern Kordofan, Darfur, as well as Chad. The Ta'aisha tribal homeland is in the far southwest of Darfur, neighbouring to the east the Habbaniya, with whom they are closely related. The Ta'aisha rose to power when one of the members of their tribe, Abdallahi ibn Muhammad, later known as the Khalifa, became an early follower of Muhammad Ahmad, who would later become the Sudanese Mahdi. During the revolution, 'Abdallahi became the strongman of the movement and was designated as senior Khalifa by the Mahdi. Following the Mahdi's death in June 1885, the Khalifa 'Abdallahi ruled the Mahdist state until its destruction by an Anglo-Egyptian army. The Khalifa during his rule brought his tribe to Central Sudan and he went on to make extensive use of his relatives and other fellow Ta'a'isha as soldiers and administrators. Throughout the Mahdist period there was constant tension between the Ta'aisha leaders and the riverain Sudanese. Several Ta'aisha amirs who survived the Mahdiyya became prominent at the re-established Darfur Sultanate of Ali Dinar, one being Arabi Dafallah, who was appointed commander of the Equatorial province with its headquarters at Rejaf under the Khalifa's rule. Having been forced in 1897 to evacuate Equatoria by Belgians advancing from the Congo, he had made his way into southern Darfur where he faced Anglo-Egyptian forces and friendly tribes sent by Kitchener in pursuit of him. He then settled in the area of the present Central African Republic-Darfur border where he came into contact with encroaching French colonial power. After an unsuccessful attack on French outposts in the region he surrendered to Sultan 'Ali Dinar with his men and their arms in 1902, he subsequently lived in Al-Fashir and took part in many of the Sultan's military expeditions. Another one was 'Ali al-Sanusi, who was a Mahdist amir under Mahmud Ahmad in Atbara and fought at Karari after which he escaped to Darfur to be one of 'Ali Dinar's best generals. Under the British colonial rule, He was appointed Nazir of the Ta'aisha in Darfur and rendered valuable service to the new administration.

The Rizeigat, or Rizigat, or Rezeigat are a Muslim and Arab tribe of the nomadic Bedouin Baggara people in Sudan's Darfur region. The Rizeigat belong to the greater Baggara Arabs fraternity of Darfur and Kordofan and speak Chadic Arabic. They are primarily nomadic herders and their journeys are dependent upon the seasons of the year. They are a branch of the Juhayna group. They are divided into the Abbala (camel-herding) Rizeigat, who live in northern Darfur and Chad, and the Baggara who inhabit south-east Darfur. In turn they are divided into several large clans, notably the Mahamid, Mahariya and Nawaiba. The ecological differences between the north and south of Sudan allowed for two different types of nomadism to evolve: camel herders in the north and cattle herders in the south.

The Islamization of the Sudan region (Sahel) encompasses a prolonged period of religious conversion, through military conquest and trade relations, spanning the 8th to 16th centuries.

The War in Darfur, also nicknamed the Land Cruiser War, is a major armed conflict in the Darfur region of Sudan that began in February 2003 when the Sudan Liberation Movement (SLM) and the Justice and Equality Movement (JEM) rebel groups began fighting against the government of Sudan, which they accused of oppressing Darfur's non-Arab population. The government responded to attacks by carrying out a campaign of ethnic cleansing against Darfur's non-Arabs. This resulted in the death of hundreds of thousands of civilians and the indictment of Sudan's president, Omar al-Bashir, for genocide, war crimes, and crimes against humanity by the International Criminal Court.

The Beni Halba is an Arab group located in the western Sudanese region of Darfur. The Beni Halba is one of the major Darfuri Baggara groups, along with the Habbaniya, Rizeigat and Ta’isha, and was granted a large hakura in southern Darfur by the sultans of independent Dar Fur. During the 1980s, recurring drought in Chad prompted several clans of Beni Halba to migrate eastwards and join their kinspeople between Geneina and Kebkabiya and Kutum. In the late 1980s, the ideology then sweeping through the region combining Arab supremacy and Islamic extremism was taken up by many Beni Halba. Under Nazir al-Hadi Issa Debaker, the Beni Halba were actively involved in attacks upon the Fur people starting in 1987 through 1989. In this period a new militia called the Janjaweed, partially drawing upon the Beni Halba, was first formed. In 1991 the Sudan People's Liberation Army, then fighting the Second Sudanese Civil War in the south of the country, sent a force under Daud Bolad to expand the conflict into Darfur. However, Bolad's force was annihilated by a combination of the army and Beni Halba fursan ("horsemen"), who then carried out reprisal attacks against Fur civilians. As a result, the Beni Halba district town of Idd al Ghanam was renamed Idd al Fursan.

