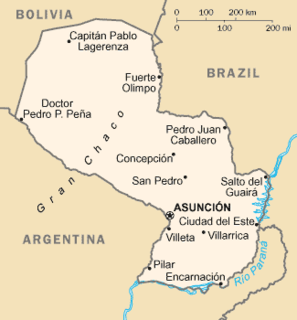
Paraguay is a country in South America, bordering Brazil, Argentina and Bolivia. The Paraguay River divides the country into strikingly different eastern and western regions. Both the eastern region and the western region gently slope toward and are drained into the Paraguay River, which separates and unifies the two regions. With the Paraneña region reaching southward and the Chaco extending to the north, Paraguay straddles the Tropic of Capricorn and experiences both subtropical and tropical climates.

Alto Paraná is a department in Paraguay. The capital is Ciudad del Este.
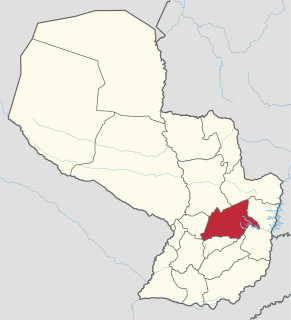
Caaguazú is a department in Paraguay. The capital is the city of Coronel Oviedo.

Caazapá is a department in Paraguay. The capital is the city of Caazapá. Among Paraguayans, the department is well known for its orange and mandarin trees, and for its forest hills. The eastern part of Caazapá is relatively undeveloped and consists of rolling hills and large swaths of Brazilian Atlantic interior rainforest between the San Rafael mountains to the south and the Ybytyruzú mountains to the north. The western part is an area of low-lying marshes and swampland area, and consists of wetlands and tributaries to eastern Paraguay's largest river, the Tebicuary. Many indigenous groups make their home in what remains of the rainforest, especially south of the unpaved highway between San Juan Nepomuceno and Tavaí. Mby'a and Guayaki people, who practice farming corn, cassava and yerba mate under the canopy of the forest live in small bands and travel mainly by foot. They are technically protected and their land is a national reserve, but illegal loggers, ranchers, and more recently, Brazilian soybean growers have encroached upon their territory. With Paraguay's weak legal infrastructure, little can be done by way of enforcement or sanctions.

Itapúa is a department in the southern region of Paraguay. The capital is the city of Encarnación. It is divided into 30 districts, more than any other district in the country.

Misiones is a department located in the southern region of Paraguay. Its capital is San Juan Bautista. The eighth of Paraguay's 17 departments, it was created in 1906, then known as the San Ignacio Department, and was not given its present name until 1945. Its current name reflects its status as home to several Jesuit Reductions, or missions.

Presidente Franco is a district and city of the Alto Paraná Department, Paraguay. Aside from being the oldest city in Alto Paraná Department, it is a place of rich exports of fruits and vegetables. Also, Presidente Franco is well known for Saltos del Monday, a 45 m tall and 120 m wide waterfall, Eastern Paraguay.

Altos is a city and district of the Cordillera Department, Paraguay.

The Iguazú National Park is a national park of Argentina, located in the Iguazú Department, in the north of the province of Misiones, Argentine Mesopotamia. It has an area of 677 km2 (261 sq mi).
The Paraguayan football league system is a series of interconnected leagues for football clubs in Paraguay.

The San Rafael National Park is a proposed national park in Paraguay covering an area of Atlantic Forest, grasslands and wetlands. Although the area was declared to be reserved for a national park in 1992, no further steps have been taken to formalize the status. The area is under threat both from large-scale farming and from small slash-and-burn farmers.

The Alto Paraná Atlantic forests, also known as the Paraná-Paraíba interior forests, is an ecoregion of the tropical moist forests biome, and the South American Atlantic Forest biome. It is located in southern Brazil, northeastern Argentina, and eastern Paraguay.
Tercera División de Paraguay, is the third division of Paraguayan football (soccer), and it is organized by the Paraguayan Football Association in the metropolitan area, and organized by the Unión del Fútbol del Interior, in the rest of the country, except Asunción and Central department.
Alto Verá is a district and town in the Itapúa Department of Paraguay.
San Pedro del Paraná is a town in the Itapúa department of Paraguay.
The biological Limoy Reserve is located in the district of Hernandarias Alto Paraná Department Paraguay, on the right bank of the river Paraná, and is one of the 8 sites for ecological reserve by the Itaipu, the largest dam in production in the world, located between Paraguay and Brazil. It is located at 160 km north of the city of Hernandarias, in the district of St. Albert. It was created in 1984 and has 14,828 hectares.

The Municipal Park Monday and its main attraction – approximately 45 m (148 ft) tall and 120 m (390 ft) wide waterfall named Saltos del Monday – are located in the Presidente Franco District, Alto Paraná Department, Paraguay, located around 25°33'40.6"S latitude and 54°38'00.1"W longitude, occupying an area of 1.6 hectares.
The 2019 Copa Paraguay was the second edition of the Copa Paraguay, Paraguay's domestic football cup competition. The competition started on 28 May 2019 and concluded on 5 December 2019. Libertad won their first title in the competition by beating defending champions Guaraní in the final by a 3–0 score. With both champions Libertad and runners-up Guaraní being already qualified for the 2020 Copa Libertadores, and third-placed team Deportivo Capiatá being relegated at the end of the season, the berth to the 2020 Copa Sudamericana the winners were originally entitled to was transferred to the Primera División aggregate table eighth-placed team, Sportivo Luqueño.













