Related Research Articles

Eleanor of Aquitaine was Duchess of Aquitaine in her own right from 1137 to 1204, Queen of France from 1137 to 1152 as the wife of King Louis VII, and Queen of England from 1154 to 1189 as the wife of King Henry II. As the heiress of the House of Poitiers, which controlled much of southwestern France, she was one of the wealthiest and most powerful women in Western Europe during the High Middle Ages. Militarily, she was a leading figure in the Second Crusade, and in a revolt in favour of her son. Culturally, she was a patron of poets such as Wace, Benoît de Sainte-Maure, and Bernart de Ventadorn, and of the arts of the High Middle Ages.

Louis VII, called the Younger, or the Young, was King of France from 1137 to 1180. He was the son and successor of King Louis VI and married Duchess Eleanor of Aquitaine, one of the wealthiest and most powerful women in western Europe. The marriage temporarily extended the Capetian lands to the Pyrenees.

Marie of France was a Capetian princess who became Countess of Champagne by her marriage to Henry I of Champagne. She served as regent of the County of Champagne three times: during Henry I's absence from 1179-1181; during the minority of their son Henry II from 1181–1187; and during Henry II's absence from 1190-1197. The daughter of Eleanor of Aquitaine and Louis VII of France, she was the sister of Alice of France and the half-sister of: William IX, Henry the Young King, Richard I, Geoffrey of Brittany, Matilda of England, Eleanor of England, Joan of England, John of England; Margaret of France, Alys of France, Agnes of France, Philip II of France; and the stepdaughter of Henry II of England, and Constance of Castile, and Adela of Champagne.
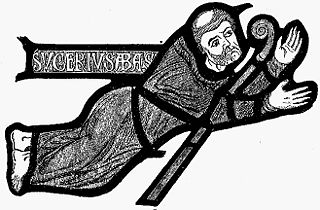
Suger was a French abbot and statesman. He was a key advisor to king Louis VI and his son Louis VII, acting as his regent during the Second Crusade, with his writings remaining seminal texts for early twelfth-century Capetian history. His supervision of the rebuilding of the Basilica of Saint-Denis where he was abbot, was instrumental in the creation of Gothic architecture.

Louis V, also known as Louis the Do-Nothing, was a king of West Francia from 979 to his early death in 987. During his reign, the nobility essentially ruled the country. Dying childless, Louis V was the last Carolingian monarch in West Francia.

The Peerage of France was a hereditary distinction within the French nobility which appeared in 1180 during the Middle Ages.

Theobald the Great (1090–1152) was count of Blois and of Chartres as Theobald IV from 1102 and was Count of Champagne and of Brie as Theobald II from 1125. Theobald held Auxerre, Maligny, Ervy, Troyes and Châteauvillain as fiefs from Odo II, Duke of Burgundy.

Lothair, sometimes called Lothair II, III or IV, was the penultimate Carolingian king of West Francia, reigning from 10 September 954 until his death in 986.
Petronilla of Aquitaine was a French noble. She was the second daughter of William X of Aquitaine and Aenor of Châtellerault. She was the elder sister of William Aigret and the younger sister of Eleanor of Aquitaine, who was Queen consort of France, later England. She is variously called Alix and Petronilla; she typically went by Alix after her marriage, while Petronilla seems to have been her childhood name.

Adbelahide, Adele, Adela or Adelaide of Aquitaine, was Queen of France by marriage to Hugh Capet, King of the Franks. Adelaide and Hugh were the founders of the Capetian dynasty of France, which would rule France until the 18th and 19th centuries. As queen consort, Adelaide had some extent of influence over her husband's governance of France. Adelaide is typically only briefly mentioned in connection to her husband, Hugh, and her son Robert II.

Adalbero was the archbishop of Reims, chancellor of Kings Lothair and Louis V of France.

The Archdiocese of Reims or Rheims is a Latin Church ecclesiastic territory or archdiocese of the Catholic Church in France. Erected as a diocese around 250 by Sixtus of Reims, the diocese was elevated to an archdiocese around 750. The archbishop received the title "primate of Gallia Belgica" in 1089.

Ralph I of Vermandois was Count of Vermandois. He was a son of Hugh, Count of Vermandois and his wife, Adelaide, Countess of Vermandois. Ralph was a grandson of Henry I of France, while Ralph's mother had been the Carolingian heiress to Herbert IV, Count of Vermandois.

Pepin I or Pepin I of Aquitaine was King of Aquitaine and Duke of Maine.

Henry of France, bishop of Beauvais (1149–1161), then archbishop of Reims (1161–1175), was the third son of King Louis VI of France and Adelaide of Maurienne.

The Diocese of Amiens is a Latin Church diocese of the Catholic Church in France. The diocese comprises the department of Somme, of which the city of Amiens is the capital.

The Breton and French Catholic diocese of Dol existed from 848 to the French Revolution. It was suppressed by the Concordat of 1801. Its see was Dol Cathedral. Its scattered territory was shared mainly by the Diocese of Rennes and the Diocese of Saint-Brieuc.
Events from the 1150s in England.

Louis II, known as Louis the Stammerer, was the king of Aquitaine and later the king of West Francia. He was the eldest son of Emperor Charles the Bald and Ermentrude of Orléans. Louis the Stammerer was physically weak and outlived his father by a year and a half.

Barthélemy de Jur was a French bishop. He was bishop of Laon from 1113 to 1151. Some documents give his name as Barthélemy de Grandson or de Joux.
References
- ↑ ...in 1148 he ventured to appear in Champagne, where he was seized with his followers by Samson, Archbishop of Reims, and brought before Eugenius III. at the Council of Rouen. ; Catholic Encyclopedia.
- ↑ 1157
- ↑ Alison Weir, Eleanor of Aquitaine, pp. 90-1.
- ↑ , in French.