Samarium fluoride may refer to:
- Samarium(III) fluoride (samarium trifluoride), SmF3
- Samarium(II) fluoride (samarium difluoride), SmF2
- Samarium(I) fluoride (samarium monofluoride), SmF known in gas form
Samarium fluoride may refer to:

Samarium is a chemical element; it has symbol Sm and atomic number 62. It is a moderately hard silvery metal that slowly oxidizes in air. Being a typical member of the lanthanide series, samarium usually has the oxidation state +3. Compounds of samarium(II) are also known, most notably the monoxide SmO, monochalcogenides SmS, SmSe and SmTe, as well as samarium(II) iodide.
SM or sm may refer to:

Samarium(III) chloride, also known as samarium trichloride, is an inorganic compound of samarium and chloride. It is a pale yellow salt that rapidly absorbs water to form a hexahydrate, SmCl3.6H2O. The compound has few practical applications but is used in laboratories for research on new compounds of samarium.
A samarium–cobalt (SmCo) magnet, a type of rare-earth magnet, is a strong permanent magnet made of two basic elements: samarium and cobalt.
Samarium chloride may refer to:
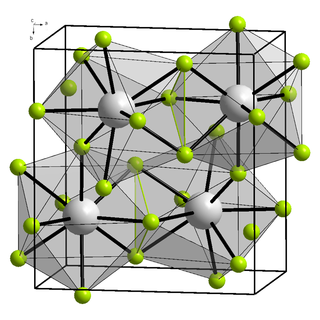
Samarium(III) fluoride (SmF3) is a slightly hygroscopic solid fluoride. Conditions/substances to avoid are: open flame, moisture, strong acids.

Samarium(II) chloride (SmCl2) is a chemical compound, used as a radical generating agent in the ketone-mediated intraannulation reaction.

Samarium(III) oxide (Sm2O3) is a chemical compound. Samarium oxide readily forms on the surface of samarium metal under humid conditions or temperatures in excess of 150°C in dry air. Similar to rust on metallic iron, this oxide layer spalls off the surface of the metal, exposing more metal to continue the reaction. The oxide is commonly white to off yellow in color and is often encountered as a highly fine dust like powder.
Samarium iodide may refer to:
Trifluorides are compounds in which one atom or ion has three fluorine atoms or ions associated. Many metals form trifluorides, such as iron, the rare-earth elements, and the metals in the groups 3, 13 and 15 of the periodic table. Most metal trifluorides are poorly soluble in water except ferric fluoride and indium(III) fluoride, but several are soluble in other solvents.
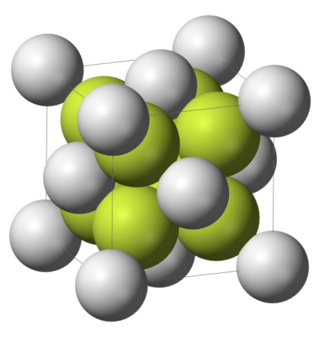
Difluorides are chemical compounds with two fluorine atoms per molecule.

Samarium(II) bromide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula SmBr
2. It is a brown solid that is insoluble in most solvents but degrades readily in air.
Samarium(III) bromide is a crystalline compound of one samarium and three bromine atoms with the chemical formula of SmBr3. Samarium(III) bromide is a dark brown powder at room temperature. The compound has a crystal structure isotypic to that of plutonium(III) bromide.
Samarium(II) fluoride is one of fluorides of samarium with a chemical formula SmF2. The compound crystalizes in the fluorite structure, and is significantly nonstoichiometric. Along with europium(II) fluoride and ytterbium(II) fluoride, it is one of three known rare earth difluorides, the rest are unstable.
Samarium(III) iodide is an inorganic compound, a salt of samarium and hydroiodic acid with the chemical formula SmI
3.
Samarium(III) phosphide is an inorganic compound of samarium and phosphorus with the chemical formula SmP.
Thulium(II) fluoride is one of the fluoride salts of the lanthanide metal thulium, with the chemical compound of TmF2. It can react with zirconium tetrafluoride at 900 °C to form TmZrF6, which has a hexagonal structure. In addition, low-temperature Mössbauer spectroscopy and some theoretical studies of thulium(II) fluoride have also been reported.
Samarium compounds are compounds formed by the lanthanide metal samarium (Sm). In these compounds, samarium generally exhibits the +3 oxidation state, such as SmCl3, Sm(NO3)3 and Sm(C2O4)3. Compounds with samarium in the +2 oxidation state are also known, for example SmI2.
Samarium bromide may refer to:

Samarium(III) phosphate is an inorganic compound, with the chemical formula of SmPO4. It is one of the phosphates of samarium.