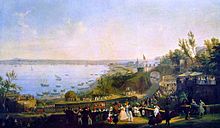Luca Giordano was an Italian late-Baroque painter and printmaker in etching. Fluent and decorative, he worked successfully in Naples, Rome, Florence, and Venice, before spending a decade in Spain.

The Astronomical Observatory of Capodimonte is the Neapolitan department of Istituto Nazionale di Astrofisica, the most important Italian institution promoting, developing and conducting scientific research in the fields of astronomy, astrophysics, and space science.

Maria Amalia Christina Franziska Xaveria Flora Walburga of Saxony was Queen of Spain from 10 August 1759 until her death in 1760 as the wife of King Charles III. Previously, she had been Queen of Naples and Sicily since marrying Charles on 19 June 1738. She was born a princess of Poland and Saxony, daughter of King Augustus III of Poland and Princess Maria Josepha of Austria. Maria Amalia and Charles had thirteen children, of whom seven survived into adulthood. A popular consort, Maria Amalia oversaw the construction of the Caserta Palace outside Naples as well as various other projects, and she is known for her influence upon the affairs of state.

The Royal Palace of Portici is a former royal palace in Portici, Southeast of Naples along the coast, in the region of Campania, Italy. Today it is the home of the Orto Botanico di Portici, a botanical garden operated by the University of Naples Federico II. These gardens were once part of the large royal estate that included an English garden, a zoo and formal parterres.

The Royal Palace of Capodimonte is a large palazzo in Naples, Italy. It was formerly the summer residence and hunting lodge of the Bourbon kings of the Two Sicilies, one of the two royal palaces in Naples. Today, it comprises the National Museum of Capodimonte and the Royal Forest. The palace was constructed on its somewhat cooler hilltop location just outside the city, with urban Naples ultimately expanding around it.

Eduardo Dalbono was an Italian painter born in Naples.

Attilio Pratella was an Italian painter, noted for his landscapes and realistic scenes of Neapolitan life.
Tito Angelini (1806–1878) was an Italian sculptor and leader of the Academy of Fine Arts in Naples, where he was born and died.

Giuseppe Cammarano was an Italian painter and leader of the Academy of Arts in his birthplace of Sciacca, Sicily.

The School of Posillipo refers to a loose group of landscape painters, based in the waterfront Posillipo neighborhood of Naples, Italy. While some among them became academicians, it was not a formal school or association.

The Accademia di Belle Arti di Napoli is a university-level art school in Naples. In the past it has been known as the Reale Istituto di Belle Arti and the Reale Accademia di Belle Arti. Founded by King Charles VII of Naples in 1752, it is one of the oldest art schools in Italy, and offers various levels of study up to and including the equivalent of an Italian laurea. It is located one block south of the church of Santa Maria di Costantinopoli, on the via of the latter church's name.
Salvatore Petruolo, was an Italian painter.

Michele Cammarano was an Italian painter who was best known for his battle scenes, although he worked with a wide variety of subjects.
Giovanni de Martino was an Italian sculptor. He made sentimental bronzes, often of street boys, fishermen or women.
Gennaro Calì was an Italian sculptor.

The Porcelain boudoir of Maria Amalia of Saxony is a rococo interior now located in the Palace of Capodimonte in Naples. It was originally made for the Palace of Portici in 1757–59, but has now been moved to the Capodimonte Palace. It is named after Maria Amalia of Saxony, queen of Naples. It consists of white porcelain panels decorated in high relief with festoons and genre scenes, drawing on the Chinoiserie popular at the time. It was designed by Giuseppe Gricci and produced in the Royal Porcelain Factory of Capodimonte, founded by Maria Amalia and her husband Charles of Bourbon in 1743.

Francis I and His Family is an 1820 oil on canvas painting by Giuseppe Cammarano, now in the National Museum of Capodimonte in Naples.
Francesco Liani was an Italian painter, mainly known for his portraits of the Neapolitan royal family.

Federigo, Vincenzo Antonio, Ludovico Zuccari was an Italian astronomer, professor of Astronomy at the Naples University, professor of Mathematical Geography at the Military Academy of Naples and director of the Astronomical Observatory of Naples.

Portrait of Cardinal Alessandro Farnese is a c. 1545 – 46 oil on canvas three-quarter-length portrait of Alessandro Farnese the Younger (1520-1589) by Titian, now in the Museo nazionale di Capodimonte in Naples.