Related Research Articles

Alagoas is one of the 27 federative units of Brazil and is situated in the eastern part of the Northeast Region. It borders: Pernambuco ; Sergipe (S); Bahia (SW); and the Atlantic Ocean (E). Its capital is the city of Maceió. It has 1.6% of the Brazilian population and produces 0.8% of the Brazilian GDP. It is made up of 102 municipalities and its most populous cities are Maceió, Arapiraca, Palmeira dos Índios, Rio Largo, Penedo, União dos Palmares, São Miguel dos Campos, Santana do Ipanema, Delmiro Gouveia, Coruripe, Marechal Deodoro, and Campo Alegre.

The São Francisco River is a large river in Brazil. With a length of 2,914 kilometres (1,811 mi), it is the longest river that runs entirely in Brazilian territory, and the fourth longest in South America and overall in Brazil. It used to be known as the Opara by the indigenous people before colonisation, and is today also known as "Velho Chico".

Maceió, formerly sometimes Anglicised as Maceio, is the capital and the largest city of the coastal state of Alagoas, Brazil. The name "Maceió" is an Indigenous term for a spring. Most maceiós flow to the sea, but some get trapped and form lakes.

Coruripe is a municipality located in the southern coast of the Brazilian state of Alagoas. Its population is 57,294 (2020) and its area is 913 km². It is the largest municipality in Alagoas by area, but among the largest municipalities of each Brazilian state, it is the smallest. It is situated at the edge of Coruripe river.

Maragogi is a municipality in the Brazilian state of Alagoas, 125 km north of the capital city of Maceió. It has 33,032 inhabitants, a city situated on the northern coast of Alagoas state, Brazil, being the easternmost city of that state.

Located in the city of Maceió, the Federal University of Alagoas is the major university in coastal state Alagoas and one of the main research centers in Brazilian north eastern region. It is located very near the city's airport.

A carranca is a type of figurehead attached to river craft which is attributed with power to protect the boatmen from the river's evil spirits. The culture in Brazil incorporated elements of the indigenous culture, so that the idea of river spirits and forest spirits can help or hinder a crossing is also natural of the Amerindian imaginary. They were once commonly found on the lower Rio São Francisco in Brazil's Northeast Region (Nordeste). The carranca is most commonly a figure of a human or an animal. They were used to identify traders operating on the São Francisco and, as with ancient figureheads, serve the superstitious as guardians on the river.

Piaçabuçu is a municipality located in the Brazilian state of Alagoas. It is the southernmost municipality in Alagoas, and lies near both São Francisco River and the Atlantic Ocean. Its population was 17,848 (2020) and its area is 240 km².
The Mundaú River is a river in northeastern Brazil. The Mundaú originates in the Borborema Plateau of Pernambuco state, and flows southeast through Pernambuco and Alagoas states to empty into the Mundaú Lagoon at Maceió, Alagoas' capital. Mundaú Lagoon is an estuary, connected to the Atlantic Ocean and Manguaba Lagoon to the south by a network of channels.
The Paraíba do Meio River is a river in Alagoas state of northeastern Brazil. It flows southeast to empty into Manguaba Lagoon, an estuarine lake connected to the Atlantic Ocean by a network of channels.

The Moxotó River is a tributary of the São Francisco River in northeastern Brazil. The Moxotó originates on the Borborema Plateau in Pernambuco state, and flows southwest to join the São Francisco. The lower portion of the river forms the border between Pernambuco state to the west and Alagoas state to the east.
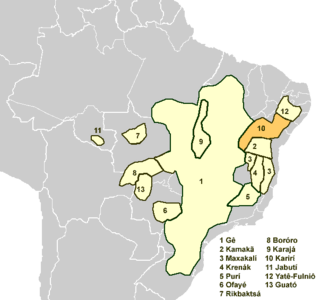
The Karirí languages, generally considered dialects of a single language, were a group of languages formerly spoken by the Kiriri people of Brazil. It was spoken until the middle of the 20th century; the 4,000 ethnic Kiriri are now monolingual Portuguese speakers, though a few know common phrases and names of medicinal plants.
Manari is a city established in 1997 in the state of Pernambuco, Brazil. The population in 2020, according to the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics, was 21,776 and the area is 344.73 km². In 2000, Manari had the lowest HDI of any municipality in the state.

Ipanema River is a river of Alagoas and Pernambuco states in eastern Brazil.

Glória is a municipality in the state of Bahia in the North-East region of Brazil. Glória covers 1,255.56 km2 (484.77 sq mi), and has a population of 15,234 with a population density of 13 inhabitants per square kilometer. It is located on the border of the states of Bahia, Pernambuco, and Alagoas on the banks of the Moxito River, now a lake as the result of the construction of Moxito Hydroelectric Power Plant.

The 2010 Northeastern Brazil rains caused widespread flooding in the second half of June 2010. The flooding mainly hit Alagoas and Pernambuco, where entire villages were carried away, killing dozens and causing hundreds to disappear.

The Pará-class monitors were a group of six wooden-hulled ironclad monitors named after Brazilian provinces and built in Brazil for the Imperial Brazilian Navy during the Paraguayan War in the late 1860s. The first three ships finished, Pará, Alagoas and Rio Grande, participated in the Passage of Humaitá in February 1868. Afterwards the remaining ships joined the first three and they all provided fire support for the army for the rest of the war. The ships were split between the newly formed Upper Uruguay and Mato Grosso Flotillas after the war. Alagoas was transferred to Rio de Janeiro in the 1890s and participated in the Fleet Revolt of 1893–94.

The Brazilian monitor Alagoas was the third ship of the Pará-class river monitors built for the Imperial Brazilian Navy during the Paraguayan War in the late 1860s. Alagoas participated in the Passage of Humaitá on 19 February 1868 and provided fire support for the army for the rest of the war. The ship was assigned to the Upper Uruguay flotilla after the war. Alagoas was transferred to Rio de Janeiro in the 1890s and participated in the Navy Revolt of 1893–94. The ship was scrapped in 1900.
Xocó is a dead and poorly attested language or languages of Brazil that is not known to be related to other languages. It is known from three populations: Xokó (Chocó) in Sergipe, Kariri-Xocó in Alagoas, and Xukuru-Kariri in Alagoas. It is not clear if these were one language or three. It is only known from a few dozen words from one Kariri-Xoco elder and three Xukuru-Kariri elders in 1961.
The Copa Alagoas is a tournament organized by Federação Alagoana de Futebol every second half of the season. The champions qualify for the Campeonato Brasileiro Série D.