Related Research Articles
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty and formerly called judicial homicide, is the state-sanctioned killing of a person as punishment for actual or supposed misconduct. The sentence ordering that an offender be punished in such a manner is known as a death sentence, and the act of carrying out the sentence is known as an execution. A prisoner who has been sentenced to death and awaits execution is condemned and is commonly referred to as being "on death row". Etymologically, the term capital refers to execution by beheading, but executions are carried out by many methods, including hanging, shooting, lethal injection, stoning, electrocution, and gassing.

Capital punishment in the United Kingdom predates the formation of the UK, having been used in Britain and Ireland from ancient times until the second half of the 20th century. The last executions in the United Kingdom were by hanging, and took place in 1964; capital punishment for murder was suspended in 1965 and finally abolished in 1969. Although unused, the death penalty remained a legally defined punishment for certain offences such as treason until it was completely abolished in 1998; the last person to be executed for treason was William Joyce, in 1946. In 2004, Protocol No. 13 to the European Convention on Human Rights became binding on the United Kingdom; it prohibits the restoration of the death penalty as long as the UK is a party to the convention.
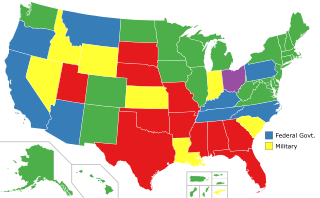
In the United States, capital punishment is a legal penalty in 27 states, throughout the country at the federal level, and in American Samoa. It is also a legal penalty for some military offenses. Capital punishment has been abolished in the other 23 states and in the federal capital, Washington, D.C. It is usually applied for only the most serious crimes, such as aggravated murder. Although it is a legal penalty in 27 states, 20 of them have authority to execute death sentences, with the other 7, as well as the federal government and military, subject to moratoriums.
Capital punishment is a legal penalty in the U.S. state of Indiana. The last person executed in the state, excluding federal executions in Terre Haute, was mass murderer Joseph Edward Corcoran in 2024.

Capital punishment is not allowed to be carried out in the U.S. state of California, due to both a standing 2006 federal court order against the practice and a 2019 moratorium on executions ordered by Governor Gavin Newsom. The litigation resulting in the court order has been on hold since the promulgation of the moratorium. Should the moratorium end and the freeze conclude, executions could resume under the current state law.
Capital punishment was abolished in 2019 in New Hampshire for persons convicted of capital murder. It remains a legal penalty for crimes committed prior to May 30, 2019.
Penelope Kenny was executed by hanging for the murder of her child in the Province of New Hampshire, along with Sarah Simpson, who was also convicted of murdering her child.
Ruth Blay was a schoolteacher executed by the Province of New Hampshire. She was the last female executed in New Hampshire.
Oscar Joseph Comery was a Canadian-American chauffeur hanged in Concord, New Hampshire for murdering his wife.

Capital punishment in Sweden was last used in 1910, though it remained a legal sentence for at least some crimes until 1973. It is now outlawed by the Swedish Constitution, which states that capital punishment, corporal punishment, and torture are strictly prohibited. At the time of the abolition of the death penalty in Sweden, the legal method of execution was beheading. It was one of the last states in Europe to abolish the death penalty.
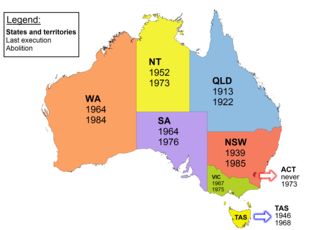
Capital punishment in Australia has been abolished in all jurisdictions since 1985. Queensland abolished the death penalty in 1922. Tasmania did the same in 1968. The Commonwealth abolished the death penalty in 1973, with application also in the Australian Capital Territory and the Northern Territory. Victoria did so in 1975, South Australia in 1976, and Western Australia in 1984. New South Wales abolished the death penalty for murder in 1955, and for all crimes in 1985. In 2010, the Commonwealth Parliament passed legislation prohibiting the re-establishment of capital punishment by any state or territory. Australian law prohibits the extradition or deportation of a prisoner to another jurisdiction if they could be sentenced to death for any crime.
Capital punishment in Saudi Arabia is a legal punishment. Most executions in the country are carried out by decapitation (beheading). Saudi Arabia is the only country that still uses this method. Capital punishment is used both for offenders of lethal crimes and non-lethal crimes, as well as juvenile offenders. Among those executed are individuals charged with non-lethal terrorism, a charge that has been used against individuals who participated in protests against the authoritarian regime in Saudi Arabia.
Kennedy v. Louisiana, 554 U.S. 407 (2008), is a landmark decision by the Supreme Court of the United States which held that the Eighth Amendment's Cruel and Unusual Punishments Clause prohibits the imposition of the death penalty for a crime in which the victim did not die and the victim's death was not intended.

Howard Long was an American convicted murderer who was executed for the 1937 murder of 10-year-old Mark Neville Jensen in Gilford, New Hampshire. Long remains the most recent person to be executed by the state of New Hampshire.

Stoning, or lapidation, is a method of capital punishment where a group throws stones at a person until the subject dies from blunt trauma. It has been attested as a form of punishment for grave misdeeds since ancient times.

Capital punishment was outlawed in the State of New York after the New York Court of Appeals declared that the statute as written was not valid under the state's constitution in 2004. However certain crimes occurring in the state that fall under the jurisdiction of the federal government are subject to the federal death penalty.
Sarah-Jane and Anna Flannagan were 19th-century New Zealand murderers. Like Caroline Whitting (1872) and Phoebe Veitch (1883) before them, but unlike Minnie Dean subsequently (1895), the two women were initially sentenced to death for the killing of Anna's illegitimate child and Sarah Jane's grandchild but were subsequently reprieved. In this instance, the intervention of the then-Governor-General of New Zealand William Onslow, 4th Earl of Onslow was required for mitigation of the death penalty to life imprisonment.
Capital punishment in Botswana is a legal penalty, and is usually applied for murder under aggravated circumstances. Executions are carried out by hanging. Despite this, Botswana’s constitution guarantees right to life. It is the only country in Southern Africa that still uses capital punishment as a punishment.

Capital punishment in the Bible refers to instances in the Bible where death is called for as a punishment and also instances where it is proscribed or prohibited. A case against capital punishment can be made from John 8, where Jesus speaks words that can be construed as condemning the practice. There are however many more Bible verses that command and condone capital punishment, and examples of it being carried out. Sins that were punishable by death include homicide, striking one's parents, kidnapping, cursing one's parents, witchcraft and divination, bestiality, worshiping other gods, violating the Sabbath, child sacrifice, adultery, incest, and male homosexual intercourse.
References
- ↑ Women who kill
- ↑ Ferland, Dr David (2014-05-27). Historic Crimes & Justice in Portsmouth, New Hampshire. Arcadia Publishing. ISBN 9781625847140.
- ↑ "First Women Executed in NH".