Throughout its history, Darfur has been the home to several cultures and kingdoms, like the mythical Tora or the Daju and Tunjur kingdoms. The recorded history of Darfur begins in the seventeenth century, with the foundation of the Fur Sultanate by the Keira dynasty. In 1875, the Anglo-Egyptian Co-dominion in Khartoum ended the dynasty. The British allowed Darfur a measure of autonomy until formal annexation in 1916. However, the region remained underdeveloped through the period of colonial rule and after independence in 1956. The majority of national resources were directed toward the riverine Arabs clustered along the Nile near Khartoum. This pattern of structural inequality and overly underdevelopment resulted in increasing restiveness among Darfuris. The influence of regional geopolitics and war by proxy, coupled with economic hardship and environmental degradation, from soon after independence led to sporadic armed resistance from the mid-1980s. The continued violence culminated in an armed resistance movement around 2003.
Ahmed Ibrahim Ali Diraige was the former governor of the Sudanese province of Darfur and late head of the National Redemption Front alliance of rebel groups in the Darfur conflict. He was residing in the United Kingdom.
Musa Hilal is a Sudanese Arab tribal chief and militia leader and adviser to the Sudanese Minister of Internal Affairs. His Um Jalul clan exercised tribal leadership of the Arab Mahamid tribe in Darfur. The Mahamid are part of a larger confederation of camel-herding (Abbala) tribes of the Northern Rizeigat. Hilal is the leader of the Janjaweed militia, which was responsible for a massive military campaign against civilians in Darfur in 2003, as part of a counterinsurgency effort against Darfur rebel groups. On 21 January 2008, the Federal Government of Sudan announced the nomination of Musa Hilal as the chief advisor of the Ministry of Federal Affairs in Sudan. This position allows Mr. Hilal to coordinate with regional leaders surrounding Darfur, as well as with Arab tribal groups, on the relations of the military regime.
Sudan has a conflict in the Darfur area of western Sudan. The Khartoum government had, in the past, given sanctuary to trans-national Islamic terrorists, but, according to the 9/11 Commission Report, ousted al-Qaeda and cooperated with the US against such groups while simultaneously involving itself in human rights abuses in Darfur. There are also transborder issues between Chad and Darfur, and, to a lesser extent, with the Central African Republic.

In May 2008, the Justice and Equality Movement (JEM), a Darfur ethnic minority rebel group, undertook a raid against the Sudanese government in the cities of Omdurman and Khartoum.

The Sultanate of Darfur was a pre-colonial state in present-day Sudan. It existed from 1603 to October 24, 1874, when it fell to the Sudanese warlord Rabih az-Zubayr and again from 1898 to 1916, when it was conquered by the British and integrated into Anglo-Egyptian Sudan. At its peak in the late 18th and early 19th century it stretched all the way from Darfur in the west to Kordofan and the western banks of the White Nile in the east, giving it the size of present-day Nigeria.
Sudanese nomadic conflicts are non-state conflicts between rival nomadic tribes taking place in the territory of Sudan and, since 2011, South Sudan. Conflict between nomadic tribes in Sudan is common, with fights breaking out over scarce resources, including grazing land, cattle and drinking water. Some of the tribes involved in these clashes have been the Messiria, Maalia, Rizeigat and Bani Hussein Arabic tribes inhabiting Darfur and West Kordofan, and the Dinka, Nuer and Murle African ethnic groups inhabiting South Sudan. Conflicts have been fueled by other major wars taking place in the same regions, in particular the Second Sudanese Civil War, the War in Darfur and the Sudanese conflict in South Kordofan and Blue Nile.

The 2020 Darfur attacks were three mass shootings that occurred in July 2020 in Darfur, Sudan. Sudan's leadership and the joint United Nations and African Union mission in Darfur (UNAMID) have connected the massacres to land conflicts relating to farming rights, typically between non-Arab tribal farmers, such as the Masalit people, and Arab Bedouin tribes, whom the government believes to be the attackers.
Sudanese society was very much in flux in the 2000s. Various factors included:
Events in the year 2021 in Sudan.










