HHV Latency Associated Transcript is a length of RNA which accumulates in cells hosting long-term, or latent, Human Herpes Virus (HHV) infections. The LAT RNA is produced by genetic transcription from a certain region of the viral DNA. LAT regulates the viral genome and interferes with the normal activities of the infected host cell.

Herpesviridae is a large family of DNA viruses that cause infections and certain diseases in animals, including humans. The members of this family are also known as herpesviruses. The family name is derived from the Greek word ἕρπειν, referring to spreading cutaneous lesions, usually involving blisters, seen in flares of herpes simplex 1, herpes simplex 2 and herpes zoster (shingles). In 1971, the International Committee on the Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) established Herpesvirus as a genus with 23 viruses among four groups. As of 2020, 115 species are recognized, all but one of which are in one of the three subfamilies. Herpesviruses can cause both latent and lytic infections.

Human Herpes Virus (HHV) Infected Cell Polypeptide 0 (ICP0) is a protein, encoded by the DNA of herpes viruses. It is produced by herpes viruses during the earliest stage of infection, when the virus has recently entered the host cell; this stage is known as the immediate-early or α ("alpha") phase of viral gene expression. During these early stages of infection, ICP0 protein is synthesized and transported to the nucleus of the infected host cell. Here, ICP0 promotes transcription from viral genes, disrupts structures in the nucleus known as nuclear dots or promyelocytic leukemia (PML) nuclear bodies, and alters the expression of host and viral genes in combination with a neuron specific protein. At later stages of cellular infection, ICP0 relocates to the cell cytoplasm to be incorporated into new virion particles.

Herpes simplex virus1 and 2, also known by their taxonomic names Human alphaherpesvirus 1 and Human alphaherpesvirus 2, are two members of the human Herpesviridae family, a set of viruses that produce viral infections in the majority of humans. Both HSV-1 and HSV-2 are very common and contagious. They can be spread when an infected person begins shedding the virus.
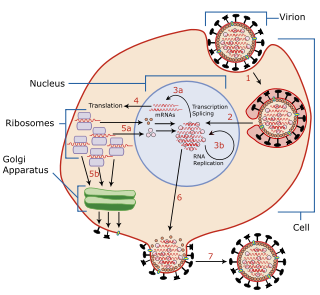
Viral entry is the earliest stage of infection in the viral life cycle, as the virus comes into contact with the host cell and introduces viral material into the cell. The major steps involved in viral entry are shown below. Despite the variation among viruses, there are several shared generalities concerning viral entry.
HHV Capsid Portal Protein, or HSV-1 UL-6 protein, is the protein which forms a cylindrical portal in the capsid of Herpes simplex virus (HSV-1). The protein is commonly referred to as the HSV-1 UL-6 protein because it is the transcription product of Herpes gene UL-6.

Poliovirus receptor-related 2 (PVRL2), also known as nectin-2 and CD112, is a human plasma membrane glycoprotein.

Poliovirus receptor-related 1 (PVRL1), also known as nectin-1 and CD111 (formerly herpesvirus entry mediator C, HVEC) is a human protein of the immunoglobulin superfamily (IgSF), also considered a member of the nectins. It is a membrane protein with three extracellular immunoglobulin domains, a single transmembrane helix and a cytoplasmic tail. The protein can mediate Ca2+-independent cellular adhesion further characterizing it as IgSF cell adhesion molecule (IgSF CAM).

Herpesvirus entry mediator (HVEM), also known as tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 14 (TNFRSF14), is a human cell surface receptor of the TNF-receptor superfamily encoded by the TNFRSF14 gene.

Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3, subunit M (eIF3m) also known as PCI domain containing 1 (herpesvirus entry mediator) (PCID1), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EIF3M gene.
Anthony (Tony) Charles Minson, PhD, FMedSci is a British virologist known for his work on the biology of herpesviruses, and a university administrator. He was the Senior Pro-Vice-Chancellor of the University of Cambridge from 2003 to 2009. He is an emeritus professor of virology at the university's Department of Pathology and an emeritus fellow of Wolfson College.
Deepak Shukla is an American molecular virologist with expertise in herpesviruses. He contributed to the discovery of HSV-1 entry receptors and establishing a link between the receptors and HSV-1 induced ocular diseases such as keratitis and retinitis. He has authored over 100 published papers and several book chapters on herpes viruses.

Herpesvirus glycoprotein B is a viral glycoprotein that is involved in the viral cell entry of Herpes simplex virus (HSV). Herpesviruses have a lipid bilayer, called the envelope, which contains twelve surface glycoproteins. For infectivity to be attained, the double stranded DNA genome of HSV must enter the host cell through means of fusion of its envelope with the cellular membrane or via endocytosis. Other viral glycoproteins involved in the process of viral cell entry include gC, gB, gD, gH, and gL, but only gC, gB, gD, and gH are required for the fusion of the HSV's envelope with the cellular membrane. It can be noted that all herpesviruses have glycoproteins gB, gH, and gL.
Proboscivirus is a genus of viruses in the order Herpesvirales, in the family Herpesviridae, in the subfamily Betaherpesvirinae. Elephants serve as natural hosts. EEHV1 is apathogenic for African elephants but causes fatal haemorrhagic disease in Asian elephants. The name "Proboscivirus" comes from the Greek word προβοσκίς or "proboscis" meaning "the elephant trunk," for which the virus accordingly uses as its means of contraction and transmission to enter the elephant's body.
David Mahan Knipe is the Higgins Professor of Microbiology and Molecular Genetics in the Department of Microbiology at the Harvard Medical School in Boston, Massachusetts and co-chief editor of the reference book Fields Virology. He returned to the Chair of the Program in Virology at Harvard Medical School in 2019, having previously held the position from 2004 through 2016 and served as interim Co-Chair of the Microbiology and Immunobiology Department from 2016 through 2018.
Roselyn J. Eisenberg is a professor at The University of Pennsylvania and a member of the University's School of Veterinary Medicine and School of Dental Medicine. The majority of Eisenberg's research is focused on the herpes simplex virus and the poxvirus and how they enter into susceptible cells. She also studies glycoproteins, vaccines, virology and microbiology.
Gabriella Campadelli-Fiume is a virologist with a primary research focus on herpes simplex virus, fusion and viral entry. She is a retired professor of virology from the University of Bologna, Italy.

Paired immunoglobin like type 2 receptor alpha is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PILRA gene.
Patricia Gail Spear is an American virologist. She is a professor emeritus of microbiology and immunology at Northwestern University in Evanston, Illinois. She is best known for her pioneering work studying the herpes simplex virus. Spear is a past president of the American Society for Virology and an elected member of the National Academy of Sciences.
Jay Clark Brown is an American molecular biologist, microbiologist, virologist, and academic. He is a Professor Emeritus in the Department of microbiology, immunology, and cancer biology at the University of Virginia School of Medicine.








