| C62 | |
|---|---|
| ILO Convention | |
| Date of adoption | June 23, 1937 |
| Date in force | July 4, 1942 |
| Classification | Construction |
| Subject | Occupational Safety and Health |
| Previous | Reduction of Hours of Work (Textiles) Convention, 1937 |
| Next | Convention concerning Statistics of Wages and Hours of Work, 1938 |
Safety Provisions (Building) Convention, 1937 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
It was established in 1937:
Considering that building work gives rise to serious accident risks which it is necessary to reduce both on humanitarian and on economic grounds, and
Having decided upon the adoption of certain proposals with regard to safety provisions for workers in the building industry with reference to scaffolding and hoisting machinery,...
The European Convention on Nationality was signed in Strasbourg on 6 November 1997. It is a comprehensive convention of the Council of Europe dealing with the law of nationality. The convention is open for signature by the member States of the Council of Europe and the non-member States which have participated in its elaboration and for accession by other non-member States. The Convention came into force on 1 March 2000 after ratification by 3 countries. As of 2021, the convention has been signed by 29 countries and ratified by 21 of those countries.

The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), also called the Law of the Sea Convention or the Law of the Sea Treaty, is an international agreement that establishes a legal framework for all marine and maritime activities. As of June 2016, 167 countries and the European Union are parties.

The Vienna Convention on the Law of Treaties (VCLT) is an international agreement that regulates treaties among sovereign states; the VCLT is a codification of customary international law and state practice concerning treaties.

The American Convention on Human Rights, also known as the Pact of San José, is an international human rights instrument. It was adopted by many countries in the Western Hemisphere in San José, Costa Rica, on 22 November 1969. It came into force after the eleventh instrument of ratification was deposited on 18 July 1978.

The Hague Conventions of 1899 and 1907 are a series of international treaties and declarations negotiated at two international peace conferences at The Hague in the Netherlands. Along with the Geneva Conventions, the Hague Conventions were among the first formal statements of the laws of war and war crimes in the body of secular international law. A third conference was planned for 1914 and later rescheduled for 1915, but it did not take place because of the start of World War I.
Ratification is a principal's approval of an act of its agent that lacked the authority to bind the principal legally. Ratification defines the international act in which a state indicates its consent to be bound to a treaty if the parties intended to show their consent by such an act. In the case of bilateral treaties, ratification is usually accomplished by exchanging the requisite instruments, and in the case of multilateral treaties, the usual procedure is for the depositary to collect the ratifications of all states, keeping all parties informed of the situation.
The International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS) is an international maritime treaty that sets minimum safety standards in the construction, equipment and operation of merchant ships. The International Maritime Organization convention requires signatory flag states to ensure that ships flagged by them comply with at least these standards.

Protocol I is a 1977 amendment protocol to the Geneva Conventions concerning the protection of civilian victims of international war, such as "armed conflicts in which peoples are fighting against colonial domination, alien occupation or racist regimes." In practice, Additional Protocol I updated and reaffirmed the international laws of war stipulated in the Geneva Conventions of 1949 to accommodate developments of warfare since the Second World War (1937–1945).
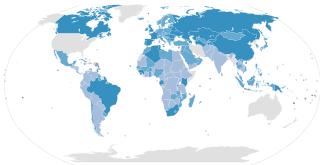
The ILO Convention Concerning Minimum Age for Admission to Employment C138, is a convention adopted in 1973 by the International Labour Organization. It requires ratifying states to pursue a national policy designed to ensure the effective abolition of child labour and to raise progressively the minimum age for admission to employment or work. It is one of eight ILO fundamental conventions. Convention C138 replaces several similar ILO conventions in specific fields of labour.
Protection against Accidents (Dockers) Convention (Revised), 1932 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Maternity Protection Convention (Revised), 1952 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
The Convention Concerning Statistics of Wages and Hours of Work, 1938 is an International Labour Organization Convention.

War can heavily damage the environment, and warring countries often place operational requirements ahead of environmental concerns for the duration of the war. Some international law is designed to limit this environmental harm.

The Prüm Convention is a law enforcement treaty which was signed on 27 May 2005 by Austria, Belgium, France, Germany, Luxembourg, the Netherlands and Spain in the town of Prüm in Germany, and which is open to all members of the European Union, 14 of which are currently parties.
The Convention on Offences and Certain Other Acts Committed on Board Aircraft, commonly called the Tokyo Convention, is an international treaty, concluded at Tokyo on 14 September 1963. It entered into force on 4 December 1969, and as of 2022 has been ratified by 187 parties.

The Maritime Labour Convention (MLC) is an International Labour Organization (ILO) convention, number 186, established in 2006 as the fourth pillar of international maritime law and embodies "all up-to-date standards of existing international maritime labour Conventions and Recommendations, as well as the fundamental principles to be found in other international labour Conventions". The other pillars are the SOLAS, STCW and MARPOL. The treaties applies to all ships entering the harbours of parties to the treaty (port states), as well as to all ships flying the flag of state party (flag states, as of 2021: over 91 per cent).
The Convention for the Suppression of Unlawful Acts against the Safety of Civil Aviation is a multilateral treaty by which states agree to prohibit and punish behaviour which may threaten the safety of civil aviation.
The Convention for the Suppression of Unlawful Acts against the Safety of Maritime Navigation or SUA Convention is a multilateral treaty by which states agree to prohibit and punish behaviour which may threaten the safety of maritime navigation.

The Treaties of the European Union are a set of international treaties between the European Union (EU) member states which sets out the EU's constitutional basis. They establish the various EU institutions together with their remit, procedures and objectives. The EU can only act within the competences granted to it through these treaties and amendment to the treaties requires the agreement and ratification of every single signatory.
The Convention on the Reduction of Cases of Multiple Nationality and on Military Obligations in Cases of Multiple Nationality is a convention signed in 1963 by the Council of Europe with the stated aim of reducing cases of multiple nationalities.